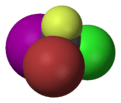
Bromochlorofluoroiodomethane
| |||
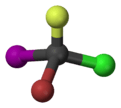 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bromo(chloro)fluoro(iodo)methane | |||
| Other names
Bromochlorofluoroiodomethane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 753-65-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 24590921 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CIBrClF | |||
| Molar mass | 273.271 g mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Bromochlorofluoroiodomethane is a hypothetical haloalkane with all four stable halogen substituents present in it.[1]
This compound can be seen as a methane molecule, whose four hydrogen atoms are each replaced with a different halogen atom. As the mirror images of this molecule are not superimposable, the molecule has two enantiomers. As one of the simplest such molecules, it is often cited as the prototypical chiral compound.[2] However since there is no synthetic route known to produce bromochlorofluoroiodomethane, the related simple chiral compound bromochlorofluoromethane is used instead when such a compound is required for research.
References
- ↑ Bromochlorofluoroiodomethane, Britannica.com
- ↑ Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations: Carbon with Three or Four Attached Heteroatoms, Volume 6, Thomas L. Gilchrist (Editor), ISBN 978-0-08-042704-1
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bromochlorofluoroiodomethane. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.