Mesabi Range
Coordinates: 47°30′36″N 93°37′48″W / 47.51000°N 93.63000°W
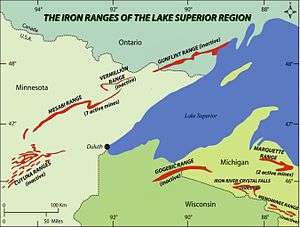

The Mesabi Iron Range is an elongate trend containing very large deposits of iron ore, and the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota. Discovered in 1866, it is the chief iron ore mining district in the United States. The district is located in northeast Minnesota, largely in Itasca and Saint Louis counties. It was extensively worked in the earlier part of the 20th century. Extraction operations declined throughout the mid-1970s but rebounded in 2005. China's growing demand for iron, along with the falling value of the U.S. dollar versus other world currencies, have made taconite production profitable again, and some mines that had closed have been reopened, while current mines have been expanded.[1]
Name
The Mesabi Range was known to the local Ojibwe as Misaabe-wajiw ("Giant mountain").[2][3] Throughout the Mesabi Range, "Mesaba" and "Missabe" spelling variations are found along with places containing "Giant" in their names.
Geology
There are three iron ranges in northern Minnesota, the Cuyuna, the Vermilion, and the Mesabi. Most of the world's iron ore, including that contained in northern Minnesota, was formed during the middle Precambrian period. During this period, erosion leveled mountains. This erosion released iron and silica into the waters of a new sea. Marine algae living in this new sea raised the level of atmospheric oxygen. This oxygen catastrophe caused the eroded iron to precipitate into the banded iron formations found in northern Minnesota and other members of the Animikie Group. Over billions of years, geological forces left behind ore deposits of varied quality and concentrations – differences that would determine how the ore was mined from place to place. On the Vermilion Range, between Soudan and Ely, lay the deepest veins of ore. There, miners worked in deep underground mines, blasting the ore from volcanic bedrock. On the Mesabi Range, stretching 100 miles (160 km) from Grand Rapids to Babbitt, soft ore lay close to the surface, where it could be scooped from open pit mines.[4]
The overall structure of the range is that of a monocline dipping 5 to 15 degrees to the southeast. Key faults include the Calumet, La Rue, Morton, Biwabik, and the Siphon. The Duluth Gabbro complex to the east has caused metamorphic changes in the Biwabik formation. The natural iron ores and the magnetite taconites occur in this Precambrian Biwabik formation, which is a cherty layer 340–750 feet (100–230 m) thick. The natural ores are located in elongated channels or tabular deposits, while the magnetite taconites occur in stratigraphic zones. Natural ores have an iron content of 51 to 57 per cent while the pellets contain 60 to 67 per cent. The natural ores are mainly mixtures of hematite and goethite.[5]:519-520,522,527-528 The most common silicate is Minnesotaite. Also of note are the presence of algal structures in the Biwabik formation.[6]
Physical extent
The Mesabi Range is 110 miles (180 km) long. Heights vary from 200–500 feet (61–152 m). The highest point, located about 5.6 miles (9.0 km) northeast of Virginia, is Pike Mountain at 1,950 feet (590 m).[7] The range trends from the northeast to the southwest, extending from Babbitt to Grand Rapids.[8]
Embarrass Mountains
The Embarrass Mountains are a small subrange of the Mesabi Range, spanning about 9 miles (14 km) through northern White Township and Hoyt Lakes in St. Louis County. Heights vary from 200–400 feet (61–122 m).[9] The highest point, at 1,940 feet (590 m), is roughly 1.9 miles (3.1 km) west of the unincorporated community of Hinsdale,[7] near the former Erie Mining Company's pits and taconite processing plant.
Mining operations



