Fostemsavir
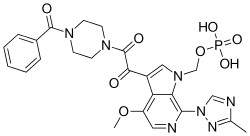 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
{3-[(4-Benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)(oxo)acetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl}methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
BMS-663068 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 864953-29-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 9494181 |
| PubChem | 11319217 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H26N7O8P | |
| Molar mass | 583.50 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fostemsavir (BMS-663068) is an experimental HIV entry inhibitor and a prodrug of temsavir (BMS-626529). It is under development by Bristol-Myers Squibb for use in the treatment of HIV infection. By blocking the gp120 receptor of the virus, it prevents initial viral attachment to the host CD4+ T cell and entry into the host immune cell; its method of action is a first for HIV drugs.[1] Because it targets a different step of the viral lifecycle, it offers promise for individuals with virus that has become highly resistant to other HIV drugs.[2] Since gp120 is a highly conserved area of the virus, the drug is unlikely to promote resistance to itself via generation of CD4-independent virus.[3]
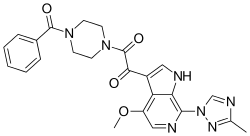
Temsavir (BMS-626529)
References
- ↑ HIV Attachment Inhibitor BMS-663068 Looks Good in Early Studies
- ↑ HIV attachment inhibitor BMS-663068 shows good safety and efficacy in phase 2b study
- ↑ Activity of the HIV-1 attachment inhibitor BMS-626529, the active component of the prodrug BMS-663068, against CD4-independent viruses and HIV-1 envelopes resistant to other entry inhibitors
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/6/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.