Siege of Leningrad
| Siege of Leningrad | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Eastern Front of World War II | |||||||
 Leningraders on Nevsky Prospect during the siege, 1942 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 725,000 | 930,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1942: 267,327 total casualties (KIA, WIA, MIA)[6] 1943: 205,937 total casualties (KIA, WIA, MIA)[7] 1944: 21,350 total casualties (KIA, WIA, MIA)[8] Total: 579,985 casualties |
Civilians:[9] 642,000 during the siege, 400,000 at evacuations | ||||||
The Siege of Leningrad, also known as the Leningrad Blockade (Russian: блокада Ленинграда, transliteration: blokada Leningrada) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken mainly by the German Army Group North against Leningrad, historically and currently known as Saint Petersburg, in the Eastern Front theatre of World War II. The siege started on 8 September 1941, when the last road to the city was severed. Although the Soviets managed to open a narrow land corridor to the city on 18 January 1943, the siege was only lifted on 27 January 1944, 872 days after it began. It was one of the longest and most destructive sieges in history and possibly the costliest in terms of casualties.[10][11]
Background
Leningrad's capture was one of three strategic goals in the German Operation Barbarossa and the main target of Army Group North. The strategy was motivated by Leningrad's political status as the former capital of Russia and the symbolic capital of the Russian Revolution, its military importance as a main base of the Soviet Baltic Fleet and its industrial strength, housing numerous arms factories.[12] By 1939 the city was responsible for 11% of all Soviet industrial output.[13] It has been reported Adolf Hitler was so confident of capturing Leningrad that he had the invitations to the victory celebrations to be held in the city's Hotel Astoria printed.[14]
Although various theories have been put forward about Nazi Germany's plans for Leningrad, including renaming the city Adolfsburg (as claimed by Soviet journalist Lev Bezymenski)[15] and making it the capital of the new Ingermanland province of the Reich in Generalplan Ost, it is clear Hitler's intention was to utterly destroy the city and its population. According to a directive sent to Army Group North on 29 September, "After the defeat of Soviet Russia there can be no interest in the continued existence of this large urban center. [...] Following the city's encirclement, requests for surrender negotiations shall be denied, since the problem of relocating and feeding the population cannot and should not be solved by us. In this war for our very existence, we can have no interest in maintaining even a part of this very large urban population."[16] Hitler's ultimate plan was to raze Leningrad to the ground and give areas north of the River Neva to the Finns.[17][18]
Preparations
German plans
Army Group North under Feldmarschall Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb advanced to Leningrad, its primary objective. Von Leeb's plan called for capturing the city on the move, but due to Hitler's recall of 4th Panzer Group (persuaded by his Chief of General Staff, Franz Halder, to transfer this south to participate in Fedor von Bock's push for Moscow),[19] von Leeb had to lay the city under siege indefinitely after reaching the shores of Lake Ladoga, while trying to complete the encirclement and reaching the Finnish Army under Marshal Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim waiting at the Svir River, east of Leningrad.[20]
Finnish military forces were north of Leningrad, while German forces occupied territories to the south.[21] Both German and Finnish forces had the goal of encircling Leningrad and maintaining the blockade perimeter, thus cutting off all communication with the city and preventing the defenders from receiving any supplies — although Finnish participation in the blockade mainly consisted of recapture of lands lost in the Winter War. The Germans planned on lack of food being their chief weapon against the citizens; German scientists had calculated the city would reach starvation after only a few weeks.[2][3][20][22][23][24]
Leningrad fortified region

On 27 June 1941, the Council of Deputies of the Leningrad administration organised "First response groups" of civilians. In the next days, Leningrad's civilian population was informed of the danger and over a million citizens were mobilised for the construction of fortifications. Several lines of defences were built along the city's perimeter to repulse hostile forces approaching from north and south by means of civilian resistance.[3][4]
In the south one of the fortified lines ran from the mouth of the Luga River to Chudovo, Gatchina, Uritsk, Pulkovo and then through the Neva River. Another line of defence passed through Peterhof to Gatchina, Pulkovo, Kolpino and Koltushy. In the north the defensive line against the Finns, the Karelian Fortified Region, had been maintained in Leningrad's northern suburbs since the 1930s, and was now returned to service. A total of 306 km (190 mi) of timber barricades, 635 km (395 mi) of wire entanglements, 700 km (430 mi) of anti-tank ditches, 5,000 earth-and-timber emplacements and reinforced concrete weapon emplacements and 25,000 km (16,000 mi)[25] of open trenches were constructed or excavated by civilians. Even the guns from the cruiser Aurora were moved inland to the Pulkovo Heights to the south of Leningrad.
Establishment
The 4th Panzer Group from East Prussia took Pskov following a swift advance and managed to reach Novgorod by 16 August. The Soviet defenders fought to the death, despite the German discovery of the Soviet defence plans on an officer's corpse. After the capture of Novgorod, General Hoepner's 4th Panzer Group continued its progress towards Leningrad.[26] However, the 18th Army — despite some 350,000 men lagging behind — forced its way to Ostrov and Pskov after the Soviet troops of the Northwestern Front retreated towards Leningrad. On 10 July, both Ostrov and Pskov were captured and the 18th Army reached Narva and Kingisepp, from where advance toward Leningrad continued from the Luga River line. This had the effect of creating siege positions from the Gulf of Finland to Lake Ladoga, with the eventual aim of isolating Leningrad from all directions. The Finnish Army was then expected to advance along the eastern shore of Lake Ladoga.[27]
Orders of battle
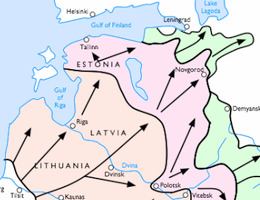
Coral up to 9 July.
Pink up to 1 September.
Green up to 5 December.
