Centaurea cyanus
| Centaurea cyanus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Cynareae |
| Genus: | Centaurea |
| Species: | C. cyanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Centaurea cyanus L. | |
Centaurea cyanus, commonly known as cornflower, is an annual flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to Europe. In the past it often grew as a weed in cornfields (in the broad sense of the word "corn", referring to grains, such as wheat, barley, rye, or oats), hence its name. It is now endangered in its native habitat by agricultural intensification, particularly over-use of herbicides, destroying its habitat; in the United Kingdom it has declined from 264 sites to just 3 sites in the last 50 years.[1] In reaction to this, the conservation charity Plantlife named it as one of 101 species it would actively work to bring 'Back from the Brink'.[2] It is also, however, through introduction as an ornamental plant in gardens and a seed contaminant in crop seeds, now naturalised in many other parts of the world, including North America and parts of Australia.
Description
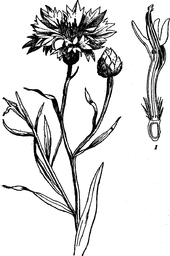
Cornflower is an annual plant growing to 16-35 inches tall, with grey-green branched stems. The leaves are lanceolate, 1–4 cm long. The flowers are most commonly an intense blue colour, produced in flowerheads (capitula) 1.5–3 cm diameter, with a ring of a few large, spreading ray florets surrounding a central cluster of disc florets. The blue pigment is protocyanin, which in roses is red.[3] It flowers all summer.[4]
Distribution
Centaurea cyanus is native to temperate Europe, but is widely naturalized outside its native range. It has been present in the British Isles as an archaeophyte (ancient introduction) since the Iron Age.[5] In Ireland, in Co.Clare (H9) Centaurea cyanus is recorded in arable fields as very rare and almost extinct.[6] while in the north-east of Ireland it was abundant before 1930s.[7]
Names
The common names bachelor's button, bluebottle, boutonniere flower, hurtsickle or cyani flower are also used.
It may also be referred to as basketflower, though the term also refers to the Plectocephalus group of Centaurea, which is probably a distinct genus. "Cornflower" is also used for chicory, and a few other Centaurea species; to distinguish C. cyanus from these it is sometimes called common cornflower.
Cultivation


It is grown as an ornamental plant in gardens, where several cultivars have been selected with varying pastel colours, including pink and purple. Cornflower is also grown for the cutflower industry in Canada for use by florists. The most common colour variety for this use is a doubled blue variety such as 'Blue Boy' or 'Blue Diadem'. White, pink, lavender and black (actually a very dark maroon) are also used but less commonly. A relative, Centaurea montana, is a perennial plant which is also cultivated as a garden plant. Cornflowers germinate quickly after planting.
Light requirements: full sun. Water requirements: high-average water daily. Soil pH requirements: neutral (6.6-7.5) to mildly alkaline (7.6-7.8).
Uses
The cornflower is considered a beneficial weed, and its edible flower can be used for culinary decoration, for example to add colour to salads. In herbalism, a decoction of cornflower is effective in treating conjunctivitis, and as a wash for tired eyes.[8]:127 Cornflowers have been used and prized historically for their blue pigment. Cornflowers are often used as an ingredient in some tea blends and herbal teas,[9] and is famous in the Lady Grey blend of Twinings.
Folklore and symbolism

In folklore, cornflowers were worn by young men in love; if the flower faded too quickly, it was taken as a sign that the man's love was not returned.[8]:126
The blue cornflower has been the national flower of Estonia since 1968 and symbolizes daily bread to Estonians. It is also the symbol of the Estonian political party, People's Union, the Finnish political party, National Coalition Party, and the Swedish political party, Liberal People's Party, and has since the dawn of the 20th century been a symbol for social liberalism there. It is the official flower of the Swedish province of Östergötland and the school flower of Winchester College and also of Dulwich College where it is said to have been the favourite flower of the founder, Edward Alleyn.
The blue cornflower was one of the national symbols of Germany.[10] This is partly due to the story that when Queen Louise of Prussia was fleeing Berlin and pursued by Napoleon's forces, she hid her children in a field of cornflowers and kept them quiet by weaving wreaths for them from the flowers. The flower thus became identified with Prussia, not least because it was the same color as the Prussian military uniform.[11] After the unification of Germany in 1871, it went on to become a symbol of the country as a whole. For this reason, in Austria the blue cornflower is a political symbol for pan-German and rightist ideas.[12][13] Members of the Freedom Party wore it at the opening of the Austrian parliament in 2006.[14]
It was also the favourite flower of Louise's son Kaiser Wilhelm I.[15] Because of its ties to royalty, authors such as Theodor Fontane have used it symbolically, often sarcastically, to comment on the social and political climate of the time.
