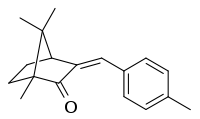
4-Methylbenzylidene camphor
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3E)-1,7,7-Trimethyl-3-[(4-methylphenyl)methylene]-2-norbornanone | |
| Other names
Enzacamene; 3-(4-Methylbenzylidene)bornan-2-one 3-(4-Methylbenzylidene)-dl-camphor | |
| Identifiers | |
| 36861-47-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | 4-MBC |
| ChemSpider | 4939160 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.386 |
| EC Number | 253-242-6 |
| PubChem | 6434217 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22O | |
| Molar mass | 254.37 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 66 to 69 °C (151 to 156 °F; 339 to 342 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Xi |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 R50 R53 |
| S-phrases | S26 S37/39 S61 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Methylbenzylidene camphor (4-MBC, enzacamene) is an organic camphor derivative that is used in the cosmetic industry for its ability to protect the skin against UV, specifically UV B radiation. As such it is used in sunscreen lotions and other skincare products claiming a SPF value. Its tradenames include Eusolex 6300 (Merck) and Parsol 5000 (DSM).
Mechanism
All the camphor sunscreens are supposed to dissipate the photon energy by cis-trans isomerisation. But for 4-MBC the quantum yield for this isomerisation is reported to be only between 0.13 - 0.3. This low quantum yield means that other photochemical processes are occurring.[2]
Endocrine disruptor
Studies have raised the issue that 4-MBC acts an endocrine disruptor. There is controversy about the estrogenic effects of 4-MBC and while one study showed only a relatively minor effect,[3] a study in Switzerland showed significant uterine growth in immature rodents.[4] In addition, there is some evidence that 4-MBC may suppress the pituitary-thyroid axis leading to hypothyroidism.[5]
The agent can also lead to a photoallergic dermatitis.
Approval status
4-MBC has been banned for use in Europe by the European Union since 2015.[6] It is approved in Canada by Health Canada. It is not approved for use in the USA by the Food and Drug Administration and it is not permitted in Japan.
See also
References
- ↑ 3-(4-METHYLBENZYLIDEN)CAMPHOR at chemicalland21.com
- ↑ Sun Protection in Man. Chapter 26: Cantrell, Ann; McGarvey, David J.; Truscott, T. George. Photochemical and photophysical properties of sunscreens.
- ↑ Mueller SO; Kling M; Arifin Firzani P; et al. (April 2003). "Activation of estrogen receptor alpha and ERbeta by 4-methylbenzylidene-camphor in human and rat cells: comparison with phyto- and xenoestrogens". Toxicol. Lett. 142 (1-2): 89–101. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00016-X. PMID 12765243.
- ↑ Sun Block has Endocrine Disruptor Chemicals, New Scientist, April 18, 2001
- ↑ IH Hamann; C Schmutzler; P Kirschmeyer; H Jarry & J Köhrle (2006). "4-Methylbenzylidene-camphor (4MBC) causes pituitary effects comparable to hypothyroidism". Endocrine Abstracts. 11: OC60.
- ↑ http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32015R1298&from=EN