Germany
- Army Group North (Feldmarschall von Leeb)[28]
- 18th Army (von Küchler)
- XXXXII Corps (2 infantry divisions)
- XXVI Corps (3 infantry divisions)
- 16th Army (Busch)
- XXVIII Corps (von Wiktorin) (2 infantry, 1 armoured divisions)
- I Corps (2 infantry divisions)
- X Corps (3 infantry divisions)
- II Corps (3 infantry divisions)
- (L Corps — Under 9th Army) (2 infantry divisions)
- 4th Panzer Group (Hoepner)
- XXXVIII Corps (von Chappuis) (1 infantry division)
- XXXXI Motorized Corps (Reinhardt) (1 infantry, 1 motorised, 1 armoured divisions)
- LVI Motorized Corps (von Manstein) (1 infantry, 1 motorised, 1 armoured, 1 panzergrenadier divisions)
- 18th Army (von Küchler)
Finland
- Finnish Defence Forces HQ (Finnish Marshal Mannerheim)[29]
- I Corps (2 infantry divisions)
- II Corps (2 infantry divisions)
- IV Corps (3 infantry divisions)
Soviet Union
- Northern Front (Lieutenant General Popov)[30]
- 7th Army (2 rifle, 1 militia divisions, 1 naval infantry brigade, 3 motorised rifle and 1 armoured regiments)
- 8th Army
- X Rifle Corps (2 rifle divisions)
- XI Rifle Corps (3 rifle divisions)
- Separate Units (3 rifle divisions)
- 14th Army
- XXXXII Rifle Corps (2 rifle divisions)
- Separate Units (2 rifle divisions, 1 Fortified area, 1 motorised rifle regiment)
- 23rd Army
- XIX Rifle Corps (3 rifle divisions)
- Separate Units (2 rifle, 1 motorised divisions, 2 Fortified areas, 1 rifle regiment)
- Luga Operation Group
- XXXXI Rifle Corps (3 rifle divisions)
- Separate Units (1 armoured brigade, 1 rifle regiment)
- Kingisepp Operation Group
- Separate Units (2 rifle, 2 militia, 1 armoured divisions, 1 Fortified area)
- Separate Units (3 rifle divisions, 4 guard militia divisions, 3 Fortified areas, 1 rifle brigade)
Of these, the 14th Army defended Murmansk and 7th Army defended Ladoga Karelia; thus they did not participate in the initial stages of the siege. The 8th Army was initially part of the Northwestern Front and retreated through the Baltics. (The 8th army was transferred to Northern Front on 14 July).
On 23 August, the Northern Front was divided into the Leningrad Front and the Karelian Front, as it became impossible for front headquarters to control everything between Murmansk and Leningrad.
Zhukov states, "Ten volunteer opolcheniye divisions were formed in Leningrad in the first three months of the war, as well as 16 separate artillery and machine-gun opolcheniye battalions."[31]:421,438
Severing lines of communication
On 6 August, Hitler repeated his order: "Leningrad first, Donetsk Basin second, Moscow third."[32] From August 1941 until January 1944, anything that happened between the Arctic Ocean and Lake Ilmen concerned the Wehrmacht's Leningrad siege operations.[4] Arctic convoys using the Northern Sea Route delivered American Lend-Lease and British food and war materiel supplies to the Murmansk railhead (although the rail link to Leningrad was cut off by Finnish armies just north of the city), as well as several other locations in Lapland.
Encirclement of Leningrad
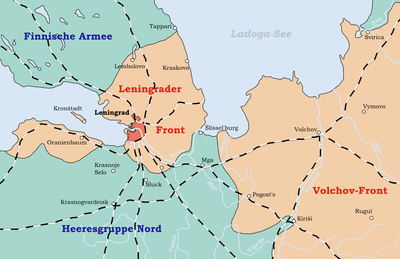
Finnish intelligence had broken some of the Soviet military codes and read their low-level communications. This was particularly helpful for Hitler, who constantly requested intelligence information about Leningrad.[4][33] Finland's role in Operation Barbarossa was laid out in Hitler's Directive 21, "The mass of the Finnish army will have the task, in accordance with the advance made by the northern wing of the German armies, of tying up maximum Russian (sic – Soviet) strength by attacking to the west, or on both sides, of Lake Ladoga".[34] The last rail connection to Leningrad was severed on 30 August, when the Germans reached the Neva River. On 8 September, the road to the besieged city was severed when the Germans reached Lake Ladoga at Shlisselburg, leaving just a corridor of land between Lake Ladoga and Leningrad which remained unoccupied by Axis forces. Bombing on 8 September caused 178 fires.[35]
On 21 September, German High Command considered how to destroy Leningrad. Occupying the city was ruled out "because it would make us responsible for food supply".[36] The resolution was to lay the city under siege and bombardment, starving its population. "Early next year we enter the city (if the Finns do it first we do not object), lead those still alive into inner Russia or into captivity, wipe Leningrad from the face of the earth through demolitions, and hand the area north of the Neva to the Finns."[37] On 7 October, Hitler sent a further directive signed by Alfred Jodl reminding Army Group North not to accept capitulation.[38]
Finnish participation

By August 1941, the Finns had advanced to within 20 km of the northern suburbs of Leningrad at the 1939 Finnish-Soviet border, threatening the city from the north; they were also advancing through East Karelia, east of Lake Ladoga, and threatening the city from the east. The Finnish forces crossed the pre-Winter War border on the Karelian Isthmus by eliminating Soviet salients at Beloostrov and Kirjasalo, thus straightening the frontline so that it ran along the old border near the shores of Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga, and those positions closest to Leningrad still lying on the pre-Winter War border.
