Burning of Falmouth
|
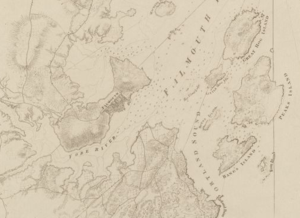
Detail from a 1777 nautical chart showing Falmouth (now Portland, Maine) | |
| Date | October 18, 1775 |
|---|---|
| Location | Falmouth, Massachusetts (present-day Portland, Maine) |
| Participants | Henry Mowat |
The Burning of Falmouth (October 18, 1775) was an attack by a fleet of Royal Navy vessels on the town of Falmouth, Massachusetts (site of the modern city of Portland, Maine, and not to be confused with the modern towns of Falmouth, Massachusetts or Falmouth, Maine). The fleet was commanded by Captain Henry Mowat.[1] The attack began with a naval bombardment which included incendiary shot, followed by a landing party meant to complete the town's destruction. The attack was the only major event in what was supposed to be a campaign of retaliation against ports that supported Patriot activities in the early stages of the American Revolutionary War.
Among the colonies, news of the attack led to rejection of British authority and the establishment of independent governments. It also led the Second Continental Congress to contest British Naval dominance by forming a Continental Navy. Both Mowat and his superior, Vice-Admiral Samuel Graves, who had ordered Mowat's expedition, suffered professionally as a consequence of the act.
Background
Following the battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, the British army was besieged in the City of Boston. The British were supported and supplied by the Royal Navy under the command of Vice-Admiral Samuel Graves, who was under Admiralty instruction to suppress the burgeoning rebellion. Under his orders, vessels were searched for military stores and potential military communications. Laid-up vessels were stripped of their masts and rudders to prevent their use by privateers and military equipment was salvaged from readily-accessible recent wrecks.[2]
Captain Henry Mowat had been in the port of Falmouth (present-day Portland, Maine) in May 1775, during Thompson's War when local Patriots captured several ships carrying supplies for Boston and weaponry from Fort Pownall at the mouth of the Penobscot River.[3] Graves' Admiralty orders (issued in July 1775 and received by him on October 4) required that he "carry on such Operations upon the Sea Coasts ... as you shall judge most effective for suppressing ... the Rebellion".[3] Graves ordered Mowat to "lay waste burn and destroy such Sea Port towns as are accessible to His Majesty's ships ... and particularly Machias where Margueritta was taken".[3]
Sailing to Falmouth
Mowat left Boston harbor on October 6, 1775[3] aboard his 16-gun[4] hydrographic survey sloop HMS Canceaux,[5] in company with the 20-gun[4] ship Cat,[6] the 12-gun[4] schooner[6] HMS Halifax,[5] the bomb sloop[6] HMS Spitfire,[5] and the supply ship[6] HMS Symmetry.[5][7] While his instructions were broad in the number of possible targets, he opted against attacks on harbors on Cape Ann, where the buildings were too widely spaced for naval cannon fire to be effective.[8] On October 16 he reached the outer parts of Falmouth harbor and anchored there.
