Duchy of Legnica
| Duchy of Legnica | ||||||||||
| Księstwo Legnickie (pl) Herzogtum Liegnitz (de) Lehnické knížectví (cs) | ||||||||||
| Silesian duchy | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
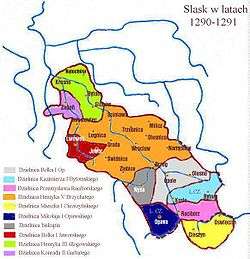 Greatest extent of territory of the Duchy
during the reign of Henry V (orange) | ||||||||||
| Capital | Legnica | |||||||||
| Government | Duchy | |||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages Early modern period | |||||||||
| • | Battle of Legnica | 1241 | ||||||||
| • | Partitioned from Lower Silesia |
1248 | ||||||||
| • | Split off Duchy of Głogów |
1251 | ||||||||
| • | Vassalized by Bohemia |
1329 | ||||||||
| • | Inheritance treaty with Brandenburg |
1537 | ||||||||
| • | Seized by Habsburg | 1675 | ||||||||
| • | Annexed by Prussia | 1742 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
The Duchy of Legnica (Polish: Księstwo Legnickie, Czech: Lehnické knížectví) or Duchy of Liegnitz (German: Herzogtum Liegnitz) was one of the Duchies of Silesia. Its capital was Legnica (Liegnitz) in Lower Silesia.

Legnica Castle had become a residence of the Silesian dukes in 1163 and from 1248 was the seat of a principality in its own right, ruled by the Silesian branch of the Piast dynasty until 1675. Formed by Bolesław II the Bald, Duke of Lower Silesia at Wrocław, Legnica shared the fate of most of the others Silesian duchies, falling into Bohemian, Austrian and eventually - after the First Silesian War - Prussian spheres of influence.
History
Legnica became famous for the Battle of Legnica (or Battle of Wahlstatt) that took place at the nearby village of Legnickie Pole (Wahlstatt) near the city on 9 April 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. The Christian army of the Polish High Duke Henry II the Pious, supported by the feudal nobility, included Poles, Bavarian miners and military orders, was decisively defeated by the Mongols. Although the Mongols killed Henry and destroyed his forces, their advance into Europe was halted when they turned back to attend to the election of a new Khagan (Grand Khan) following the death in the same year of Ögedei Khan. Minor celebrations are held annually in Legnica to commemorate the battle.
After Henry's II death his eldest son Bolesław II the Bald followed him as ruler of Lower Silesia until in 1248 his younger brother Henry III the White came of age and claimed his rights of succession. Backed by the nobility of Wrocław, Henry forced the duke to cede central parts of the Lower Silesian duchy to him, while Bolesław himself retired to Legnica. Furthermore he came into conflict with his younger brother Konrad, who, originally predestined for an ecclesiastical career as Bishop of Passau, also demanded his distributive share and had to be paid off by Bolesław with the newly created Duchy of Głogów in 1251.
Nevertheless Bolesław's son Henry V the Fat, who succeeded his father in 1278, was able to enlarge the duchy's territories by defeating his cousin Henry IV Probus of Wrocław and, with support of King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia succeeding him as Duke in 1290, thus re-reuniting the Legnica and Wrocław duchies. As after the death of Henry V in 1296 his eldest son Bolesław III the Generous was still a minor, King Wenceslaus took over his guardianship, strengthening the Bohemian influence in Silesia. In 1303 Bolesław III was betrothed to Wenceslaus' daughter Margaret and to no avail tried to follow the extinct Přemyslid dynasty on the Bohemian throne in 1306. He was not able to retain the united duchy and in 1311 Lower Silesia was split again, with Wrocław going to his younger brother Henry VI the Good. Even Bolesław's rule over Legnica was contested by his brother Władysław and in 1329 he had to pay homage to the Bohemian King John of Luxembourg to secure his reign.
As the duchy's capital at the beginning of the 14th century, Legnica was an important city of Central Europe, with a population of approximately 16,000 residents. The city began to expand quickly after the discovery of gold in the Kaczawa.
