Ardeadactylus
| Ardeadactylus longicollum Temporal range: Late Jurassic, 152 Ma | |
|---|---|
| | |
| SMNS 56603, the neotype of Ardeadactylus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Clade: | †Euctenochasmatia |
| Genus: | †Ardeadactylus Bennett, 2013 |
| Species: | †A. longicollum |
| Binomial name | |
| Ardeadactylus longicollum (von Meyer, 1854) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Pterodactylus longicollum von Meyer, 1854 (type) | |
Ardeadactylus (from Ardea – meaning "heron", and also a name of a genus of herons – and dactylus, meaning "finger") is an extinct genus of pterodactylid archaeopterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, southern Germany. It contains a single species, Ardeadactylus longicollum, which was originally thought to be a species of Pterodactylus.[1]
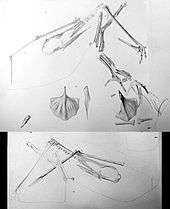
Only two specimens of Ardeadactylus are known to exist currently: SMNS 56603 (earlier SMNS 5802) found in 1874, a specimen from Nusplingen initially thought to belong to the species Pterodactylus suevicus Quenstedt (currently Cycnorhamphus)[2] and the neotype of the species, and JME-SOS 2428, a specimen held at Jura Museum in Eichstätt. Other known specimens, including the holotype designated by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer when he named the type species Pterodactylus longicollum in 1854,[3] were lost during World War II.[1] The original holotype, consisting of the skull, neck and anterior torso, had been found near Eichstätt in 1853 and was that year acquired for the Herzoglich Leuchtenbergische Naturalien-Kabinett by Professor Ludwig Frischmann.[3] Its destruction motivated Peter Wellnhofer to assign a neotype in 1970.[4]
Ardeadactylus is suspected to be a heron–like, long–necked long–legged piscivore.[1] It was similar to Pterodactylus antiquus in its general body form, but seems to have been larger. Bennett (2013) estimated the wingspan of the neotype specimen to be 1.45 metres (4.8 ft); the referred specimen from the Jura Museum is more or less 10% larger.[1] A. longicollum had fewer, fifteen per jaw, and relatively larger teeth than P. antiquus, possibly indicating that it preyed on larger fishes than Pterodactylus.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bennett, S. C. (2013). "New information on body size and cranial display structures of Pterodactylus antiquus, with a revision of the genus". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 87 (2): 269–289. doi:10.1007/s12542-012-0159-8.
- ↑ Fraas, O., 1878, "Über Pterodactylus suevicus, Qu., von Nusplingen", Palaeontographica, 25: 163-174
- 1 2 Meyer, C.E.H. von, 1854, "Mittheilungen an Professor Bronn: Anthracotherium Dalmatinum vom Monte Promina u.a. A.; Chelydra Decheni aus Braunkohle des Siebengebirges; Wirbelthier-Reste aus dem Basalttuff-Konglomerat zu Glimbach an der Rabenau; angebliches Vorkommen von Agnotherium antiquum und Hyaena spelaea; fossile Reste im lithographischen Schiefer von Nusplingen bei Spaichingen; Eryon Schuberti; Litogaster; Pemphix; Pterodactylus longicollum n. sp. in Solenhofener Schiefer; Acrosaurus Frischmanni von da; Reptilien und Cancer-Arten im Kressenberger Nummuliten-Gestein", Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie, Geognosie, Geologie und Petrefaktenkunde 1854: 47-58
- ↑ Wellnhofer, P., 1970, "Die Pterodactyloidea (Pterosauria) der Oberjura-Plattenkalke Süddeutschlands", Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Mathematisch-Wissenschaftlichen Klasse, Abhandlungen 141: 1–133