Governorates of Bahrain
| Governorates of Bahrain محافظات البحرين (Arabic) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Kingdom of Bahrain |
| Number | 4 Governorates |
| Populations | 91,450 (Southern Governorate) – 497,000 (Capital Governorate) |
| Areas | 98 km2 (38 sq mi) (Capital Governorate) – 1,130 km2 (438 sq mi) (Southern Governorate) |
| Government | governate government, National government |
| Subdivisions | Constituencey |
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Bahrain |
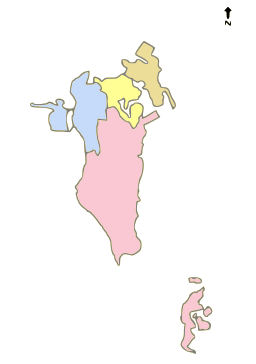
There are four Governorates in Bahrain; the Capital, Northern, Southern and Muharraq. There had previously been five until September 2014, when the Central Governorate was abolished. [1]
History
The first municipality in Bahrain was the 8-member Manama municipality which was established in July 1919.[2] Members of the municipality were elected annually; the municipality was said to have been the first municipality to be established in the Arab world.[2] The municipality was in charge of cleaning roads and renting buildings to tenants and shops. By 1929, it undertook road expansions as well as opening markets and slaughterhouses.[2] In 1958, the municipality started water purification projects.[2] In 1960, Bahrain comprised four municipalities including Manama, Hidd, Al Muharraq, and Riffa.[3] Over the next 30 years, the 4 municipalities were divided into 12 municipalities as settlements such as Hamad Town and Isa Town grew.[3] These municipalities were administered from Manama under a central municipal council whose members are appointed by the king.[4] After September 22nd, 2014, Bahrain was split into four governorates. These governorates are:
| Map | Governorate | Population (2014) | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Yellow Capital Governorate | 532,000 | 68 | |
| Gold Muharraq Governorate | 216,000 | 57 | |
| Light Blue Northern Governorate | 326,000 | 175 | |
| Pink Southern Governorate | 166,000 | 480 |
The first municipal elections to be held in Bahrain after independence in 1971, was in 2002.[5] The most recent was in 2014.
Constituencies
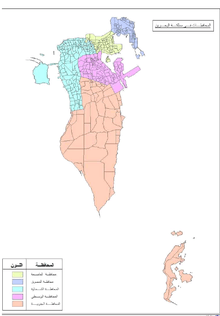
A specific number of adjacent city blocks are grouped together to form an area (listed as area 1, area 2 etc.). Each of these areas forms a constituency in the country's electorate. Every four years, elections are held in these constituencies, with each constituency electing its own MP. The most recent election was in the Bahraini parliamentary by-election in 2011.
Each governorate also has its own municipality council, with separate elections for them.
See also
External links
References
- ↑ The Gulf Daily News
- 1 2 3 4 "History of Municipalities". Ministry of Municipalities Affairs and Urban Planning – Kingdom of Bahrain. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- 1 2 "Governorates of Bahrain". Statoids. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ↑ "Bahrain Government". Permanent Mission of the Kingdom of Bahrain to the United Nations. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ↑ "Three Polls, Three Different Approaches". The Estimate. 17 May 2002. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 5 July 2012.