Dixie
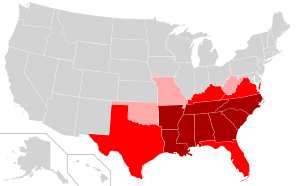
Dixie is a historical nickname for the Southern United States.
"Dixie" as a region

As a definite geographic location within the United States, "Dixie" is usually defined as the eleven Southern states that seceded in late 1860 and early 1861 to form the new confederation named the Confederate States of America. They are (in order of secession): South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee. Missouri and Kentucky were the 12th and 13th to secede, but were technically both union and confederate.
However, the location and boundaries of "Dixie" have become, over time, more limited, vernacular, and mercurial. Today, it is most often associated with those parts of the Southern United States where traditions and legacies of the Confederate era and the antebellum South live most strongly.[5]
Many businesses in the South contain "Dixie" in their name as an identifier, such as supermarket chain Winn-Dixie.
Origin of the name

According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the origins of this nickname remain obscure. According to A Dictionary of Americanisms on Historical Principles (1951), by Mitford M. Mathews, three theories most commonly attempt to explain the term:
- The word "Dixie" refers to currency issued first by the Citizens State Bank (located in the French Quarter of New Orleans) and then by other banks in Louisiana.[6] These banks issued ten-dollar notes,[7] labeled "Dix", French for "ten", on the reverse side. The notes were known as "Dixies" by English-speaking southerners, and the area around New Orleans and the French-speaking parts of Louisiana came to be known as "Dixieland". Eventually, usage of the term broadened to refer to the Southern states in general.
- The word preserves the name of a "Mr. Dixy", a slave owner on Manhattan Island, where slavery was legal until 1827 (see History of slavery in New York). His rule was so kind that "Dixy's Land" became famed far and wide as an elysium abounding in material comforts.
- "Dixie" derives from Jeremiah Dixon, a surveyor of the Mason–Dixon line which defined the border between Maryland and Pennsylvania, and, for the most part, free and slave states. (Delaware, a Union border state, and slave state up to the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment, lay outside the "Dixie" side of the survey line.)
Songs
"I Wish I Was in Dixie"


"I Wish I Was in Dixie" is a popular song about the South. It was allegedly written by composer Daniel Emmett, a Northerner from Mount Vernon, Ohio, and published in 1859. Emmett's claims of the origin of the song were many and varied. According to one such version, Emmett was taught the song by the Snowden family of African American musicians, then freemen of color, with the lyrics coming from a letter written longingly of life in the south by Evelyn Snowden to her father. Emmett's blackface minstrel-show troupe debuted the song that same year in New York City when they needed a song to lengthen their presentation and it became an immediate hit. As with other minstrel show numbers, the song was performed in blackface and in exaggerated Black English vernacular. The song proved extremely popular and became widely known simply as "Dixie". The song has also been published as "Dixie's Land".
The song became the unofficial anthem of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. The tune's minstrel-show origins have created a strong association of "Dixie" with the Old South, despite the fact that it was written in the North. As a result, some today perceive the song as offensive and racist while others see it as an honorable part of Southern heritage. Abraham Lincoln, upon hearing of the Confederate surrender at Appomattox, asked the military band to play Dixie.[8][9]
 |
|
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Oh, Soo. "Which states do you think belong in the South?". Vox. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ↑ Wilson, Charles & William Ferris Encyclopedia of Southern Culture ISBN 978-0-8078-1823-7; Univ. of Pennsylvania Telsur Project Telsur Map of Southern Dialect
- ↑ Vance, Rupert Bayless, Regionalism and the South, Univ. of North Carolina Press, 1982, p. 166 "West Virginia is found to have its closest attachment to the Southeast on the basis of agriculture and population."
- ↑ David Williamson (June 2, 1999). "UNC-CH surveys reveal where the 'real' South lies". Retrieved 22 Feb 2007.
- ↑ ""Where Does the South Begin?"". The Atlantic. 28 Jan 2011.
- ↑ "Dixie" Originated From Name "Dix" An Old Currency - New Orleans American May 29 1916, Vol. 2 No. 150, Page 3 Col. 1 Louisiana Works Progress Administration (WPA), LOUISiana Digital Library
- ↑ Ten Dollar Note George Francois Mugnier Collection, LOUISiana Digital Library
- ↑ Herbert, David, Lincoln, pp. 580 (Simon and Schuster, 1996)
- ↑ "Lincoln Called For Dixie, from NY Times archives,7 February 1909" (PDF). The New York Times. February 7, 1909.
References
- John Shelton Reed (with J. Kohl and C. Hanchette) (1990). The Shrinking South and the Dissolution of Dixie. Social Forces. pp. 69 (September 1990): 221–233.
- Sacks, Howard L. and Judith Rose. Way Up North In Dixie. (Smithsonian Institution Press, 1993)
Coordinates: 34°N 86°W / 34°N 86°W