Lunokhod programme
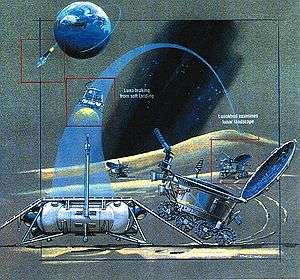
Lunokhod (Russian: Луноход, "Moonwalker") was a series of Soviet robotic lunar rovers designed to land on the Moon between 1969 and 1977.
The 1969 Lunokhod 1A (Lunokhod 0, Lunokhod No.201) was destroyed during launch, the 1970 Lunokhod 1 and the 1973 Lunokhod 2 landed on the moon and Lunokhod 3 (Lunokhod No.205, planned for 1977) was never launched. The successful missions were in operation concurrently with the Zond and Luna series of Moon flyby, orbiter and landing missions.
The Lunokhods were primarily designed to support the Soviet manned moon missions during Moon race. Instead, they were used as remote-controlled robots for exploration of the lunar surface and return its pictures after the successful Apollo manned lunar landings and cancellation of Soviet manned moon program.
The Lunokhods were transported to the lunar surface by Luna spacecraft, which were launched by Proton-K rockets. The moon lander part of the Luna spacecraft for Lunokhods were similar to the ones for sample return missions. The Lunokhods were designed by Alexander Kemurdzhian[1] at Lavochkin.
Not until the 1997 Mars Pathfinder was another remote-controlled vehicle put on an extraterrestrial body. In 2010, nearly forty years after the 1971 loss of signal from Lunokhod 1, the NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter photographed its tracks and final location, and researchers, using a telescopic pulsed-laser rangefinder, detected the robot's retroreflector.[2]
Development

Lunokhod's original primary mission was the back-up for L3 manned moon expeditions and for the later Zvezda lunar base.
For mission safety, weeks before the manned mission on LK lander, an LK-R lander in unmanned L3 lunar expedition complex and two Lunokhod automated rovers would be sent to the Moon for preliminar study of surface around LK-R and LK sites, for work as radio beacons for precision landings of LK-R and LK, and for visual estimate of status of them. LK-R used as a reserve escape craft in case of disability to start from Moon of LK and Lunokhods used by cosmonaut for transfer to LK-R in necessity and for regular research. This manned version of Lunokhod were additionally equipped with oxygen stock with hose socket, standing pads and manual control for the cosmonaut in front part.
In mid-1968, at the facility KIP-10 or NIP-10 (КИП-10 or НИП-10)[3] in the secret village Shkolnoye (ru:Школьное (Крым) - closed town Simferopol-28), near Simferopol, a lunodrom (лунодром - moondrome) was built. It covered an area of one hectare (120 meters by 70 meters) and was very similar to some parts of the lunar surface. It was constructed using more than 3,000 cubic meters of soil, and included 54 craters up to 16 m in diameter and around about 160 rocks of various sizes.[4] The whole area was surrounded with bricks, painted in gray and black. It was used to analyze problems with the Lunokhod chassis and to cosmonaut's skill of control the one.[5][6] Closed town Simferopol-28 - the facility was the most significant tracking facility in the Soviet Union, contains the largest number of antennas, the largest area, and the most personnel of any of the Soviet tracking facilities. The facility was one of a network of ten facilities which contain earth satellite vehicle tracking equipment and provide command/control for Soviet near-space civil and military events. Additionally, this facility was support all lunar programs of Soviet Union in association with the Evpatoria Deep Space Tracking Facility.[7][8]
At least four complete vehicles were constructed, with the serial numbers 201, 203, 204 and 205.
Lunokhod 201
After years of secret engineering development and training, the first Lunokhod (vehicle 8ЕЛ№201) was launched on February 19, 1969. Within a few seconds the rocket disintegrated and the first Lunokhod was lost. The rest of the world did not learn of the rocket's valuable payload until years later.[9] The failure resulted in the radioactive heat source, Polonium 210, being spread over a large region of Russia.[10]
Lunokhod 1
After the destruction of the original Lunokhod, Soviet engineers began work immediately on another lunar vehicle. Lunokhod 1 (vehicle 8ЕЛ№203) was the first of two unmanned lunar rovers successfully landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. Lunokhod was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on another world.
