Magazine (artillery)

Magazine is the name for an item or place within which ammunition or other explosive material is stored. It is taken originally from the Arabic word "makhāzin" (مخازن), meaning "(gunpowder) magazine or storeroom", via Italian and Middle French.[1]
The term is also used for a place where large quantities of ammunition are stored for later distribution, or an ammunition dump. This usage is less common.
Field magazines
In the early history of tube artillery drawn by horses (and later by mechanized vehicles), ammunition was carried in separate unarmored wagons or vehicles. These soft-skinned vehicles were extremely vulnerable to enemy fire and to explosions caused by a weapons malfunction.
Therefore, as part of setting up an artillery battery, a designated place would be used to shelter the ready ammunition. In the case of batteries of towed artillery the temporary magazine would be placed, if possible, in a pit, or natural declivity, or surrounded by sandbags or earthworks. Circumstances might require the establishment of multiple field magazines so that one lucky hit or accident would not disable the entire battery.
Naval magazines
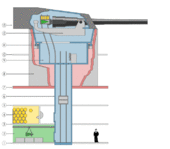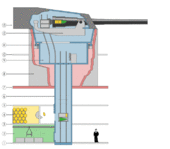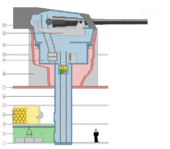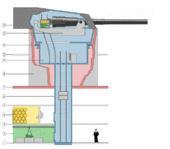
The ammunition storage area aboard a warship is referred to as a magazine or the "ship's magazine" by sailors.
Historically, when artillery was fired with gunpowder, a warship's magazines were built below the water line — especially since the magazines could then be readily flooded in case of fire or other dangerous emergencies on board the ship. An open flame was never allowed inside the magazine.
More modern warships use semi-automated or automated ammunition hoists. The path through which the naval artillery's ammunition passed typically has blast-resistant airlocks and other safety devices, including provisions to flood the compartment with seawater in an emergency.
The separation of shell and charge gave the storage of the former the name "shell room" and the latter "powder room".
.jpg)
Surface warships that have carried torpedoes, and ones that still do (such as the Mark 46 torpedo for antisubmarine warfare), have had torpedo magazines for carrying these dangerous antiship and antisubmarine weapons in well-defended compartments.
With the advent of missile-equipped warships, the term missile "magazine" has also been applied to the storage area for guided missiles on the ship, usually carried below the main decks of the warships. For ships with both forward and aft surface-to-air missile launchers, there are at least two missile magazines. Sometimes the magazines of guided-missile frigates and guided-missile destroyers have carried or do carry a mixture of various types of missiles: surface-to-air missiles, antisubmarine missiles such as the ASROC missile, and antiship missiles such as the Harpoon missile. See especially the Oliver Hazard Perry-class frigates, owned by several different navies around the world, in which one 40-missile magazine carries a mixture of all three types of missiles: surface-to-air, surface-to-surface, and surface-to-underwater.
In aircraft carriers, the magazines are required to store not only the aircraft carrier's own defensive weapons, but all of the weapons for her warplanes, including rapid-fire gun ammunition, air-to-air missiles such as the Sidewinder missile, air-to-surface missiles such as the Maverick missile, Mk 46 ASW torpedoes, Joint Direct Attack Munitions, "dumb bombs", HARM missiles, and antiship missiles such as the Harpoon missile and the Exocet missile.
Nuclear weapons storage
Nearly every detail of nuclear weapons storage is classified, although many of the same principles of an ammunition dump would apply. The one consistent factor is the greatly increased security compared to that afforded to the storage of other weapons.
In naval usage, most nuclear weapons are stored fitted to launch vehicles in the launch position. Their vertical launching system tubes (for nuclear armed cruise missiles) and missile tubes (for submarine-launched ballistic missiles) could technically be described as magazines. Nuclear weapon magazines also exist for other nuclear weapons such as nuclear gravity bombs and air-launched cruise missiles aboard aircraft carriers, and on other surface ships armed with nuclear depth charges though it is believed that since the end of the Cold War that most nations have progressively retired these weapons or chosen to store these weapons on land.[2]
The United States employs the Weapons Storage and Security System (WS3) for storing its tactical nuclear weapons in Europe.[3]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Magazines (artillery). |
External links
References
- ↑ Harper, Dzouglas. magazine. Dictionary.com Online Etymology Dictionary. Accessed September 01, 2013.
- ↑ Nonstrategic Nuclear Weapons. Amy F. Woolf. Congressional Research Service. 2016. https://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/nuke/RL32572.pdf
- ↑ U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Europe - Review of Post-Cold War Policy, Force Levels, and War Planning. Hans M. Kristensen. Natural Resources Defense Council. 2005. https://www.nrdc.org/sites/default/files/euro.pdf