Censavudine
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 4'-ethynylstavudine, festinavir |
| PubChem (CID) | 3008897 |
| ChemSpider | 2278330 |
| UNII |
6IE83O6NGA |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL124363 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 209894 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
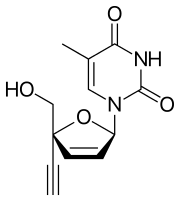
| Formula | C12H12N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 248.235 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Censavudine (INN),[1] is an investigational new drug being developed by Bristol Myers-Squibb for the treatment of HIV infection. Censavudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is active against HIV resistant to both abacavir and tenofovir, making the drug a candidate for people with multi-drug resistant (MDR) strains of the virus. Censavudine is a derivative of stavudine (d4T), but is less toxic. It was originally developed at Yale University.[2]
Renaming
Until 2013, censavudine has been known as festinavir, but the name was changed to avoid confusion with HIV protease inhibitors which all bear class suffix "–navir" (e.g. tipranavir, lopinavir, saquinavir etc.).
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Proposed International Nonproprietary Names: List 110" (PDF). World Health Organization. pp. 409–410.
- ↑ Alcorn, Keith (21 December 2010). "Bristol-Myers Squibb buys festinavir, new NRTI active against MDR HIV". aidsmap.com. aidsmap. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.