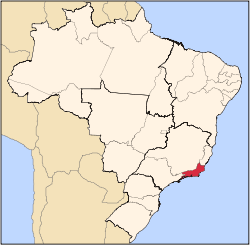
Guapimirim
| Guapimirim | |
|---|---|
|
Dedo de Deus mountain (God's finger) | |
 Location in Rio de Janeiro | |
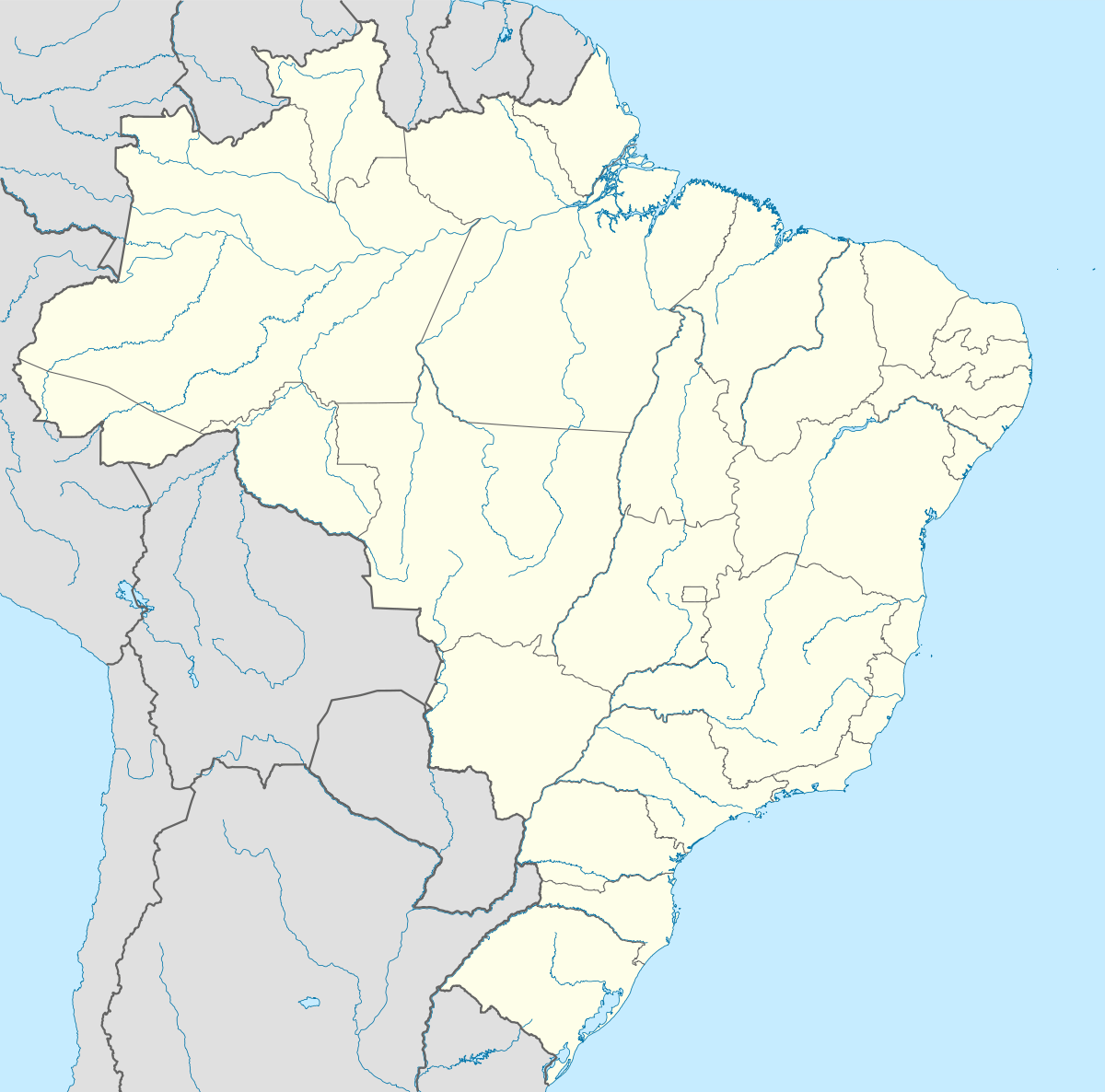 Guapimirim Location in Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 22°32′13″S 42°58′55″W / 22.536944°S 42.981944°WCoordinates: 22°32′13″S 42°58′55″W / 22.536944°S 42.981944°W | |
| Country | Brazil |
| State | Rio de Janeiro |
| Area | |
| • Total | 360.813 km2 (139.311 sq mi) |
Guapimirim (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈɡwapiˈmiɾĩ], from Tupi 'little spring', guapi 'spring', mirim 'little'), is a city in the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan Area, and a municipality located in Rio de Janeiro state, southeastern Brazil.
Geography
It is on Guanabara Bay, 84 kilometers north of the city of Rio de Janeiro, at an altitude of 48 meters.
The population of Guapimirim was 51,487 in 2010, and its area is 361 km².[1] It is the 37th most populous municipality in the state of Rio de Janeiro.
The municipality is located in a valley at the base of the Finger of God peak in the Organ Mountains. It borders the municipalities of: Teresópolis and Petrópolis (north), Itaboraí (south), Waterfalls Macacu (east), and Magé and Guanabara Bay (west).
Conservation
The municipality contains part of the Central Rio de Janeiro Atlantic Forest Mosaic, created in 2006.[2] It held 24% of the 4,920 hectares (12,200 acres) Paraíso Ecological Station, created in 1987 and now integrated into the Três Picos State Park.[3] It contains 4% of the 46,350 hectares (114,500 acres) Três Picos State Park, created in 2002.[4] It contains part of the 19,508 hectares (48,210 acres) Bacia do Rio Macacu Environmental Protection Area, created in 2002.[5] The municipality contains the 15,582 hectares (38,500 acres) Guapi-Guapiaçú Environmental Protection Area, created in 2004.[6] It contains 42% of the 1,936 hectares (4,780 acres) Guanabara Ecological Station, created in 2006.[7]
Features
Seventy percent of its territory is within the Guapimirim Environmental Protection Area, a coastal marine nature preserve also in the municipalities of Itaboraí, Magé, and São Gonçalo.
Guapimirim Municipality, together with the municipalities of Petrópolis, Teresópolis, Freiburg, Mage, Sao Jose do Rio Preto Valley, Three Rivers, Commander Levy Gasparian, Areal, and Waterfalls Macacu — make up the tourist region known as Imperial Green Mountain.
References
- ↑ IBGE -
- ↑ Costa, Cláudia; Lamas, Ivana; Fernandes, Rosan (December 2010), Planejamento Estratégico do Mosaico Central Fluminense (PDF) (in Portuguese), Reserva da Biosfera da Mata Atlântica, p. 13, retrieved 2016-10-02
- ↑ ESEC do Paraíso (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-10-03
- ↑ PES dos Três Picos (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-10-03
- ↑ APA da Bacia do Rio Macacu (in Portuguese), INEA: Instituto estadual do ambiente, retrieved 2016-10-07
- ↑
- Pedreira, Bernadete da Conceição C.G.; Cardoso Fidalgo, Elaine Cristina; Camardelli Uzeda, Mariella; Alves da Costa, Michell Douglas (December 2011), "Áreas Prioritárias para Recuperação na Região da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Guapi-Macacu, RJ" (PDF), Boletim de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento (in Portuguese), ISSN 1678-0892, retrieved 2016-10-10
- ↑ ESEC da Guanabara (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-10-05