Aleutian Arc
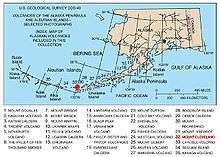
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc in the U.S. state of Alaska. It consists of a number of active and dormant volcanoes that have formed as a result of subduction along the Aleutian Trench. Although taking its name from the Aleutian Islands, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Aleutian Arc extends through the Alaska Peninsula following the Aleutian Range to the Aleutian Islands.[1]
The Aleutian Arc reflects subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate. It extends 3,000 km (1,900 mi) from the Kamchatka Peninsula in the west to the Gulf of Alaska in the east. Unimak Pass at the southwestern end of the Alaska Peninsula marks the eastward transition from an intra-oceanic in the west to a continental arc in the east. Due to the arcuate geometry of the trench, the relative velocity vector changes from almost trench-normal in the Gulf of Alaska to almost trench-parallel in the west. Along the oceanic part of the subduction zone, convergence varies from 6.3 cm (2.5 in) per year to the north-northwest in the east to 7.4 cm (2.9 in) per year towards the northwest in the west.[2]
Volcanoes
Volcanoes within the volcanic arc include:
- Mount Adagdak
- Mount Akutan
- Mount Amak
- Mount Amukta
- Mount Aniakchak
- Augustine Volcano
- Black Peak
- Bogoslof Island
- Mount Carlisle
- Mount Chiginagak
- Cleveland Volcano
- Cold Bay Volcano
- Mount Dana
- Davidof Volcano
- Mount Denison
- Devils Desk
- Mount Douglas
- Mount Dutton
- Mount Emmons
- Fourpeaked Mountain
- Mount Frosty
- Gareloi Volcano
- Mount Gilbert
- Mount Griggs
- Hayes Volcano
- Mount Iliamna
- Isanotski Peaks
- Mount Kaguyak
- Mount Kanaga
- Kasatochi Island
- Mount Katmai
- Mount Kialagvik
- Kiska
- Korovin Volcano
- Mount Kukak
- Mount Kupreanof
- Mount Mageik
- Makushin Volcano
- Mount Martin
- Novarupta
- Nunivak Island
- Mount Okmok
- Mount Pavlof
- Pavlof Sister
- Pogromni Volcano
- Mount Recheshnoi
- Mount Redoubt
- Saint Paul Island
- Mount Seguam
- Segula Island
- Semisopochnoi Island
- Mount Shishaldin
- Snowy Mountain
- Mount Spurr
- Mount Steller
- Tanaga
- Trident Volcano
- Ugashik-Peulik
- Mount Veniaminof
- Mount Vsevidof
- Mount Westdahl
- Yantarni Volcano
References
- ↑ A Policy for Rapid Mobilization of USGS OBS (RMOBS) - Alaska Volcanoes
- ↑ DeMets, C., and T. Dixon, (1999) New kinematic models for Pacific-North America motion from 3 Ma to present, 1: Evidence for steady motion and biases in the NUVEL-1A model, Geophys. Res. Lett., 26, 1921-1924 PDF
External links
Coordinates: 52°17′N 174°09′W / 52.28°N 174.15°W