The cornflower is also often seen as an inspiration for the German Romantic symbol of the Blue Flower.
Due to its traditional association with Germany, the cornflower has been made the official symbol of the annual German-American Steuben Parade.
In France the Bleuet de France is the symbol of the 11th November 1918 armistice and, as such, a common symbol for veterans (especially the now defunct poilus of World War I), similar to the Remembrance poppies worn in the United Kingdom and in Canada.[16]
The cornflower is also the symbol for motor neurone disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.[17]
Cornflowers are sometimes worn by Old Harrovians.
A Cornflower design (Blue Cornflower) was used by Corning Glass Works for the initial release of Corning Ware Pyroceram Cookware. Its popularity in the United States, Canada, United Kingdom and Australia was so high that it became the symbol of Corning Glass Works. The production of Blue Cornflower Corning Ware (known as Pyrosil Ware & Pyroflam in Europe) spanned over 30 years, with initial production from 1958 to 1988 and a second short run from 1993-1994 marking the 35th anniversary of their flagship consumer product. Corning Ware is no longer produced by Corning Glass Works, as the Consumer Products Division was sold to Borden, Inc./World Kitchen LLC. in 1998. Production of Pyroceram was discontinued in the United States and Canada by World Kitchen in 2000 in lieu of stoneware products, however, the popularity of the Blue Cornflower Corning Ware pattern (as well as a growing market for Pyroceram cookware) pushed World Kitchen, LLC. into a re-introduce Pyroceram Cookware imported from France in 2009 with the familiar Cornflower pattern.
In paintings
 Sergei Osipov. Cornflowers. 1976
Sergei Osipov. Cornflowers. 1976 Igor Grabar. Group portrait with cornflowers. 1914
Igor Grabar. Group portrait with cornflowers. 1914
See also
References
- ↑ "Action plan for Centaurea cyanus". Ukbap.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2009-02-21. Retrieved 2009-11-05.
- ↑ Gopher Systems Ltd, Pewsey, Wiltshire, UK - Web Design & Development in Southern England. "Plantlife website". Plantlife.org.uk. Retrieved 2009-11-05.
- ↑ Shiono M, Matsugaki N, Takeda K (2005). "Structure of the blue cornflower pigment". Nature. 436 (7052): 791. doi:10.1038/436791a. PMID 16094358.
- ↑ Rose, Francis (1981). The Wild Flower Key. Frederick Warne & Co. pp. 386–387. ISBN 0-7232-2419-6.
- ↑ "Online atlas of the British & Irish flora: Centaurea cyanus (Cornflower)". Biological Records Centre and Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ Skeffington, M.S. (2015). "Cornflower (Centaurea cynanus L.) and Good-king-henry (Chenopodium bonus-henricus L.)". Irish Naturalists' Journal. 34: 27–31.
- ↑ Hackney, P. (1992). Stewart & Corry's Flora of the North-east of Ireland (Third ed.). Institute of Irish Studies and The Queen's University of Belfast. ISBN 0-85389-446-9.
- 1 2 Howard, Michael (1987). Traditional Folk Remedies. Century.
- ↑ Archived December 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Cleene, Marcel; Lejeune, Marie Claire (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Herbs. Man & Culture.
The Cornflower was once the floral emblem of Germany (hence the German common name Kaiserblume).
- ↑ Reid, Marilyn (2007). Mythical Flower Stories. Lulu.com. p. 40. ISBN 978-1-84753-521-4.
- ↑ Whiteside, Andrew G. (1993). Pan-Germanism: Anti-Semitism in Mass-Style Politics. Current Research on Anti-Semitism: Hostages of Modernization. 3/2. de Gruyter. p. 691.
- ↑ Unowsky, Daniel L. (2005). The Pomp and Politics of Patriotism: Imperial Celebrations in Habsburg Austria, 1848–1916. Purdue University Press. p. 157.
- ↑ "Anklänge an illegale NSDAPler". ORF.at. 30 October 2006.
- ↑ Coulter, Lynn (2009). Gardening with Heirloom Seeds: Tried-and-True Flowers, Fruits, and Vegetables for a New Generation. ReadHowYouWant.com, Limited. p. 165. ISBN 978-1-4587-2217-1.
- ↑ "Le Bleuet de France - Page d'accueil". Bleuetdefrance.fr. Retrieved 2009-11-05.
- ↑ "The Cornflower - an ALS symbol". Als.ca. 2004-05-31. Retrieved 2009-11-05.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Centaurea cyanus. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Centaurea cyanus |
| Look up centaurea cyanus in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Flora Europaea: Centaurea cyanus
- UK Biodiversity Action Plan: Centaurea cyanus
- Briefing sheet on Centaurea cyanus from page
