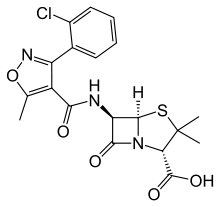
Cloxacillin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cloxapen |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM |
| ATC code | J01CF02 (WHO) QJ51CF02 (WHO) QS01AA90 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37 to 90% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Biological half-life | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
61-72-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6098 |
| DrugBank |
DB01147 |
| ChemSpider |
5873 |
| UNII |
O6X5QGC2VB |
| KEGG |
D07733 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:49566 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL891 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molar mass | 435.88 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin.
Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, which does not allow the beta-lactamases to bind. This drug has a weaker antibacterial activity than benzylpenicillin, and is devoid of serious toxicity except for allergic reactions.
Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by Beecham.[1] It is sold under a number of trade names, including Cloxapen, Cloxacap, Tegopen and Orbenin. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most important medication needed in a basic health system.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ David Greenwood (2008). Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph. Oxford University Press US. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- ↑ "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.