A Bohemian vassal from 1329 on, the political weakness of the duchy continued, caused by domestic conflicts between Bolesław's sons Wenceslaus and Louis the Fair strengthening the influences of the Holy Roman Empire. When in 1419 the Legnica branch of the Silesian Piasts became extinct with the death of Duke Wenceslaus II, the duchy fell to Duke Louis II of Brzeg. As Louis himself had no male heirs, Legnica was annexed as a ceased fief by the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1449. Nevertheless five years later the duchy was restored and given to Frederick I, the son of Louis' daughter Hedwig.
The Protestant Reformation was introduced in the duchy as early as 1522 and the population became Lutheran. After the death of the Bohemian King Louis II at Mohács in 1526, the Lands of the Bohemian Crown including the Legnica fiefdom were inherited by the Habsburg Monarchy. The first map of Silesia was made by native son Martin Helwig in 1561.
In 1675, Legnica passed to direct Habsburg rule after the death of the last Silesian Piast duke, George William, the son of Duke Christian of Brzeg, despite an inheritance pact concluded with Brandenburg in 1537. For King Frederick II of Prussia the old dispute was a pretext to justify his campaign during the First Silesian War. In 1742 most of Silesia including Legnica became part of the Prussia after Empress Maria Theresa's defeat in the War of the Austrian Succession; it lost most of its privileges after being annexed by Prussia.
Dukes of Legnica
- 1248–1278 Bolesław II the Bald, eldest son of the Polish High Duke Henry II the Pious, jointly with
- 1248–1251 Konrad I, brother, Duke of Głogów from 1251
- 1278–1296 Henry V, son of Bolesław II, also Duke of Wrocław from 1290
- 1296–1311 Bolesław III the Generous, son, also Duke of Wrocław, Duke of Brzeg from 1311, jointly with
- 1296–1311 Henry VI the Good, brother, sole Duke of Wrocław from 1311
- 1296–1312 Władysław
- 1312–1342 Bolesław III the Generous, again
- 1342–1345 Wenceslaus I, son, jointly with
- 1342–1346 Louis I the Fair, brother, Duke of Brzeg from 1358
- 1346–1364 Wenceslaus I, again
- 1364–1409 Rupert I, son, jointly with
- 1364–1413 Wenceslaus II, brother, also Bishop of Wrocław and Duke of Nysa from 1382
- 1364–1394 Bolesław IV, brother
- 1364–1398 Henry VIII, brother, also Bishop of Kujawy from 1389
- 1413–1436 Louis II, grandson of Louis I the Fair, also Duke of Brzeg since 1399
Line extinct, seized by Bohemia
- 1436–1453 claimed by Louis III of Oława, nephew of Louis II, and his sons John I of Lüben and Henryk X of Chojnów
- 1454–1488 Frederick I, son of John I of Lüben, also Duke of Brzeg from 1481
- 1488–1495 John II, son, jointly with
- 1488–1547 Frederick II, brother, also Duke of Brzeg 1503–1505 and from 1521
- 1488–1521 George I, also Duke of Brzeg from 1503
- 1547–1551 Frederick III, son of Frederick II, deposed
- 1551–1556 Henry XI, son, under regency of his uncle Duke George II of Brzeg
- 1556–1559 Frederick III, again, deposed,
- 1559–1576; 1580–1581 Henry XI, again, twice restored and again deposed, jointly with
- 1571–1596 Frederick IV, brother
- 1596–1602 Joachim Frederick, son of George II of Brzeg, Duke of Brezeg since 1595
- 1602–1612 John Christian, son, also Duke of Brzeg, jointly with
- 1602–1653 George Rudolph, brother
- 1653–1654 George III, son of John Christian, also Duke of Brzeg since 1633, jointly with
- 1663–1664 George III, again, jointly with
- 1663–1672 Christian, again, also Duke of Brzeg from 1664
- 1672–1675 George William, son, also Duke of Brzeg
Male line of Silesian Piasts extinct.
Sources
- Rudolf Žáček, Dějiny Slezska v datech, Libri Praha 2003, ISBN 80-7277-172-8
Coordinates: 51°12′30″N 16°09′37″E / 51.208333°N 16.160278°E