According to Soviet claims, the Finnish advance was stopped in September through resistance by the Karelian Fortified Region;[39] however Finnish troops had already earlier in August 1941 received orders to halt the advance after reaching their goals, some of which lay beyond the pre-Winter War border. After reaching their respective goals, the Finns halted their advance and started moving troops to East Karelia.[40][41]
For the next three years, the Finns did little to contribute to the battle for Leningrad, maintaining their lines.[42] Their headquarters rejected German pleas for aerial attacks against Leningrad[43] and did not advance farther south from the Svir River in occupied East Karelia (160 kilometres northeast of Leningrad), which they had reached on 7 September. In the southeast, the Germans captured Tikhvin on 8 November, but failed to complete their encirclement of Leningrad by advancing further north to join with the Finns at the Svir River. On 9 December, a counter-attack of the Volkhov Front forced the Wehrmacht to retreat from their Tikhvin positions to the River Volkhov line.[3][4]
On 6 September 1941, Germany's Chief of Staff Alfred Jodl visited Helsinki. His main goal was to persuade Mannerheim to continue the offensive. In 1941, President Ryti declared to the Finnish Parliament that the aim of the war was to restore the territories lost during the Winter War and gain more territories in the east to create a "Greater Finland".[44][45][46] After the war, Ryti stated: "On August 24, 1941 I visited the headquarters of Marshal Mannerheim. The Germans aimed us at crossing the old border and continuing the offensive to Leningrad. I said that the capture of Leningrad was not our goal and that we should not take part in it. Mannerheim and Minister of Defense Walden agreed with me and refused the offers of the Germans. The result was a paradoxical situation: the Germans could not approach Leningrad from the north..." In fact the German and Finnish armies maintained the siege together until January 1944, but there was little, or no systematic shelling or bombing from the Finnish positions.[21] Mannerheim had spent most of his career in the Imperial Russian Army stationed at old St. Petersburg.[47]
The proximity of the Finnish positions – 33–35 km (21–22 mi) from downtown Leningrad – and the threat of a Finnish attack complicated the defence of the city. At one point, the defending Front Commander, Popov, could not release reserves opposing the Finnish forces to be deployed against the Wehrmacht because they were needed to bolster the 23rd Army's defences on the Karelian Isthmus.[48] Mannerheim terminated the offensive on 31 August 1941, when the army had reached the 1939 border. Popov felt relieved, and redeployed two divisions to the German sector on 5 September.[49]
Subsequently, the Finnish forces reduced the salients of Beloostrov and Kirjasalo,[50] which had threatened their positions at the sea coast and south of the River Vuoksi.[50] Lieutenant General Paavo Talvela and Colonel Järvinen, the commander of the Finnish Coastal Brigade responsible for Ladoga, proposed to the German headquarters the blocking of Soviet convoys on Lake Ladoga. The German command formed the 'international' naval detachment (which also included the Italian XII Squadriglia MAS) under Finnish command and the Einsatzstab Fähre Ost under German command. These naval units operated against the supply route in the summer and autumn of 1942, the only period the units were able to operate as freezing waters then forced the lightly equipped units to be moved away, and changes in front lines made it impractical to reestablish these units later in the war.[21][33][51][52]
Defensive operations

The Leningrad Front (initially the Leningrad Military District) was commanded by Marshal Kliment Voroshilov. It included the 23rd Army in the northern sector between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga, and the 48th Army in the western sector between the Gulf of Finland and the Slutsk–Mga position. The Leningrad Fortified Region, the Leningrad garrison, the Baltic Fleet forces, and Koporye, Southern and Slutsk–Kolpino operational groups were also present.
Defence of civilian evacuees
According to Zhukov, "Before the war Leningrad had a population of 3,103,000 and 3,385,000 counting the suburbs. As many as 1,743,129, including 414,148 children were evacuated" between 29 June 1941 and 31 March 1943. They were moved to the Volga area, the Urals, Siberia and Kazakhstan.[31]:439
By September 1941, the link with the Volkhov Front (commanded by Kirill Meretskov) was severed and the defensive sectors were held by four armies: 23rd Army in the northern sector, 42nd Army on the western sector, 55th Army on the southern sector, and the 67th Army on the eastern sector. The 8th Army of the Volkhov Front had the responsibility of maintaining the logistic route to the city in coordination with the Ladoga Flotilla. Air cover for the city was provided by the Leningrad military district PVO Corps and Baltic Fleet naval aviation units.
The defensive operation to protect the 1,400,000 civilian evacuees was part of the Leningrad counter-siege operations under the command of Andrei Zhdanov, Kliment Voroshilov, and Aleksei Kuznetsov. Additional military operations were carried out in coordination with Baltic Fleet naval forces under the general command of Admiral Vladimir Tributs. The Ladoga Flotilla under the command of V. Baranovsky, S.V. Zemlyanichenko, P.A. Traynin, and B.V. Khoroshikhin also played a major military role in helping with evacuation of the civilians.
Bombardment

By 8 September, German forces had largely surrounded the city, cutting off all supply routes to Leningrad and its suburbs. Unable to press home their offensive, and facing defences of the city organised by Marshal Zhukov, the Axis armies laid siege to the city for "900 days and nights."[31]
The air attack of 19 September was particularly brutal. It was the heaviest air raid Leningrad would suffer during the war, as 276 German bombers hit the city killing 1,000 civilians. Many of those killed were recuperating from battle wounds in hospitals that were hit by German bombs. Six air raids occurred that day. Five hospitals were damaged in the bombing, as well as the city's largest shopping bazaar. Hundreds of people had run from the street into the store to take shelter from the air raid.[53][54]
Artillery bombardment of Leningrad began in August 1941, increasing in intensity during 1942 with the arrival of new equipment. It was stepped up further during 1943, when several times as many shells and bombs were used as in the year before. Torpedoes were often used for night bombings by the Luftwaffe. Against this, the Soviet Baltic Fleet Navy aviation made over 100,000 air missions to support their military operations during the siege.[55] German shelling and bombing killed 5,723 and wounded 20,507 civilians in Leningrad during the siege.[56]
Supplying the defenders


To sustain the defence of the city, it was vitally important for the Red Army to establish a route for bringing a constant flow of supplies into Leningrad. This route was effected over the southern part of Lake Ladoga and the corridor of land which remained unoccupied by Axis forces between Lake Ladoga and Leningrad. Transport across Lake Ladoga was achieved by means of watercraft during the warmer months and land vehicles driven over thick ice in winter (hence the route becoming known as "The Ice Road"). The security of the supply route was ensured by the Ladoga Flotilla, the Leningrad PVO Corps, and route security troops. Vital food supplies were thus transported to the village of Osinovets, from where they were transferred and transported over 45 km via a small suburban railway to Leningrad.[57] The route would also be used to evacuate civilians from the besieged city. This was because no evacuation plan had been made available in the chaos of the first winter of the war, and the city was completely isolated until 20 November 1941, when the ice road over Lake Ladoga became operational.
This road was named the Road of Life (Russian: Дорога жизни). As a road it was very dangerous. There was the risk of vehicles becoming stuck in the snow or sinking through broken ice caused by the constant German bombardment. Because of the high winter death toll the route also became known as the "Road of Death". However, the lifeline did bring military and food supplies in and took civilians and wounded soldiers out, allowing the city to continue resisting their enemy.