Luna 17 was launched on November 10, 1970 at 14:44:01 UTC. After reaching Earth parking orbit, the final stage of Luna 17's launching rocket fired to place it into a trajectory towards the Moon (November 10, 1970 at 14:54 UTC). After two course correction manoeuvres (on November 12 and 14) it entered lunar orbit on November 15, 1970 at 22:00 UTC.
The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains on November 17, 1970 at 03:47 UTC. The lander had dual ramps from which the payload, Lunokhod 1, could descend to the lunar surface. At 06:28 UT the rover moved onto the Moon's surface.
To be able to work in vacuum a special fluoride based lubricant was used for the mechanical parts and the electric motors (one in each wheel hub) were enclosed in pressurised containers.[11][12]
The rover ran during the lunar day, stopping occasionally to recharge its batteries via the solar panels. At night the rover hibernated until the next sunrise, heated by the radioisotope heater unit.
Rover description


Lunokhod 1 was a lunar vehicle formed of a tub-like compartment with a large convex lid on eight independently powered wheels. Its length was 2.3 metres. Lunokhod 1 was equipped with a cone-shaped antenna, a highly directional helical antenna, four television cameras, and special extendable devices to impact the lunar soil for density measurements and mechanical property tests.
An X-ray spectrometer, an X-ray telescope, Cosmic Ray Detector, and a Laser device were also included. The vehicle was powered by batteries which were recharged during the lunar day by a solar cell array mounted on the underside of the lid. During the lunar nights, the lid was closed and a polonium-210 heat source kept the internal components at operating temperature.
The rover stood 135 cm (4 ft 5 in) high and had a mass of 840 kg (1,850 lb). It was about 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) long and 160 cm (4 ft 11 in) wide and had eight wheels each with an independent suspension, motor and brake. The rover had two speeds, approximately 1 and 2 km/h (0.6 and 1.2 mph).
Payload
- Cameras (two TV & four panoramic telephotometers)
- RIFMA X-ray fluorescence spectrometer
- RT-1 X-ray telescope
- PrOP odometer/penetrometer
- RV-2N radiation detector
- TL laser retroreflector
Lunokhod 2
Lunokhod 2 (vehicle 8ЕЛ№204) was the second and more advanced of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod program. The launcher put the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit on January 8, 1973, followed by translunar injection. On January 12, 1973, Luna 21 was braked into a 90 by 100 km (56 by 62 miles) lunar orbit.
The Luna 21 spacecraft landed on the Moon and deployed the second Soviet lunar rover, Lunokhod 2. The primary objectives of the mission were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study mechanical properties of the lunar surface material.
The landing occurred on January 15, 1973 at 23:35 UT in Le Monnier crater at 25.85 degrees N, 30.45 degrees E.
After landing, the Lunokhod 2 took TV images of the surrounding area, then rolled down a ramp to the surface at 01:14 UT on 1973-01-16 and took pictures of the Luna 21 lander and landing site.
Rover description
Lunokhod 2 was equipped with three slow-scan television cameras, one mounted high on the rover for navigation, which could return high resolution images at different rates—3.2, 5.7, 10.9 or 21.1 seconds per frame (not frames per second). These images were used by a five-man team of controllers on Earth who sent driving commands to the rover in real time.[13] There were four panoramic cameras mounted on the rover.
Power was supplied by a solar panel on the inside of a round hinged lid which covered the instrument bay, which would charge the batteries when opened. A polonium-210 radioactive heat source was used to keep the rover warm during the long lunar nights.
Scientific instruments included a soil mechanics tester, Solar X-ray experiment, an astrophotometer to measure visible and ultraviolet light levels, a magnetometer deployed in front of the rover on the end of a 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) boom, a radiometer, a photodetector (Rubin-1) for laser detection experiments, and a French-supplied laser corner reflector.
