Cupressaceae
| Cupressaceae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Cupressus sempervirens foliage and cones | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae Bartlett[1] |
| Subfamilies[2] | |
| |
Cupressaceae is a conifer family, the cypress family, with worldwide distribution. The family includes 27–30 genera (17 monotypic), which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130–140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or (rarely) dioecious trees and shrubs 1–116 m (3 ft 3 in–380 ft 7 in) tall. The bark of mature trees is commonly orange- to red- brown and of stringy texture, often flaking or peeling in vertical strips, but smooth, scaly or hard and square-cracked in some species.
Description

The leaves are arranged either spirally, in decussate pairs (opposite pairs, each pair at 90° to the previous pair) or in decussate whorls of three or four, depending on the genus. On young plants, the leaves are needle-like, becoming small and scale-like on mature plants of many genera; some genera and species retain needle-like leaves throughout their lives. Old leaves are mostly not shed individually, but in small sprays of foliage (cladoptosis); exceptions are the leaves on shoots, which develop into branches, which eventually fall off individually when the bark starts to flake. Most are evergreen with the leaves persisting 2–10 years, but three genera (Glyptostrobus, Metasequoia and Taxodium) are deciduous or include deciduous species.
The seed cones are either woody, leathery, or (in Juniperus) berry-like and fleshy, with one to several ovules per scale. The bract scale and ovuliferous scale are fused together except at the apex, where the bract scale is often visible as a short spine (often called an umbo) on the ovuliferous scale. As with the foliage, the cone scales are arranged spirally, decussate (opposite) or whorled, depending on the genus. The seeds are mostly small and somewhat flattened, with two narrow wings, one down each side of the seed; rarely (e.g. Actinostrobus) triangular in section with three wings; in some genera (e.g. Glyptostrobus and Libocedrus), one of the wings is significantly larger than the other, and in some others (e.g. Juniperus, Microbiota, Platycladus, and Taxodium) the seed is larger and wingless. The seedlings usually have two cotyledons, but in some species up to six. The pollen cones are more uniform in structure across the family, 1–20 mm long, with the scales again arranged spirally, decussate (opposite) or whorled, depending on the genus; they may be borne singly at the apex of a shoot (most genera), in the leaf axils (Cryptomeria), in dense clusters (Cunninghamia and Juniperus drupacea), or on discrete long pendulous panicle-like shoots (Metasequoia and Taxodium).
Cupressaceae is a widely distributed conifer family, with a near-global range in all continents except for Antarctica, stretching from 71°N in arctic Norway (Juniperus communis) south to 55°S in southernmost Chile (Pilgerodendron uviferum), while Juniperus indica reaches 5200 m altitude in Tibet, the highest altitude reported for any woody plant. Most habitats on land are occupied, with the exceptions of polar tundra and tropical lowland rainforest (though several species are important components of temperate rainforests and tropical highland cloud forests); they are also rare in deserts, with only a few species able to tolerate severe drought, notably Cupressus dupreziana in the central Sahara. Despite the wide overall distribution, many genera and species show very restricted relictual distributions, and many are endangered species.
Classification
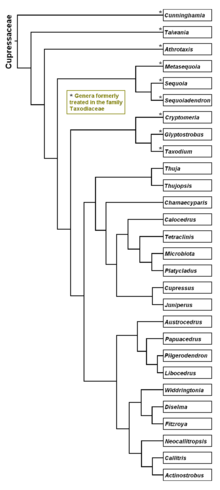
The family Cupressaceae is now widely regarded as including the Taxodiaceae, previously treated as a distinct family, but now shown not to differ from the Cupressaceae in any consistent characteristics. The one exception in the former Taxodiaceae is the genus Sciadopitys, which is genetically distinct from the rest of the Cupressaceae, and is now treated in its own family, Sciadopityaceae.
The family is divided into seven subfamilies, based on genetic and morphological analysis (Gadek et al. 2000, Farjon 2005; a more complete phylogeny, based on 10,000 nucleotides of plastid, mitochondrial, and nuclear sequence from 122 species, representing all genera is provided in Mao et al. 2012):
- Subfamily Cunninghamhioideae (Zucc. ex Endl.) Quinn[3]
- Cunninghamia R.Br.