Effect on the city
The two-and-a-half year siege caused the greatest destruction and the largest loss of life ever known in a modern city.[21][58] On Hitler's express orders, most of the palaces of the Tsars, such as the Catherine Palace, Peterhof Palace, Ropsha, Strelna, Gatchina, and other historic landmarks located outside the city's defensive perimeter were looted and then destroyed, with many art collections transported to Nazi Germany.[59] A number of factories, schools, hospitals and other civil infrastructure were destroyed by air raids and long range artillery bombardment.

The 872 days of the siege caused extreme famine in the Leningrad region through disruption of utilities, water, energy and food supplies. This resulted in the deaths of up to 1,500,000[60] soldiers and civilians and the evacuation of 1,400,000 more, mainly women and children, many of whom died during evacuation due to starvation and bombardment.[2][3][4] Piskaryovskoye Memorial Cemetery alone in Leningrad holds half a million civilian victims of the siege. Economic destruction and human losses in Leningrad on both sides exceeded those of the Battle of Stalingrad, the Battle of Moscow, or the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The siege of Leningrad is the most lethal siege in world history, and some historians speak of the siege operations in terms of genocide, as a "racially motivated starvation policy" that became an integral part of the unprecedented German war of extermination against populations of the Soviet Union generally.[61][62]

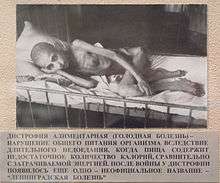
Civilians in the city suffered from extreme starvation, especially in the winter of 1941–42. From November 1941 to February 1942 the only food available to the citizen was 125 grams of bread per day, of which 50–60% consisted of sawdust and other inedible admixtures. For about two weeks at the beginning of January 1942, even this food was available only for workers and military personnel. In conditions of extreme temperatures, down to −30 °C (−22 °F), and city transport being out of service, even a distance of a few kilometers to a food distributing kiosk created an insurmountable obstacle for many citizens. Deaths peaked in January–February 1942 at 100,000 per month, mostly from starvation.[63] People often died on the streets, and citizens soon became accustomed to the sight of death.
Cannibalism
While reports of cannibalism appeared in the winter of 1941–42, NKVD records on the subject were not published until 2004. Most evidence for cannibalism that surfaced before this time was anecdotal. Anna Reid points out that "for most people at the time, cannibalism was a matter of second-hand horror stories rather than direct personal experience."[64] Indicative of Leningraders' fears at the time, police would often threaten uncooperative suspects with imprisonment in a cell with cannibals.[65] Dimitri Lazarev, a diarist during the worst moments in the Leningrad siege, recalls his daughter and niece reciting a terrifying nursery rhyme adapted from a pre-war song:
- A dystrophic walked along
With a dull look
In a basket he carried a corpse's arse.
I'm having human flesh for lunch,
This piece will do!
Ugh, hungry sorrow!
And for supper, clearly
I'll need a little baby.
I'll take the neighbours',
Steal him out of his cradle.[66]
NKVD files report the first use of human meat as food on 13 December 1941.[67] The report outlines thirteen cases which range from a mother smothering her eighteen-month-old to feed her three older children to a plumber killing his wife to feed his sons and nieces.[67]
By December 1942, the NKVD arrested 2,105 cannibals dividing them into two legal categories: corpse-eating (trupoyedstvo) and person-eating (lyudoyedstvo). The latter were usually shot while the former were sent to prison. The Soviet Criminal Code had no provision for cannibalism so all convictions were carried out under Code Article 59–3, "special category banditry".[68]
Instances of person-eating were significantly lower than that of corpse-eating; of the 300 people arrested in April 1942 for cannibalism, only 44 were murderers.[69] 64% of cannibals were female, 44% were unemployed, 90% were illiterate, 15% were rooted inhabitants, and only 2% had any criminal records. More cases occurred in the outlying districts than the city itself. Cannibals were often unsupported women with dependent children and no previous convictions, which allowed for a certain level of clemency in legal proceedings.[70]
Given the scope of mass starvation, cannibalism was relatively rare.[71] Far more common was murder for ration cards. In the first six months of 1942, Leningrad witnessed 1,216 such murders. At the same time, Leningrad was experiencing its highest casualty rate, as high as 100,000 people per month. Lisa Kirschenbaum notes "that incidents of cannibalism provided an opportunity for emphasizing that the majority of Leningraders managed to maintain their cultural norms in the most unimaginable circumstances."[71]
Soviet relief of the siege

On 9 August 1942, the Symphony No. 7 "Leningrad" by Dmitri Shostakovich was performed by the Leningrad Radio Orchestra. The concert was broadcast on loudspeakers placed in all the city and also aimed towards the enemy lines. The same day had been previously designated by Hitler to celebrate the fall of the city with a lavish banquet at Leningrad's Astoria Hotel,[72] and was a few days before the Sinyavino Offensive.
Sinyavino Offensive
The Sinyavino Offensive was a Soviet attempt to break the blockade of the city in early autumn 1942. The 2nd Shock and the 8th armies were to link up with the forces of the Leningrad Front. At the same time the German side was preparing an offensive, Operation Nordlicht (Northern Light), to capture the city, using the troops freed up after the capture of Sevastopol.[73] Neither side was aware of the other's intentions until the battle started.
The offensive started on 27 August 1942, with some small-scale attacks by the Leningrad front on the 19th, pre-empting "Nordlicht" by a few weeks. The successful start of the operation forced the Germans to redirect troops from the planned "Nordlicht" to counterattack the Soviet armies. The counteroffensive saw the first deployment of the Tiger tank, though with limited success. After parts of the 2nd Shock Army were encircled and destroyed, the Soviet offensive was halted. However the German forces had to also abandon their offensive on Leningrad.
Operation Iskra

The encirclement was broken in the wake of Operation Iskra (Spark), a full-scale offensive conducted by the Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts. This offensive started in the morning of 12 January 1943. After fierce battles the Red Army units overcame the powerful German fortifications to the south of Lake Ladoga, and on 18 January 1943 the Volkhov Front's 372nd Rifle Division met troops of the 123rd Rifle Brigade of the Leningrad Front, opening a 10–12 km (6.2–7.5 mi) wide land corridor, which could provide some relief to the besieged population of Leningrad.