Payload
- Cameras (three TV & four panoramic telephotometers)
- RIFMA-M X-ray fluorescence spectrometer
- X-ray telescope
- PROP odometer/penetrometer
- RV-2N-LS radiation detector
- TL laser retroreflector
- AF-3L UV/visible astrophotometer
- SG-70A magnetometer
- Rubin 1 photodetector
Lunokhod 3


Lunokhod 3 (vehicle 8ЕЛ№205) was built for a Moon landing in 1977 as Luna 25,[14] but never flew to the Moon due to lack of launchers and funding. It remains at the NPO Lavochkin museum.[15]
Results
During its 322 Earth days of operations, Lunokhod 1 traveled 10.5 km (6.5 miles) and returned more than 20,000 TV images and 206 high-resolution panoramas.[16] In addition, it performed twenty-five soil analyses with its RIFMA x-ray fluorescence spectrometer and used its penetrometer at 500 different locations.
Lunokhod 2 operated for about 4 months, covered 42 km (26 miles) of terrain,[17] including hilly upland areas and rilles, and held the record for the longest distance of surface travel of any extraterrestrial vehicle until 2014.[9] It sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 TV pictures. Many mechanical tests of the surface, laser ranging measurements, and other experiments were completed during this time.
For comparison, the similarly sized NASA Mars Exploration Rovers, Spirit and Opportunity had, by their fifth anniversary in January 2009, traveled a total of 21 km (13 miles) and transmitted over 125,000 images.[18]
Chernobyl legacy
According to a French documentary TV film Tank on the Moon by Jean Afanassieff, the Lunokhod design returned to limelight 15 years later due to the Chernobyl nuclear power plant disaster on April 26, 1986.[19] The East German-built remote controlled bulldozers available to Soviet civil defense troops weighed dozens of tons – too heavy to operate on the remaining parts of the partially collapsed reactor building roof. Human laborers could not be employed effectively to shovel debris, since work shifts were limited to 90 second intervals due to intense ionizing radiation.[20]
Lunokhod designers were called back from retirement, and in two weeks rovers were made which used nuclear decay heat sources for internal rack climate control, their electronic systems were already hardened to resist radiation.[19] This benefit allowed the 1986 designers to quickly devise a derived vehicle type for nuclear disaster recovery work. On July 15, two rovers, called STR-1,[9] were delivered to the Chernobyl accident zone and proved useful for clearing debris, earning awards for the designers. Due to extremely high radiation levels, all rovers eventually failed, and human workers (later named liquidators) were called in.[19][21]
Locations and ownership

Until 2010, the final location of Lunokhod 1 was uncertain by a few kilometers.[22] Lunar laser ranging experiments had failed to detect a return signal from its retroreflector since the 1970s.[23] On March 17, 2010, Albert Abdrakhimov found both the lander and the rover[24] in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter image M114185541RC.[25] On April 22, Tom Murphy (UCSD) and Russet McMillan at the Apache Point Observatory detected the robot's retroreflector using the Apache Point telescopic pulsed-laser rangefinder.[2]
Lunokhod 2 continues to be detected by lunar laser ranging experiments and its position is known to sub-meter accuracy. Ownership of Lunokhod 2 and the Luna 21 lander was sold by the Lavochkin Association for US$68,500 in December 1993 at a Sotheby's auction in New York[26] (although the catalog incorrectly lists lot 68A as Luna 17/Lunokhod 1).[27] The buyer was computer gaming entrepreneur and astronaut's son Richard Garriott (also known by his gaming character Lord British), who stated in a 2001 interview: "I purchased Lunakod 21 [sic] from the Russians. I am now the world's only private owner of an object on a foreign celestial body. Though there are international treaties that say no government shall lay claim to geography off planet earth, I am not a government. Summarily, I claim the moon in the name of Lord British!"[28] In 2007, Garriott said he is the owner of Lunokhod 2.[29][30]
See also
- Exploration of the Moon
- Google Lunar X PRIZE
- Mars Exploration Rovers
- Mars Pathfinder
- Tank on the Moon
References
- ↑ "Lunochod's chief designer is dead" (250). Cosmic Mirror. March 6, 2003.
- 1 2 Bleicher, Ariel (August 2010). "Forgotten Soviet Moon Rover Beams Light Back to Earth". IEEE Spectrum.
- ↑ Луноходы (History of Lunokhods in NIP-10)
- ↑ Photo of crater on a old soviet moondrome.
- ↑ Космическая энциклопедия (in Russian). September 18, 2008.