- Subfamily Taiwanioideae L.C.Li[3]
- Taiwania Hayata
- Subfamily Athrotaxidoideae L.C.Li[3]
- Athrotaxis D.Don – Tasmanian cedar
- Subfamily Sequoioideae Saxton[3]
- Sequoia Endl. – coast redwood
- Sequoiadendron J.Buchholz – giant sequoia
- Metasequoia Hu & W.C.Cheng – dawn redwood
- Subfamily Taxodioideae Endl. ex K.Koch[3]
- Taxodium Rich. – bald cypress
- Glyptostrobus Endl. – Chinese swamp cypress
- Cryptomeria D.Don – sugi
- × Taxodiomeria
- Subfamily Callitroideae Saxton[4]
- Callitris Vent. – cypress-pine
- Actinostrobus Miq. – cypress-pine
- Neocallitropsis Florin
- Widdringtonia Endl.
- Diselma Hook.f.
- Fitzroya Hook.f. ex Lindl. – alerce
- Austrocedrus Florin & Boutelje
- Libocedrus Endl.
- Pilgerodendron Florin
- Papuacedrus H.L.Li
- Subfamily Cupressoideae Rich. ex Sweet[5]
- Thuja L. – thuja or arborvitae
- Thujopsis Siebold & Zucc. ex Endl. – hiba
- Chamaecyparis Spach – cypress
- Fokienia A.Henry & H.H.Thomas – Fujian cypress
- Calocedrus Kurz – incense-cedar
- Tetraclinis Mast.
- Microbiota Kom.
- Platycladus Spach – Chinese arborvitae
- Xanthocyparis Farjon & T. H. Nguyên – cypress
- Cupressus L. – cypress
- Juniperus L. – juniper
A 2010 study of Actinostrobus and Callitris places the three species of Actinostrobus within an expanded Callitris based on analysis of 42 morphological and anatomical characters.[6]
Superlatives
The family is notable for including the largest, tallest, and stoutest individual trees in the world, and also the second longest lived species in the world:
- Largest - Giant Sequoia, 1486.9 m³ trunk volume
- Tallest - Coast Redwood, 115.55 m tall
- Second stoutest - Montezuma Cypress or Ahuehuete, 11.42 m diameter (after African Baobab)
- Second oldest - Sarv-e_Abarkuh, estimated 4000 years (AbarKouh, Yazd, Iran) Alerce, 3622 years (after Great Basin Bristlecone Pine)
In addition to the above, many other members of the family list among the tallest, most massive, stoutest and most long-lived tree species in the world, including Taiwania, Sugi, Western Redcedar, Incense Cedar, Tibetan Cypress, and Formosan Cypress among others.
Uses

Many of the species are important timber sources, especially in the genera Calocedrus, Chamaecyparis, Cryptomeria, Cunninghamia, Cupressus, Sequoia, Taxodium, and Thuja. These and several other genera are also important in horticulture. Junipers are among the most important evergreen shrubs, groundcovers and small evergreen trees, with hundreds of cultivars selected, including plants with blue, grey, or yellow foliage. Chamaecyparis and Thuja also provide hundreds of dwarf cultivars as well as trees, including Lawson's cypress and the infamous hybrid Leyland cypress. Dawn redwood is widely planted as an ornamental tree because of its excellent horticultural qualities, rapid growth and status as a living fossil. Giant sequoia is a popular ornamental tree and is occasionally grown for timber. Giant sequoia, Leyland cypress, and Arizona cypress are grown to a small extent as Christmas trees.
Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) is the national tree of Japan, and Ahuehuete (Taxodium mucronatum) the national tree of Mexico. Coast redwood and giant sequoia were jointly designated the state tree of California and are famous California tourist attractions. Redwood National and State Parks and several parks including Giant Sequoia National Monument protect almost half the remaining stands of Coast Redwoods and Giant sequoias. Bald cypress is the state tree of Louisiana. Bald cypress, often festooned with Spanish moss, of southern swamps are another tourist attraction. They can be seen at Big Cypress National Preserve in Florida. Bald cypress "knees" are often sold as knick knacks, made into lamps or carved to make folk art. Monterey cypress is another famous picturesque tree often visited by tourists and photographers.