Lifting the siege
The siege continued until 27 January 1944, when the Soviet Leningrad-Novgorod Strategic Offensive expelled German forces from the southern outskirts of the city. This was a combined effort by the Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts, along with the 1st and 2nd Baltic Fronts. The Baltic Fleet provided 30% of aviation power for the final strike against the Wehrmacht.[55] In the summer of 1944, the Finnish Defence Forces were pushed back to the other side of the Bay of Vyborg and the Vuoksi River.
Timeline
1941

- April: Hitler intends to occupy and then destroy Leningrad, according to plan Barbarossa and Generalplan Ost[74]
- 22 June: The Axis powers' invasion of Soviet Union begins with Operation Barbarossa.
- 23 June: Leningrad commander M. Popov, sends his second in command to reconnoitre defensive positions south of Leningrad.[75]
- 29 June: Construction of the Luga defence fortifications (Russian: Лужский оборонительный рубеж) begins[76] together with evacuation of children and women.
- June–July: Over 300,000 civilian refugees from Pskov and Novgorod escaping from the advancing Germans come to Leningrad for shelter. The armies of the North-Western Front join the front lines at Leningrad. Total military strength with reserves and volunteers reaches 2 million men involved on all sides of the emerging battle.
- 19–23 July: First attack on Leningrad by Army Group North is stopped 100 km (62 mi) south of the city.
- 27 July: Hitler visits Army Group North, angry at the delay. He orders Field Marshal von Leeb to take Leningrad by December.[74]
- 31 July: Finns attack the Soviet 23rd Army at the Karelian Isthmus, eventually reaching northern pre-Winter War Finnish-Soviet border.
- 20 August – 8 September: Artillery bombardments of Leningrad hit industries, schools, hospitals and civilian houses.
- 21 August: Hitler's Directive No.34 orders "Encirclement of Leningrad in conjunction with the Finns."[77]
- 20–27 August: Evacuation of civilians is blocked by attacks on railways and other exits from Leningrad.[78]
- 31 August: Finnish forces go on the defensive and straighten their front line.[41] This involves crossing the 1939 pre-Winter War border and occupation of municipalities of Kirjasalo and Beloostrov.[41]
- 6 September: German High Command's Alfred Jodl fails to persuade Finns to continue offensive against Leningrad.[43]
- 2–9 September: Finns capture the Beloostrov and Kirjasalo salients and conduct defensive preparations.[50][79]
- 8 September: Land encirclement of Leningrad is completed when the German forces reach the shores of Lake Ladoga.[21][74]
- 10 September: Joseph Stalin appoints General Zhukov to replace Marshal Voroshilov as Leningrad Front and Baltic Fleet commander.[31]:400[80]
- 12 September: The largest food depot in Leningrad, the Badajevski General Store, is destroyed by a German bomb.[81]
- 15 September: von Leeb has to remove the 4th Panzer Group from the front lines and transfer it to Army Group Center for the Moscow offensive.[82]
- 19 September: German troops are stopped 10 km (6.2 mi) from Leningrad. Citizens join the fighting at the defence lines.

- 22 September: Hitler directs that "Saint Petersburg must be erased from the face of the Earth".[83]
- 22 September: Hitler declares, "....we have no interest in saving lives of the civilian population."[83]
- 8 November: Hitler states in a speech at Munich: "Leningrad must die of starvation."[21]
- 10 November: Soviet counter-attack begins, forcing Germans to retreat from Tikhvin back to the Volkhov River by 30 December, preventing them from joining Finnish forces stationed at the Svir River east of Leningrad.[84]
- December: Winston Churchill wrote in his diary "Leningrad is encircled, but not taken."[85]
- 6 December: Great Britain declared war on Finland. This was followed by declaration of war from Canada, Australia, India and New Zealand.[86]
1942
- 7 January: Soviet Lyuban Offensive Operation is launched; it lasts 16 weeks and is unsuccessful, resulting in the loss of the 2nd Shock Army.
- January: Soviets launch battle for the Nevsky Pyatachok bridgehead in an attempt to break the siege. This battle lasts until May 1943, but is only partially successful. Very heavy casualties are experienced by both sides.
- 4–30 April: Luftwaffe operation Eis Stoß (ice impact) fails to sink Baltic Fleet ships iced in at Leningrad.[87]
- June–September: New German railway-mounted artillery bombards Leningrad with 800 kg (1,800 lb) shells.
- August: The Spanish Blue Division (División Azul) transferred to Leningrad.
- 9 August 1942: The Symphony No. 7 "Leningrad" by Dmitri Shostakovich was performed in the city.
- 14 August – 27 October: Naval Detachment K clashes with Leningrad supply route on Lake Ladoga.[21][33][52]
- 19 August: Soviets begin an eight-week-long Sinyavino Offensive, which fails to lift the siege, but thwarts German offensive plans (Nordlicht).[88]
1943
- January–December: Increased artillery bombardments of Leningrad.
- 12–30 January: Operation Iskra penetrates the siege by opening a land corridor along the coast of Lake Ladoga into the city. The blockade is broken.
- 10 February – 1 April: The unsuccessful Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda attempts to lift the siege.
1944
- 14 January – 1 March: Several Soviet offensive operations begin, aimed at ending the siege.
- 27 January: Siege of Leningrad ends. Germans forces pushed 60–100 km away from the city.
- January: Before retreating the German armies loot and destroy the historical Palaces of the Tsars, such as the Catherine Palace, Peterhof Palace, the Gatchina Palace and the Strelna Palace. Many other historic landmarks and homes in the suburbs of St. Petersburg are looted and then destroyed, and a large number of valuable art collections are moved to Nazi Germany.
