Colestipol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Colestid, Cholestabyl |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682157 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (suspension or tablets) |
| ATC code | C10AC02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Excretion | Faeces, in complex with bile acids |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
26658-42-4 37296-80-3 (HCl) |
| PubChem (CID) | 62816 |
| DrugBank |
DB00375 |
| ChemSpider | none |
| UNII |
K50N755924 |
| KEGG |
C06925 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1201678 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | (C4H10N3)m(C3H6O)n |
| | |
Colestipol (trade names Colestid, Cholestabyl) is a bile acid sequestrant used to lower blood cholesterol, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL).[1][2] It is also used to reduce stool volume and frequency, and in the treatment of chronic diarrhea.[3]
Like cholestyramine, colestipol works in the gut by trapping bile acids and preventing them from being reabsorbed. This leads to decreased enterohepatic recirculation of bile acids, increased synthesis of new bile acids by the liver from cholesterol, decreased liver cholesterol, increased LDL receptor expression, and decreasing LDL in blood.[4]
Side effects
The following notable side effects may occur:[2]
- gastrointestinal tract disturbances, especially (mild, occasionally severe) constipation
- sometimes increase in VLDL and triglyceride synthesis
Interactions
Colestipol can bind to a number of drugs and nutrients in the gut and inhibit or delay their absorption. Such substances include:[2]
- thiazide diuretics, furosemide
- gemfibrozil
- benzylpenicillin, tetracycline
- digoxin
- lipid-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Contraindications
Colestipol is contraindicated in hypertriglyceridemia (high level of triglycerides in the blood).
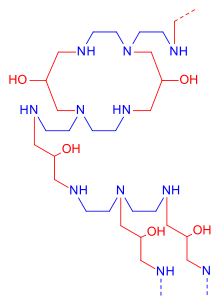
Chemistry
Colestipol is a copolymer of diethylenetriamine (DETA) —or tetraethylenepentamine according to some sources[5][6]— and epichlorohydrin.[7][8] The structure drawing (top right) shows the DETA moieties in blue and the epichlorohydrin moieties in red.
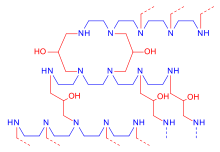 Alternative chemical structure, with tetraethylenepentamine instead of diethylenetriamine; formula (C8H18N5)m(C3H6O)n |
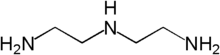 The constituent DETA 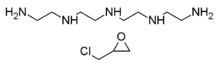 The constituents tetraethylenepentamine (top) and epichlorohydrin (bottom) |
Notes and references
- ↑ Handelsman, Y. (2011). "Role of Bile Acid Sequestrants in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes". Diabetes Care. 34: S244–S250. doi:10.2337/dc11-s237. PMID 21525463.
- 1 2 3 Drugs.com: Colestipol Hydrochloride
- ↑ http://www.medicinenet.com/colestipol/article.htm
- ↑ Mutschler, Ernst; Schäfer-Korting, Monika (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 523. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- ↑ Clinical Pharmacology: Colestipol structure
- ↑ Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Care Group: Colestipol structure
- ↑ Haberfeld, H, ed. (2009). Austria-Codex (in German) (2009/2010 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 3-85200-196-X.
- ↑ Steinhilber, D; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M; Roth, HJ (2005). Medizinische Chemie (in German). Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag. p. 433. ISBN 3-7692-3483-9.