Iron(II) lactate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ferrous 2-hydroxypropanoate | |
| Other names
Iron dilactate Iron(II) lactate E585 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 5905-52-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 20839 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.098 |
| E number | E585 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem | 22197 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10FeO6 | |
| Molar mass | 233.99 g/mol |
| Appearance | greenish-white powder |
| Melting point | 500 °C (932 °F; 773 K) |
| trihydrate: 2.1 g/100ml (10 °C) 8.5 g/100ml (100 °C) dihydrate: 2% (25 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | soluble in alkali citrates negligible in alcohol insoluble in ether |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
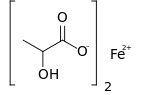
Ferrous lactate, or iron(II) lactate, is a chemical compound consisting of one atom of iron (Fe2+) and two lactate anions. It has the chemical formula Fe(C3H5O3)2.
Uses
It is used as a food additive with E number E585. It is an acidity regulator and colour retention agent, and is also used to fortify foods with iron.
Safety
It is toxic and may cause irritation. Avoid inhalation of dusts. Remove all contamination, rinse with plenty of water. May cause some health symptoms including nausea after ingestion both acute and delayed.[1]
References
- 1 2 Iron(II) lactate dihydrate MSDS at Jost Chemical
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.