During the siege, 3,200 residential buildings, 9,000 wooden houses were burned, and 840 factories and plants were destroyed in Leningrad and suburbs.[89]
Later evaluation
Controversial issues
Controversy over Finnish participation
Almost all historians regard the siege as a German operation and do not consider that the Finns effectively participated in the siege. Russian historian Nikolai Baryshnikov argues that active Finnish participation did occur, but other historians have been mostly silent about it, most likely due to the friendly nature of post-war Soviet–Finnish relations.[90] The main issues which count in favor of the former view are: (a) the Finns mostly stayed at the pre-Winter War border at the Karelian Isthmus (with small exceptions to straighten the frontline), despite German wishes and requests, and (b) they did not bombard the city from planes or with artillery and did not allow the Germans to bring their own land forces to Finnish lines. Baryshnikov explains that the Finnish military in the region was strategically dependent on the Germans, and lacked the required means and will to press the attack against Leningrad any further.[91]
Soviet deportation of civilians with enemy nations ethnic origin – Germans and Finns
Deportations of Finns and Germans from the Leningrad area to inhospitable areas of the Soviet Union began in March 1942 using the Road of Life.[92] However, the situation in Leningrad during the blockade was worse in comparison with the eastern areas where most of the city residents were evacuated. Inhospitable areas of the Soviet Union hosted millions of the evacuees; many factories, universities, and theaters were also evacuated there.[93]
Commemoration, monuments

Leningrad Siege and Defence Museum
Even during the siege itself, war artifacts were collected, and shown to public by the city authorities, such as the German airplane that was shot down and fell to the ground in Tauricheskiy Garden (ru: Таврический сад). Such objects were displayed as a sign of people's courage and gathered in a specially allocated building of the former 19с Salt Warehouses (Соляной городок). The exhibition was soon turned into a full-scale Museum of Leningrad Defence (now Государственный мемориальный музей обороны и блокады Ленинграда). Several years after the World War II, in late 1940s – early 1950s, Stalin's supposed jealousy of Leningrad city leaders caused their destruction in the course of politically-motivated demonstrative trials forming the after-WWII Leningrad Affair (the pre-war one followed in 1934 the assassination of the popular city ruler Sergey Kirov). Now another generation of state and Communist Party functionaries of the city was wiped out, supposedly for publicly overestimating the importance of the city as an independent fighting unit and their own roles in winning over the enemy. Their brainchild, the Leningrad Defence Museum, was also destroyed, and many valuable exhibits were destroyed.
The museum was revived in late 1980s with the then wave of glasnost, when new shocking facts were published, showing both heroism of the wartime city and hardships and even cruelties of the period. The exhibition opened in its originally allocated building, but has not yet regained its original size and area, most of its former premises having been given before its revival over to the military and other governmental offices. Plans for a new modern building of the museum have been suspended due to the financial crisis, but under the present Defence Secretary Sergey Shoigu promises have been made to expand the museum at its present location.
Monuments: The Green Belt of Glory and memorial cemeteries
Commemoration of the siege got a second wind during the 1960s. Local workers of art dedicated their achievements to the Victory and memory of the war they saw. A leading local poet and war participant Mikhail Dudin suggested erecting a ring of monuments on the places of heaviest siege-time fighting and linking them into a belt of gardens around the city showing where the advancing enemy armies were stopped forever. That was the beginning of the Green Belt of Glory (ru: Зелёный пояс Славы).
On 29 October 1966, a monument entitled Broken Ring (of the Siege, ru:Разорванное кольцо) was erected at the 40th km of the Road of Life, on the shore of Lake Ladoga near the village of Kokkorevo. Designed and created by Konstantin Simun, the monument pays tribute not only to the lives saved via the frozen Ladoga, but also the many lives broken by the blockade.
The Monument to the Heroic Defenders of Leningrad (ru:Монумент героическим защитникам Ленинграда) was erected on 9 May 1975 in Victory Square, Saint Petersburg.[94] The monument is a huge bronze ring with a gap in it, pointing towards the site that the Soviets eventually broke through the encircling German forces. In the centre a Russian mother cradles her dying soldier son. The monument has an inscription saying "900 days 900 nights". An exhibit underneath the monument contains artifacts from this period, such as journals.
In later years, smaller-scale objects were added, such as memorial plaques to sources of water – a Siege-time Water-well and a river Ice-hole (Rus. polynya).
Memorial cemeteries
During the siege, numerous deaths of civilians and soldiers led to considerable expansion of burial places later memorialised, of which the best known is Piskaryovskoye Memorial Cemetery.
See also
- World War II casualties
- List of famines
- Effect of the Siege of Leningrad on the city
- Operation Nordlicht (Northern Light)
- Consequences of Nazism
- Hero-City Obelisk
- Piskaryovskoye Memorial Cemetery
- Leningrad Affair
- Axis powers
- Eastern Front
- Operation Barbarossa
References
Notes
- ↑ Baryshnikov 2003; Juutilainen 2005, p. 670; Ekman, P-O: Tysk-italiensk gästspel på Ladoga 1942, Tidskrift i Sjöväsendet 1973 Jan.–Feb., pp. 5–46.
- 1 2 3 Brinkley & Haskey 2004, p. 210
- 1 2 3 4 5 Wykes 1972, pp. 9–21
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Carell 1966, pp. 205–210
- ↑ http://ww2stats.com/cas_ger_okh_dec41.html
- ↑ http://ww2stats.com/cas_ger_okh_dec42.html
- ↑ http://ww2stats.com/cas_ger_okh_dec43.html
- ↑ http://ww2stats.com/cas_ger_okh_dec44.html
- 1 2 3 Glantz 2001, pp. 179
- ↑ The Siege of Leningrad, 1941 – 1944
- ↑ Walzer, Michael (1977). Just and Unjust Wars. p. 160. ISBN 978-0465037070.
More civilians died in the siege of Leningrad than in the modernist infernos of Hamburg, Dresden, Tokyo, Hiroshima, and Nagasaki, taken together.
- ↑ Carell 1963
- ↑ Saint Petersburg-The Soviet Period,"Saint Petersburg." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Web. 19 Jul. 2011.
- ↑ Orchestral manoeuvres (part one). From the Observer
- ↑ Bezymenskiĭ, Lev (1968). Sonderakte "Barbarossa". Deutsche Verlag-Anstalt. p. 204.
- ↑ Reid 2011, pp. 134–135
- ↑ In a conversation held on 27 November 1941 with the Finnish Foreign Minister Witting, Hitler stated that Leningrad was to be razed to the ground and then given to the Finns, with the River Neva forming the new post-war border between the German Reich and Finland.
- ↑ Hannikainen, Olli; Vehviläinen (2002). Finland in the Second World War: between Germany and Russia. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-333-80149-9.
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 129
- 1 2 Carell 1966, pp. 205–208
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Baryshnikov 2003
- ↑ Higgins 1966
- ↑ Miller 2006, pp. 67
- ↑ Willmott, Cross & Messenger 2004
- ↑ Bidlack, Richard (2013). The Leningrad Blockade. New Haven: Yale University press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0300198164.
