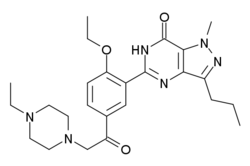
Acetildenafil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| MedlinePlus | a699015 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Acetildenafil |
| CAS Number |
831217-01-7 |
| ChemSpider |
23976138 |
| UNII |
TP0E2BW57H |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H34N6O3 |
| Molar mass | 466.574 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Acetildenafil (hongdenafil) is a synthetic drug which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is an analog of sildenafil (Viagra)[1] which has been detected in numerous different brands of supposedly "herbal" aphrodisiac products sold to boost libido and alleviate erectile dysfunction.[2]
A range of designer analogs of licensed PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil and vardenafil have been detected in recent years in over-the-counter herbal aphrodisiac products,[3][4][5][6] in an apparent attempt to circumvent both the legal restrictions on sale of erectile dysfunction drugs, which are prescription-only medicines in most Western countries, and the patent protection which allows sale of these drugs by competitors only with permission from the patent holders (typically, under a license from the inventors) and to introduce efficacy into otherwise ineffective herbal products. These compounds have been demonstrated to display PDE5 inhibitory activity in vitro and presumably have similar effects when consumed, but have undergone no formal testing in either humans or animals, and as such may represent significant health risks to consumers of these products due to their unknown safety profile.[2][7] Some attempts have been made to ban these drugs as unlicensed medicines, but progress has been slow so far, as even in those jurisdictions which have laws targeting designer drugs, the laws are drafted to ban analogs of illegal drugs of abuse, rather than analogs of prescription medicines. However, at least one court case has resulted in a product being taken off the market.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ Blok-Tip, L; Zomer, B; Bakker, F; Hartog, KD; Hamzink, M; Ten Hove, J; Vredenbregt, M; De Kaste, D (2004). "Structure elucidation of sildenafil analogues in herbal products". Food additives and contaminants. 21 (8): 737–48. doi:10.1080/02652030412331272467. PMID 15370823.
- 1 2 Poon, WT; Lam, YH; Lai, CK; Chan, AY; Mak, TW (2007). "Analogues of erectile dysfunction drugs: an under-recognised threat". Hong Kong Academy of Medicine. 13 (5): 359–63. PMID 17914141.
- ↑ Venhuis, B; De Kaste, D (2012). "Towards a decade of detecting new analogues of sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil in food supplements: A history, analytical aspects and health risks.". J Pharm Biomed Anal. 69: 196–208. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2012.02.014. PMID 22464558.
- ↑ Zou, P; Oh, SS; Hou, P; Low, MY; Koh, HL (2006). "Simultaneous determination of synthetic phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors found in a dietary supplement and pre-mixed bulk powders for dietary supplements using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry". Journal of Chromatography A. 1104 (1–2): 113–22. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.11.103. PMID 16364350.
- ↑ Gratz, SR; Gamble, BM; Flurer, RA (2006). "Accurate mass measurement using Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry for structure elucidation of designer drug analogs of tadalafil, vardenafil and sildenafil in herbal and pharmaceutical matrices". Rapid communications in mass spectrometry : RCM. 20 (15): 2317–27. doi:10.1002/rcm.2594. PMID 16817245.
- ↑ Hou, P; Zou, P; Low, MY; Chan, E; Koh, HL (2006). "Structural identification of a new acetildenafil analogue from pre-mixed bulk powder intended as a dietary supplement". Food additives and contaminants. 23 (9): 870–5. doi:10.1080/02652030600803856. PMID 16901855.
- ↑ Oh, SS; Zou, P; Low, MY; Koh, HL (2006). "Detection of sildenafil analogues in herbal products for erectile dysfunction". Journal of toxicology and environmental health. Part A. 69 (21): 1951–58. doi:10.1080/15287390600751355. PMID 16982533.
- ↑ Venhuis, BJ; Blok-Tip, L; De Kaste, D (2008). "Designer drugs in herbal aphrodisiacs". Forensic Science International. 177 (2–3): e25–7. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2007.11.007. PMID 18178354.