Larak Island
| Native name: <span class="nickname" ">جزیره لارک | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
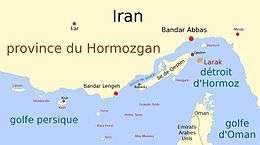
| Location | Strait of Hormuz |
| Coordinates | 26°51'12" N 56°21'20" E [1] |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Persian Gulf |
| Area | 49 km2 (19 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 81 m (266 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Province | Hormozgan |
| County | Qeshm County |
| Largest settlement | Larak Shahri (pop. 466) |
 Iran | |
| Location |
Larak Island Iran |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 26°53′15.8″N 56°21′21.0″E / 26.887722°N 56.355833°E |
| Year first constructed | 2008 |
| Construction | concrete tower |
| Tower shape | cylindrical tower with balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | unpainted tower |
| Height | 18 metres (59 ft) |
| Focal height | 40 metres (130 ft) |
| Light source | solar power |
| Range | 18 nautical miles (33 km; 21 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl (2) W 10s. |
| Admiralty number | D7337.5 |
| NGA number |
28669[2] [3] |
Larak Island (also Lark Island) is an island off the coast of Iran in the Persian Gulf, which has been one of Iran's major oil export points since 1987.The narrowest part of the Strait of Hormuz at distance of 24 miles (39 km) lies between the island and the Omani-owned Quoin Island.[4]
History
During their occupation in the 16th century, the Portuguese built fortresses here, as well as on the nearby Qeshm and Hormuz Islands.[5] The island contains an Iranian military base which maintains several Chinese-made Silkworm HY-2 surface-to-surface missiles placed there in 1987.[6]
A floating terminal was established on Larak Island in June 1986.[7] The island was bombed by Iraq in November and December 1986, as part of the Iran–Iraq War. As part of Operation Praying Mantis, the Iranian frigate Sahand was sunk by the United States Navy, 200 meters southwest of Larak Island. On 14 May 1988, the large 564,739 dwt Liberian supertanker, Seawise Giant, whilst carrying crude Iranian oil, was sunk by Iraqi anti-ship missiles off the coast of Larak Island.[8]
Demographics
Larak Island is located in the Larak Rural District, which is within the Shahab District. Two settlements are on the island: Larak Shahri and Larak Kuhi.[9] Larak Shahri is the largest of the two villages, with a population of 466 people and 98 families.
Nature
The waters around Larak Island are one of the most diverse coral reef areas in the environment of the Persian Gulf. There are 37 species of scleractinian corals identified around Larak Island.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ "Larak Island Map, Weather and Photos". GetAMap. Retrieved 26 May 2013.
- ↑ Iran The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 1st october 2016
- ↑ NGA List of Lights – Pub.112 Retrieved 1st October 2016
- ↑ Joyner, Christopher C. (1 January 1990). The Persian Gulf War: Lessons for Strategy, Law, and Diplomacy. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-313-26710-9.
- ↑ Near East/South Asia Report. Foreign Broadcast Information Service. 1983. p. 58.
- ↑ Metz, Helen Chapin (1989). Iran: A Country Study. Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. p. 257.
- ↑ Conflict and Cooperation in the Gulf Region. Springer. 22 January 2009. p. 74. ISBN 978-3-531-91337-7.
- ↑ Lloyd's Nautical Year Book. Lloyd's. 1988. p. 147.
- ↑ "Larak Kuhi: map, population, location". TipTopGlobe. Retrieved 26 May 2013.
- ↑ J. Vajed Samiei; K. Dab; P. Ghezellou; A. Shirvani (3 April 2013). "Some scleractinian corals (Scleractinia: Anthozoa) of Larak Island, Persian Gulf". Zootaxa. 3636 (1). doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3636.1.5.
External links
Coordinates: 26°51′N 56°21′E / 26.850°N 56.350°E