Leningrad Strategic Defensive
| Leningrad Strategic Defensive | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Eastern Front of World War II | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 517,000 troops | 725,000 troops | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| about 60,000 |
about 345,000, of which 214,000 were killed in action or taken prisoner. 733,300 small arms, 1492 tanks, 9889 guns and mortars, 1,702 combat aircraft | ||||||
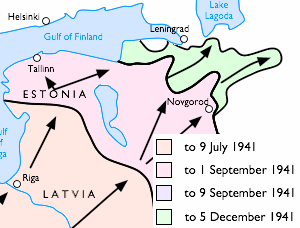
Leningrad Strategic Defensive Operation is the name Soviet historiography for the defensive operations of the Red Army and Soviet Navy during World War II from 10 July to 30 September 1941. The following operations are considered as part of the strategic operation:
- Tallinn Defensive 10 July – 10 August 1941
- Kingisepp-Luga Defensive 10 July – 23 September 1941
- Soltsy-Dno Offensive 15–20 July 1941
- Staraia-Russa Offensive 8–23 August 1941
- Demyansk Defensive 6–26 September 1941
Area and Period Covered During the Operation
Territory
The campaign was conducted in the area to the northwest of the Kalinin Region to the Baltic Sea. In the north the land line of operations was limited to the shores of the Gulf of Finland, north of the Gulf Soviet troops were engaged in the Arctic-Karelia Strategic Defensive and the defense of the Hanko Peninsula. In the east the German troops reached the southern shore of Lake Ladoga, south along the Kirisha River to Kirishi, then south along the Volkhov River to Veliky Novgorod, including the city, then along the western side of Lake Ilmen to Staraya Russa, from there to the north end of Lake Vella and from the western boundary of the lake to the north shore of Lake Seliger to the region west of Peno. South of the border demarcation operated the forces of German Army Group Center. The width of the fighting front was roughly 450 kilometers and advanced a total of 270-300 kilometers due to Soviet withdrawals.
Period
The operation took place from 10 July to 30 September lasting a total of 83 days.
Operations immediately preceding the campaign in time and space was the Baltic Strategic Defensive Operation. Operations continued on the outskirts of Leningrad include the 1st and 2nd Sinyavino operations from 10 September - 28 October 1941. The Tikhvin Defensive from 16 October - 18 November 1941. To the south only the Demyansk Offensive from 7 January - 25 May 1942 took place.
The end of the Leningrad Strategic Defensive is followed by the Siege of Leningrad which would last from 8 September 1941 - 27 January 1944.
Order of Battle
Germany
German forces involved in the operation consisted of Army Group North, consisting of the 16th and 18th Armies, and the 4th Panzer Group. The ground forces were supported by Luftflotte 1 which was reinforces by the 8th Fliegercorps as the operation progressed.
At the beginning of the operation the 18th Army was in Estonia. During the German offensive in the Baltic from 22 June to 9 July 1941, the 18th Army pursued the 8th Army from its position on the border. The Soviet 8th Army was able to break contact and establish new defensive lines farther to the rear of the pre-war borders. On 10 July the 18th Army was positioned with its left flank occupying positions north of the city of Pärnu, along the Pärnu River through the Võhma District and then south-east to Tartu and Peipsi.
The 4th Panzer Group was located in the army group in the area of Pskov - Ostrov, with a bulge to the north-east of Slavkovich. On the left flank of the bulge was the 41st Motorized Corps and on the right was the 56th Motorized Corps.
The 16th Army was on the southern flank of the Army Group around the Velikaya River and west of Novorzhev.
Course of the Operation
Rough