Baton Rouge, Louisiana ("red stick") was named after the decay-resistant red wood of Juniperus virginiana, used by Native Americans in the region for waymarking. Its heartwood is fragrant and used in clothes chests, drawers and closets to repel moths. It is a source of juniper oil used in perfumes and medicines. The wood is also used as long lasting fenceposts and for bows. The fleshy cones of Juniperus communis are used to flavour gin.
Calocedrus decurrens is the main wood used to make wooden pencils and is also used for cupboards and chests. Native Americans and early European explorers used Thuja leaves as a cure for scurvy. Distillation of Fokienia roots produces an essential oil called pemou oil used in medicine and cosmetics.
The pollen of many genera of Cupressaceae is allergenic, causing major hay fever problems in areas where they are abundant, most notably with sugi in Japan.
Several genera are an alternate host of Gymnosporangium rust, which damages apples and other related trees in the subfamily Maloideae.
References
- ↑ Watson, Frank D.; James E. Eckenwalder. "Cupressaceae Bartlett: Redwood or Cypress Family". eFloras. Missouri Botanical Garden. Retrieved 6 September 2013.
- ↑ Bosma, Hylke F.; Kunzmann, Lutz; Kvaček, Jiří; van Konijnenburg-van Cittert, Johanna H.A. (August 2012). "Revision of the genus Cunninghamites (fossil conifers), with special reference to nomenclature, taxonomy and geological age". Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. Elsevier. 182: 20–31. doi:10.1016/j.revpalbo.2012.06.004.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Armin Jagel, Veit Dörken: Morphology and morphogenesis of the seed cones of the Cupressaceae - part I. Cunninghamioideae, Athrotaxoideae, Taiwanioideae, Sequoioideae, Taxodioideae. In: Bulletin of the Cupressus Conservation Project, 3(3): 117-136 (PDF)
- ↑ Armin Jagel, Veit Dörken: Morphology and morphogenesis of the seed cones of the Cupressaceae - part III. Callitroideae. In: Bulletin of the Cupressus Conservation Project 4(3): 91-103 (PDF)
- ↑ Armin Jagel, Veit Dörken: Morphology and morphogenesis of the seed cones of the Cupressaceae - part II. Cupressoideae. In: Bulletin of the Cupressus Conservation Project 4(2): 51-78 (PDF)
- ↑ Piggin, J., and Bruhl, J.J. (2010). Phylogeny reconstruction of Callitris Vent. (Cupressaceae) and its allies leads to inclusion of Actinostrobus within Callitris. Australian Systematic Botany 23: 69-93.
- Farjon, A. (1998). World Checklist and Bibliography of Conifers. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 300 p. ISBN 1-900347-54-7.
- Farjon, A. (2005). Monograph of Cupressaceae and Sciadopitys. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ISBN 1-84246-068-4.
- Farjon, A., Hiep, N. T., Harder, D. K., Loc, P. K., & Averyanov, L. (2002). A new genus and species in the Cupressaceae (Coniferales) from northern Vietnam, Xanthocyparis vietnamensis. Novon 12: 179–189.
- Gadek, P. A., Alpers, D. L., Heslewood, M. M., & Quinn, C. J. (2000). Relationships within Cupressaceae sensu lato: a combined morphological and molecular approach. American Journal of Botany 87: 1044–1057. Available online.
- Little, D. P., Schwarzbach, A. E., Adams, R. P. & Hsieh, Chang-Fu. (2004). The circumscription and phylogenetic relationships of Callitropsis and the newly described genus Xanthocyparis (Cupressaceae). American Journal of Botany 91 (11): 1872–1881. Available online.
- Mao, K., Milne, R. I., Zhang, L., Peng, Y., Liu, J., Thomas, P., Mill, R. R. and S. S. Renner. (2012). Distribution of living Cupressaceae reflects the breakup of Pangea. Proceedings of the National Academy, USA 109(20): 7793-7798 -Open Access.
- Arboretum de Villardebelle Cone images of many species
- Gymnosperm Database: Cupressaceae
- Flora of China - Cupressaceae
- Flora of North America - Cupressaceae
- ×Taxodiomeria peizhongii tree named ‘Dongfangshan’ US PP17767 P3
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cupressaceae. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Cupressaceae |