- ↑ Carruthers, Bob (2011). Panzers at War 1939–1942. Warwickshire: Coda books. ISBN 978-1781591307.
- ↑ Хомяков, И (2006). История 24-й танковой дивизии ркка (in Russian). Санкт-Петербург: BODlib. pp. 232 с.
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 367
- ↑ National Defence College 1994, pp. 2:194,256
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 351
- 1 2 3 4 Zhukov, Georgy (1974). Marshal of Victory, Volume I. Pen and Sword Books Ltd. p. 399,415,425. ISBN 9781781592915.
- ↑ Higgins 1966, pp. 151
- 1 2 3 Juutilainen & Leskinen 2005, pp. 187–9
- ↑ Führer Directive 21. Operation Barbarossa
- ↑ "St Petersburg – Leningrad in the Second World War" 9 May 2000. Exhibition. The Russian Embassy. London
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 132
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 133
- ↑ "Nuremberg Trial Proceedings Vol. 8", from The Avalon Project at Yale Law School
- ↑ Карта обстановки на фронте 23 Армии к исходу 11.09.1941 (in Russian). Архив Министерства обороны РФ. фонд 217 опись 1221 дело 33. 1941.
- ↑ Raunio, Ari; Kilin, Juri (2007). Jatkosodan hyökkäystaisteluja 1941. Keuruu: Otavan kirjapaino Oy. pp. 153–159. ISBN 978-951-593-069-9.
- 1 2 3 National Defence College 1994, p. 2:261
- ↑ Glantz 2001, pp. 166
- 1 2 National Defence College 1994, p. 2:260
- ↑ Vehviläinen & McAlister 2002
- ↑ Пыхалов, И. (2005). Великая Оболганная война (in Russian). ISBN 5-699-10913-7. Retrieved 2007-09-25.
Со сслылкой на Барышников В. Н. "Вступление Финляндии во Вторую мировую войну. 1940–1941 гг." СПб, 2003, с. 28
- ↑ "И вновь продолжается бой...". Андрей Сомов. Центр Политических и Социальных Исследований Республики Карелия. (in Russian). Politika-Karelia. 2003-01-28. Archived from the original on 2007-11-17. Retrieved 2007-09-25.
- ↑ Zaloga, Steven J. (October 20, 2015). Gustaf Mannerheim (Command). Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1472814428.
- ↑ Glantz 2001, pp. 33–34
- ↑ Platonov 1964
- 1 2 3 National Defence College 1994, pp. 2:262–267
- ↑ YLE: Kenraali Talvelan sota (in Finnish)
- 1 2 Ekman, P-O: Tysk-italiensk gästspel på Ladoga 1942, Tidskrift i Sjöväsendet 1973 Jan.–Feb., pp. 5–46.
- ↑ Bombing of Leningrad
- ↑
- 1 2 Гречанюк, Дмитриев & Корниенко 1990
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 130
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 201
- ↑ Spencer C. Tucker (23 December 2009). A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East. ABC-CLIO. p. 1929. ISBN 978-1-85109-672-5.
- ↑ Nicholas, Lynn H. (1995). The Rape of Europa: the Fate of Europe's Treasures in the Third Reich and the Second World War. Vintage Books
- ↑ Salisbury 1969, pp. 590f
- ↑ Ganzenmüller 2005, pp. 17,20
- ↑ Barber & Dzeniskevich 2005
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 284
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 286
- ↑ Salisbury E. Harrison. The 900 Days: The Siege of Leningrad. New York: Harper and Row, 1969. p. 481
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 354
- 1 2 Reid 2011, p. 287
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 291
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 288
- ↑ Reid 2011, p. 292
- 1 2 Lisa A. Kirschenbaum (4 September 2006). The Legacy of the Siege of Leningrad, 1941–1995: Myth, Memories, and Monuments. Cambridge University Press. p. 239. ISBN 978-1-139-46065-1.
- ↑ Vulliamy, Ed (25 November 2001). "Orchestral manoeuvres (part 1)". The Guardian. Retrieved 13 December 2012.
- ↑ E. Manstein. Lost Victories. Ch 10
- 1 2 3 Cartier 1977
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 31
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 42
- ↑ Higgins 1966, pp. 156
- ↑ The World War II. Desk Reference. Eisenhower Center director Douglas Brinkley. Editor Mickael E. Haskey. Grand Central Press, 2004. Page 8.
- ↑ "Approaching Leningrad from the North. Finland in WWII (На северных подступах к Ленинграду)" (in Russian).
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 64
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 114
- ↑ Glantz 2001, p. 71
- 1 2 Hitler, Adolf (1941-09-22). "Directive No. 1601" (in Russian).
- ↑ Carell 1966, pp. 210
- ↑ Churchill, Winston (2000) [1950]. The Grand Alliance. The Second World War. 3 (The Folio Society ed.). London: Cassel & Co.
- ↑ pp. 98–105, Finland in the Second World War, Bergharhn Books, 2006
- ↑ Bernstein, AI; Бернштейн, АИ (1983). "Notes of aviation engineer (Аэростаты над Ленинградом. Записки инженера — воздухоплавателя. Химия и Жизнь №5)" (in Russian). pp. с. 8–16.
- ↑ Glantz 2001, pp. 167–173
- ↑ Siege of 1941–1944
- ↑ Baryshnikov 2003, p. 3
- ↑ Baryshnikov 2003, p. 82
- ↑ Klaas 2010
- ↑ Куманев, Г.А. "ВОЙНА И ЭВАКУАЦИЯ В СССР. 1941–1942" (in Russian). Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ↑ "Monument to the Heroic Defenders of Leningrad, St. Petersburg, Russia". Retrieved 26 September 2015.