The people of Falmouth had mixed reactions to the presence of the British fleet. Some recognized the Canceaux and believed there was no danger; but militia members remembering Thompson's War were more suspicious. The next day was windless: Mowat kedged the ships into the inner harbor and anchored them near the town. He sent one of his lieutenants ashore with a proclamation stating that he was there to "execute a just punishment" for the town's state of rebellion. He gave the townspeople two hours to evacuate.[8]
As soon as they received this ultimatum, the townspeople sent a deputation to plead with Mowat for mercy. He promised to withhold fire if the town swore an oath of allegiance to King George. They must also surrender all their small arms and powder, along with their gun carriages. In response, the people of Falmouth began to move out of the town. No oaths were sworn. A small number of muskets were surrendered, but no gun carriages.[8]
Attack
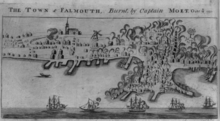
Mowat had set a deadline of 9:00 am on October 18 for the town's response. By 9:40 the town appeared to be deserted, so he ran a red flag up the Canceaux's masthead, and ordered the fleet to begin firing. Incendiary cannonballs set fire to the harbor installations and most of the town's houses and public buildings.[8] One witness reported:
The firing began from all the vessels with all possible briskness, discharging on all parts of the town ... a horrible shower of balls from three to nine pounds weight, bombs, carcasses, live shells, grapeshot and musketballs. ... The firing lasted, with little cessation, until six o'clock.[9]
When the bombardment appeared inadequate to Mowat, he sent a landing party to set fire to any buildings that had survived.[10] The town militia offered little significant resistance, as most were helping their families to safety. In spite of this, some of the landed British marines were killed or wounded.[11] By evening, according to Mowat, "the body of the town was in one flame".[12]
Aftermath
Following the bombardment, Mowat went on to Boothbay, where he set fire to a few houses and raided for livestock, but his expedition was faltering to an end. The decks of some of his ships had been inadequately braced for prolonged gunnery, and many of his guns had jumped their mounts. He returned to Boston, and remained there as winter was setting in. When Admiral Graves was relieved in December 1775, these punitive raids were gradually abandoned.[10] One of the last, undertaken to avenge British military losses to revolutionary Patriots, was the burning of Norfolk, Virginia, on January 1, 1776, instigated by Lord Dunmore, the Royal Governor of the Colony of Virginia.[13]
Damage assessment
More than 400 buildings and houses were recorded as damaged or destroyed by fire.[14] In his report to Graves, Mowat stated that eleven small vessels were destroyed in the harbor itself, and four captured, at the cost of one man killed and one wounded.[10] The people were left to fend for themselves for the winter. A visitor to the town reported that, a month later, there was "no lodging, eating or housekeeping in Falmouth".[12]
On October 26, the town formed a committee to raise funds for the distressed families. More than 1,000 people (out of an estimated population of 2,500), including at least 160 families, had been left homeless by the raid.[15][16] The Massachusetts Provincial Congress authorized £250 to be paid to the distressed families, and arranged for the distribution of up to 15 bushels of corn to those left destitute. As late as 1779, additional grants were made to needy families in Falmouth.[16] Despite numerous earlier entreaties to a wide variety of parties, significant recompense was not made until 1791, when Congress granted two tracts of land as compensation. These tracts became the towns of New Portland and Freeman. The town of Falmouth accounted losses in the raid at over £50,000.[17]
The citizens of Falmouth began rebuilding their town. In 1784 they built over 40 homes and 10 shops. By 1797 over 400 homes had been built, or rebuilt, along with factories, offices, and municipal buildings.[18] Part of the Falmouth Neck was politically separated in 1786 to form the city of Portland.[19]
Political reaction
News of the raid caused uproar in the colonies. Propagandists emphasised its cruelty.[10] The Massachusetts Provincial Congress authorized the issue of letters of marque, licensing privateer actions against the British navy.[20] The Second Continental Congress heard of the event just as word arrived of King George's Proclamation of Rebellion. Outraged by the news, Congress recommended that some provinces adopt self-rule and that Royal Navy ships in South Carolina be seized.[21] The attack on Falmouth stimulated Congress to advance its plans for establishment of a Continental Navy. It authorized the commissioning of two ships on October 30 "for the protection and defense of the united Colonies".[22] The Falmouth incident was again mentioned on November 25, when Congress passed legislation described by John Adams as "the true origin of the American Navy".[23]
When news of the event first reached England, it was dismissed as rebel propaganda.[24] When the reports were confirmed, Graves' superior, Lord George Germain expressed surprise rather than offence, noting that "I am to suppose that Admiral Graves had good reason for the step he took", in spite of orders (not received by Graves until after Mowat had sailed for Falmouth) to not take such acts unless the town clearly refused to do business with the British.[10] Graves was relieved of his command in December 1775, in part due to his failure to suppress the rebel naval forces.[25] Germain issued the orders before Falmouth burned.[26]
News of the event also reached the French government, who were carefully monitoring political developments in North America. The French foreign secretary wrote: "I can hardly believe this absurd as well as barbaric procedure on the part of an enlightened and civilized nation."[24]
Mowat's career suffered as a result of his actions. He was repeatedly passed over for promotion, and achieved it only when he downplayed his role in the event, or omitted it entirely from his record.[25]
Similar acts of reprisal
On August 30, 1775, Royal Naval Captain James Wallace, commanding HMS Rose, fired into the town of Stonington, Connecticut, after the townspeople there prevented Rose's tender from capturing a vessel it had chased into the harbor. Apparently not seeking to burn the town, he did not fire any heated rounds or incendiaries.[27] Wallace also fired on the town of Bristol, Rhode Island, in October 1775, after its townspeople refused to deliver livestock to him.[28]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Sometimes spelled Mowatt
- ↑ Duncan, pp. 215–216
- 1 2 3 4 Duncan, p. 216
- 1 2 3 Goold's gun count includes swivel guns, but not the mortars of the bomb sloop Spitfire. Half (or fewer) of this count were carriage-mounted cannon. Other references indicate Canceaux carried 8 cannon, and Halifax carried 6.