- ↑ http://www.panoramio.com/photo/8994008
- ↑ NATIONAL PHOTOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION CENTER June 1969 SIMFEROPOL SPACEFLIGHT CENTER
- ↑ Infinity Beckoned by Jay Gallentine
- 1 2 3 "Tank on the Moon". The Nature of Things with David Suzuki. December 6, 2007. CBC-TV. Archived from the original on December 26, 2008.
- ↑ Karacalıoğlu, Göktuğ (January 6, 2014). "Energy Resources for Space Missions". Space Safety Magazine. Retrieved January 18, 2014.
- ↑ "Den ryska månbilen". Vetenskapens värld (in Swedish). 11 February 2008. SVT2.
- ↑ "Moon applications". Synlube Lube-4-Life.
- ↑ http://www.astronaut.ru/luna/crew.htm
- ↑ Harvey, Brian. Soviet and Russian Lunar Exploration. p. 280. ISBN 9780387218960. Retrieved 2014-04-20.
- ↑ Chaikin, Andy (February–March 2004). "The Other Moon Landings". Air & Space.
- ↑ "Lunokhod 1 Panoramas". planetology.ru. Retrieved April 30, 2013.
- ↑ Wall, Mike (July 11, 2013). "NASA Moon Probe Helps Revise Off-Planet Driving Record | Lunokhod 2". Space.com. Retrieved July 12, 2013.
- ↑ "Public Events Mark Mars Rovers' Five-Year Anniversary" (Press release). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. January 12, 2009.
- 1 2 3 Zarowny, Andrew (March 16, 2011). "Lunokhod: From the Moon to Chernobyl, the Little Robot That Could!". Right Pundits. Retrieved June 21, 2016.
- ↑ McDougal, Heather (February 19, 2009). "Lunokhod and the Art of Space". Cabinet of Wonders. Retrieved June 21, 2016.
- ↑ Anderson, Christopher (January 20, 1990). "Soviet Official Admits That Robots Couldn't Handle Chernobyl Cleanup". The Scientist. Canada. Retrieved June 21, 2016.
- ↑ Stooke, P.J. (2005). Lunar laser ranging and the location of Lunokhod 1 (PDF). Lunar & Planetary Science XXXVI.
- ↑ David, Leonard (March 27, 2006). "Lunar Lost & Found: The Search for Old Spacecraft". SPACE.com.
- ↑ Lakdawalla, Emily (March 17, 2010). "And now for Luna 17 and Lunokhod 1". Planetary Report.
- ↑ "LROC Observation M114185541R". Arizona State University.
- ↑ Kluger, Jeffrey (April 1994). "The Bloc on the Block". Discover magazine.
- ↑ Sotheby's Catalogue - Russian Space History, Addendum, Lot 68A, December 11, 1993
- ↑ Yans, Cindy (April 13, 2001). "Lord British, we hardly knew ye". Computer Games Magazine. via Demiurg.net.
- ↑ "The Astronaut's Son's Secret Sputnik". CollectSPACE. October 2, 2007.
- ↑ Garriott, Owen (December 10, 2007). "Sputnik: 50 Years, One Month, Two Weeks Later". Are We Alone (Interview). Interview with Seth Shostak. SETI Institute.
Further reading
- Vinogradov, A. P., ed. (1971). Peredvizhnaya Laboratoriya na Lune Lunokhod-1. Tom 1 (in Russian). Moscow: Nauka.
- Barsukov, V. L., ed. (1978). Peredvizhnaya Laboratoriya na Lune Lunokhod-1. Tom 2 (in Russian). Moscow: Nauka.
External links
![]() Media related to Lunokhod program at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lunokhod program at Wikimedia Commons
- Lunar and Planetary Department Moscow University
- Exploring the Moon (1969-1976) - a diary of significant events in Soviet lunar exploration, including those associated with the Lunokhod programme
- Don P. Mitchell's catalog of Soviet Moon Images including many from the Lunokhod programme
- Lunakhod article at Lunarpedia
- Tests of breadboard models of lunokhods on moonodrome(лунодром - moondrome in Russian) near Simferopol in 1969
- Remote control lunokhods and planetrovers (Russian)
- Crews lunokhods (Russian)
- Details of the cameras used in the Lunokhods (about half way down the page, or search the page for "Lunokhod")