Bibliography
- Barber, John; Dzeniskevich, Andrei (2005), Life and Death in Besieged Leningrad, 1941–44, Palgrave Macmillan, New York, ISBN 1-4039-0142-2
- Baryshnikov, N. I. (2003), Блокада Ленинграда и Финляндия 1941–44 (Finland and the Siege of Leningrad), Институт Йохана Бекмана
- Glantz, David (2001), The Siege of Leningrad 1941–44: 900 Days of Terror, Zenith Press, Osceola, WI, ISBN 0-7603-0941-8
- Goure, Leon (1981), The Siege of Leningrad, Stanford University Press, Palo Alto, CA, ISBN 0-8047-0115-6
- Granin, Daniil Alexandrovich (2007), Leningrad Under Siege, Pen and Sword Books Ltd, ISBN 978-1-84415-458-6
- Kirschenbaum, Lisa (2006), The Legacy of the Siege of Leningrad, 1941–1995: Myth, Memories, and Monuments, Cambridge University Press, New York, ISBN 0-521-86326-0
- Klaas, Eva (2010), Küüditatu kirjutas oma mälestused raamatuks (in Estonian: A Deportee Published His Memories in Book) (in Estonian), Virumaa Teataja
- Lubbeck, William; Hurt, David B. (2010), At Leningrad's Gates: The Story of a Soldier with Army Group North, Casemate, ISBN 1-935149-37-7
- Platonov, S. P. (ed.) (1964), Bitva za Leningrad, Voenizdat Ministerstva oborony SSSR, Moscow
- Reid, Anna (2011), Leningrad: The Epic Siege of World War II, 1941–1944, Bloomsbury Publishing, ISBN 978-0-8027-7882-6
- Salisbury, Harrison Evans (1969), The 900 Days: The Siege of Leningrad, Da Capo Press, ISBN 0-306-81298-3
- Simmons, Cynthia; Perlina, Nina (2005), Writing the Siege of Leningrad. Women's diaries, Memories, and Documentary Prose, University of Pittsburgh Press, ISBN 978-0-8229-5869-7
- Willmott, H. P.; Cross, Robin; Messenger, Charles (2004), The Siege of Leningrad in World War II, Dorling Kindersley, ISBN 978-0-7566-2968-7
- Wykes, Alan (1972), The Siege of Leningrad, Ballantines Illustrated History of WWII
Further reading
- Backlund, L. S. (1983), Nazi Germany and Finland, University of Pennsylvania. University Microfilms International A. Bell & Howell Information Company, Ann Arbor, Michigan
- Baryshnikov, N. I.; Baryshnikov, V. N. (1997), Terijoen hallitus, TPH
- Baryshnikov, N. I.; Baryshnikov, V. N.; Fedorov, V. G. (1989), Finlandia vo vtoroi mirivoi voine (Finland in the Second World War), Lenizdat, Leningrad
- Baryshnikov, N. I.; Manninen, Ohto (1997), Sodan aattona, TPH
- Baryshnikov, V. N. (1997), Neuvostoliiton Suomen suhteiden kehitys sotaa edeltaneella kaudella, TPH
- Bethel, Nicholas; Alexandria, Virginia (1981), Russia Besieged, Time-Life Books, 4th Printing, Revised
- Brinkley, Douglas; Haskey, Mickael E. (2004), The World War II. Desk Reference, Grand Central Press
- Carell, Paul (1963), Unternehmen Barbarossa — Der Marsch nach Russland
- Carell, Paul (1966), Verbrannte Erde: Schlacht zwischen Wolga und Weichsel (Scorched Earth: The Russian-German War 1943–1944), Verlag Ullstein GmbH, (Schiffer Publishing), ISBN 0-88740-598-3
- Cartier, Raymond (1977), Der Zweite Weltkrieg (The Second World War), R. Piper & CO. Verlag, München, Zürich
- Churchill, Winston S., Memoires of the Second World War. An abridgment of the six volumes of The Second World War, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, ISBN 0-395-59968-7
- Clark, Alan (1965), Barbarossa. The Russian-German Conflict 1941–1945, Perennial, ISBN 0-688-04268-6
- Fugate, Bryan I. (1984), Operation Barbarossa. Strategy and Tactics on the Eastern Front, 1941, Presidio Press, ISBN 978-0-89141-197-0
- Ganzenmüller, Jörg (2005), Das belagerte Leningrad 1941–1944, Ferdinand Schöningh Verlag, Paderborn, ISBN 3-506-72889-X
- Гречанюк, Н. М.; Дмитриев, В. И.; Корниенко, А. И. (1990), Дважды, Краснознаменный Балтийский Флот (Baltic Fleet), Воениздат
- Higgins, Trumbull (1966), Hitler and Russia, The Macmillan Company
- Jokipii, Mauno (1987), Jatkosodan synty (Birth of the Continuation War), ISBN 951-1-08799-1
- Juutilainen, Antti; Leskinen, Jari (2005), Jatkosodan pikkujättiläinen, Helsinki
- Kay, Alex J. (2006), Exploitation, Resettlement, Mass Murder. Political and Economic Planning for German Occupation Policy in the Soviet Union, 1940 – 1941, Berghahn Books, New York, Oxford
- Miller, Donald L. (2006), The Story of World War II, Simon & Schuster, ISBN 0-7432-2718-2
- National Defence College (1994), Jatkosodan historia 1–6, Porvoo, ISBN 951-0-15332-X
- Seppinen, Ilkka (1983), Suomen ulkomaankaupan ehdot 1939–1940 (Conditions of Finnish foreign trade 1939–1940), ISBN 951-9254-48-X
- Симонов, Константин (1979), Записи бесед с Г. К. Жуковым 1965–1966, Hrono
- Suvorov, Victor (2005), I Take My Words Back, Poznań, ISBN 9666968746
- Vehviläinen, Olli; McAlister, Gerard (2002), Finland in the Second World War: Between Germany and Russia, Palgrave
Fiction related to the Siege of Leningrad
- Benioff, David (2008), City of Thieves, Viking Penguin, ISBN 978-0-670-01870-3
- Yelena's Leningrad, Author, Des Dillon. Publisher: lulu.com (12 Jan. 2012). Language: English. ISBN 978-1471033926
External links
| the Siege of Leningrad | |
|
| |
|
|
- Leningrad blockade part1 on YouTube (Retrieved on 29 June 2008)
- 900days. A documentary about the Siege of Leningrad by Jessica Gorter.
- "In the vortex of congealed time", by Oleg Yuriev. An overview of the literature of the Siege of Leningrad.
- The Siege of Leningrad. A collection of documents, articles and links to photographs and footage.
- ↑ ОТЕЧЕСТВЕННАЯ ИСТОРИЯ. Тема 8 (in Russian). Ido.edu.ru. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ↑ Фотогалерея: "От Волги До Берлина. Основные операции советской армии, завершившие разгром врага." (in Russian). victory.tass-online.ru (ИТАР-ТАСС). Retrieved 2008-10-26.