- 1 2 3 4 Goold, William The Burning of Portland 19 February 1873
- ↑ Symmetry may have carried guns, because other references indicate she fired during the Battle of Bunker Hill; but Goold describes her as a magazine for the bomb sloop during this engagement. As a safety measure to prevent loss of a ship through accidental ignition of unfired incendiary carcasses, carcasses were transferred by lighter from a non-firing ship to the bomb sloop as needed.
- 1 2 3 4 Duncan, p. 217
- ↑ Miller, p. 47
- 1 2 3 4 5 Duncan, p. 218
- ↑ Willis, p. 520
- 1 2 Miller, p. 48
- ↑ Fiske, p. 211
- ↑ Willis, p. 521
- ↑ Conforti, p. 60
- 1 2 Willis, pp. 521–523
- ↑ Willis, p. 524
- ↑ Conforti, p. 62
- ↑ Willis, p. 582
- ↑ Burke, p. 281
- ↑ Fiske, pp. 192–193
- ↑ Miller, pp. 48–49
- ↑ Miller, p. 49
- 1 2 Nelson, p. 146
- 1 2 Duncan, p. 219
- ↑ Nelson, p. 273
- ↑ Caulkins, p. 516
- ↑ Charles, pp. 168–169
References
- Burke, Edmund (1780). An Impartial History of the War in America. London: R. Faulder. OCLC 6187693.
- Caulkins, Frances Manwaring; Griswold, Cecelia (1895). History of New London, Connecticut: From the First Survey of the Coast in 1612 to 1860. New London, Connecticut: H. D. Utley. OCLC 1856358.
- Charles, Patrick J (2008). Irreconcilable Grievances: The Events That Shaped American Independence. Westminster, Maryland: Heritage Books. ISBN 978-0-7884-4566-8. OCLC 212838026.
- Conforti, Joseph (2007). Creating Portland: History and Place in Northern New England. Durham, NH: UPNE. ISBN 978-1-58465-449-0. OCLC 154804541.
- Duncan, Roger F (1992). Coastal Maine: A Maritime History. New York: Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-03048-8. OCLC 24142698.
- Fiske, John (1902). The Historical Writings of John Fiske, Volume 10. Boston: Houghton, Mifflin. OCLC 1658057.
- Miller, Nathan (1974). Sea of Glory: The Continental Navy fights for Independence 1775–1783. New York: David McKay. ISBN 978-0-679-50392-7. OCLC 844299.
- Nelson, James L (2008). George Washington's Secret Navy: How the American Revolution Went to Sea. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-149389-5. OCLC 212627064.
- Willis, William (1865). The History of Portland, from 1632 to 1864: With a Notice of Previous Settlements, Colonial Grants, and Changes of Government in Maine (2nd ed.). Portland, Maine: Bailey & Noyes. OCLC 2341166.
External links
- Images of Mowat's Proclamation at the Library of Congress: Page 1, Page 2
- Image and transcript of Mowat's report of the event
- Image and transcript of a letter describing the burning
- MPBN program article on the burning
Coordinates: 43°39′17″N 70°15′13″W / 43.65472°N 70.25361°W