Rose (topology)
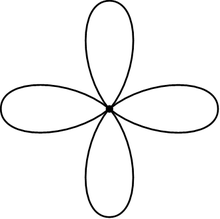
In mathematics, a rose (also known as a bouquet of n circles) is a topological space obtained by gluing together a collection of circles along a single point. The circles of the rose are called petals. Roses are important in algebraic topology, where they are closely related to free groups.
Definition

A rose is a wedge sum of circles. That is, the rose is the quotient space C/S, where C is a disjoint union of circles and S a set consisting of one point from each circle. As a cell complex, a rose has a single vertex, and one edge for each circle. This makes it a simple example of a topological graph.
A rose with n petals can also be obtained by identifying n points on a single circle. The rose with two petals is known as the figure eight.
Relation to free groups

The fundamental group of a rose is free, with one generator for each petal. The universal cover is an infinite tree, which can be identified with the Cayley graph of the free group. (This is a special case of the presentation complex associated to any presentation of a group.)
The intermediate covers of the rose correspond to subgroups of the free group. The observation that any cover of a rose is a graph provides a simple proof that every subgroup of a free group is free (the Nielsen–Schreier theorem)
Because the universal cover of a rose is contractible, the rose is actually an Eilenberg–MacLane space for the associated free group F. This implies that the cohomology groups Hn(F) are trivial for n ≥ 2.
Other properties
- Any connected graph is homotopy equivalent to a rose. Specifically, the rose is the quotient space of the graph obtained by collapsing a spanning tree.
- A disc with n points removed (or a sphere with n + 1 points removed) deformation retracts onto a rose with n petals. One petal of the rose surrounds each of the removed points.
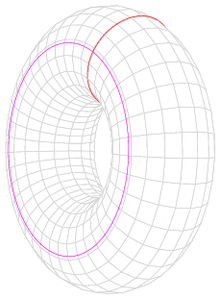
- A torus with one point removed deformation retracts onto a figure eight, namely the union of two generating circles. More generally, a surface of genus g with one point removed deformation retracts onto a rose with 2g petals, namely the boundary of a fundamental polygon.
- A rose can have infinitely many petals, leading to a fundamental group which is free on infinitely many generators. The rose with countably infinitely many petals is similar to the Hawaiian earring: there is a continuous bijection from this rose onto the Hawaiian earring, but the two are not homeomorphic.
See also
References
- Hatcher, Allen (2002), Algebraic topology, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-79540-0
- Munkres, James R. (2000), Topology, Englewood Cliffs, N.J: Prentice Hall, Inc, ISBN 0-13-181629-2
- Stillwell, John (1993), Classical topology and combinatorial group theory, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-97970-0