Ink sac
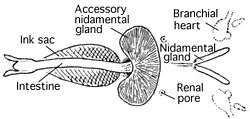
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all coeloids (squid, octopus and cuttlefish) which dwell in light conditions have an ink sac, which can be used to expel a cloud of dark ink in order to confuse predators.[1]
The ink sac is a muscular bag which originated as an extension of the hind gut; it is a modified hypobranchial gland.[2] It lies beneath the gut and opens into the anus, into which its contents – almost pure melanin – can be squirted; its proximity to the base of the funnel means that the ink can be distributed by ejected water as the cephalopod uses its jet propulsion.[1] The ejected cloud of melanin is bound by mucus particles, so it forms a lump approximately the size and shape of the cephalopod, fixing the predator's attention while the mollusc itself makes a hasty escape.[1]
A general level of provocation is necessary to trigger an octopus to release its ink, as it is biologically costly to produce. Some species can even use their ink to stun or numb their predators.
References
- 1 2 3 Boyle, Peter; Rodhouse, Paul (2004). Cephalopods : ecology and fisheries. Ames, Iowa: Blackwell. doi:10.1002/9780470995310.ch2. ISBN 0-632-06048-4.
- ↑ Nair, J.R., D. Pillai, S.M. Joseph, P. Gomathi, P.V. Senan & P.M. Sherief (2011). "Cephalopod research and bioactive substances." (PDF). Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences 40(1): 13–27.


