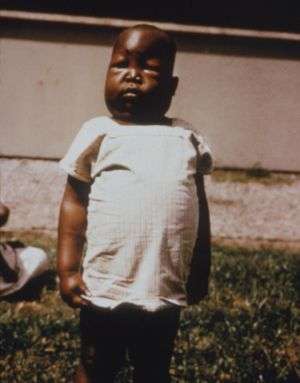
Anasarca
| Anasarca | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | R60.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 782.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 9148 |
| MedlinePlus | 003103 |
| MeSH | D004487 |
Anasarca, or extreme generalized edema, is a medical condition characterized by widespread swelling of the skin due to effusion of fluid into the extracellular space.[1]
It is usually caused by liver failure (cirrhosis of the liver), renal failure/disease, right-sided heart failure, as well as severe malnutrition/protein deficiency. The increase in salt and water retention caused by low cardiac output can also result in anasarca as a long term maladaptive response.
It can also be created from the administration of exogenous intravenous fluid. Certain plant-derived anticancer chemotherapeutic agents, such as docetaxel, cause anasarca through a poorly understood capillary leak syndrome.[2]
In Hb Barts, the high oxygen affinity results in poor oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues, resulting in anasarca.
References
- ↑ Kumar Vinay. Robbins and Coltran pathologic basis of disease. 8th ed. p.112; Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2010. ISBN 978-0-8089-2402-9
- ↑ Semb K A, Aamdal S, Oian P. "Capillary protein leak syndrome appears to explain fluid retention in cancer patients who receive docetaxel treatment". Journal of Clinical Oncology. October 1998. vol. 16 no. 10 3426-3432