Iron-bearing rocks were noted by the Minnesota State Geologist Henry H. Eames in 1866. Iron ore was discovered north of Mountain Iron, Minnesota on 16 Nov. 1890 by J.A. Nichols of the Merritt brothers. The range was defined by 1900. Initially underground mines were employed but these gave way to open pits so that by 1902, half the operations were conducted this way. The last underground mine closed in 1960. Natural ores eventually gave way to iron-ore concentrates from magnetite taconite so that by 1965 one third of production came from these pellets.[5]
Iron ore is currently mined only from open pits, although some mines operated underground early on.[10] The Soudan Underground Mine is the oldest mine in Minnesota. In the late 19th century prospectors searching for gold in northern Minnesota discovered extremely rich veins of hematite at this site, often containing more than 65% iron. An open pit mine began operation in 1882, and moved to underground mining by 1900. The mine was worked until the end of active mining in 1962, and was then donated to the State of Minnesota to use for educational purposes.
Much of the softer ore was formed close to the surface, allowing mining operations to be conducted via open pit mines. The world's largest open pit iron ore mine is the Hull-Rust-Mahoning Open Pit Iron Mine in Hibbing. In the early years of mining from the late 19th century until the 1950s, mining focus was on high grade ore that could be processed into steel without much change. However, when that supply dried up, focus shifted to lower-grade ore (taconite) which requires extensive processing at large mining-processing facilities before moving to port. The mined ore is then transported, primarily by the Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway, to the ports of Two Harbors and Duluth. At Duluth, trains of up to eighty 100-ton open cars are moved out on massive ore docks to be dumped into "lakers" of up to 60,000 tons weight for movement to steel mills in Indiana and Ohio.
Open pit mines that are no longer worked are a common feature along the Iron Range. Some of these sites have been redeveloped for other uses. For instance, the Virginia Pilot is a project which focuses on redeveloping the grounds adjacent to the old mines into low- to moderate-income residential space. The Hill-Annex Mine is now a state park and offers tours to visitors who wish to learn about mine operations. Tours are guided by former mine workers.
Currently, there are six mining-processing facilities in operation on the Iron Range. Cliffs Natural Resources owns and operates Northshore Mining, which has mining operations in Babbitt and crushing, concentrating (grinding) and pelletizing operations in Silver Bay, along with United Taconite which has mining operations in Eveleth and crushing, concentrating and pelletizing operations in Forbes. Arcelor Mittal owns and operates the Minorca Mine and Plant with mining operations near Biwabik and Gilbert and a crushing, concentrating and pelletizing facility near Virginia (47°32′34″N 92°31′01″W / 47.5428°N 92.5169°W). United States Steel owns and operates both KeeTac (47°23′57″N 93°04′33″W / 47.3992°N 93.0759°W) and Minntac (47°29′50″N 92°36′50″W / 47.49730°N 92.61401°W) with mining and processing facilities in Keewatin and Mountain Iron respectively. The last facility is Hibbing Taconite which operates a mine and plant between the cities of Hibbing and Chisholm. Although Arcelor Mittal owns a majority stake in Hibbing Taconite, the operating agent is actually a minority owner, Cliffs Natural Resources. United States Steel is also a minority stakeholder in Hibbing Taconite.
In addition, Essar Steel is building a mine/plant near Nashwauk that has plans to not only mine and process the taconite, but eventually to produce steel on-site ready for shipment around the world. Steel Dynamics and Kobe Steel own Mesabi Nugget (47°31′41″N 92°07′18″W / 47.5280°N 92.1216°W) near Hoyt Lakes which does not yet mine its own material, but does produce high-iron content nuggets. Magnetation, Inc. is another company currently working the Iron Range, but their focus is reclaiming leftover iron from ore dumps with company-designed high-power magnetic separators to produce concentrate to sell and ship throughout the world.
Labor strikes

Several large-scale strikes took place on the Mesabi Iron Range during the early 1900s. The first began on July 20, 1907 after the Western Federation of Miners (WFM) asked Oliver Iron Mining Company for, among other demands, an eight-hour work day and a pay raise. The strike lasted two months and resulted in thousands of workers being blacklisted.[11]
In June 1913, the WFM organized a strike of the copper companies in the region, again demanding shorter hours and better pay. This unsuccessful strike lasted 265 days and is known as the Copper Country Strike of 1913–1914.[12]
On June 25, 1916, a miner left his shift after being paid less than the contracted rate. His action led to the Mesabi range strike of 1916. The Industrial Workers of the World quickly supported the strike for better pay and shorter hours. In September 1916, the workers voted to resume work, assuming a failed strike. However, shortly after returning to work a 10% raise in wages was issued for workers throughout the Range.[13]
Notable natives and residents
- Joe Bretto, professional hockey player, Chicago Black Hawks.
- Vincent Bugliosi, prosecutor of Charles Manson.
- Bruce Carlson, United States Air Force general, Director of the National Reconnaissance Office.
- Steve Deger, nonfiction author.
- Bob Dylan (born Robert Zimmerman in Duluth), musician, singer-songwriter, Rock and Roll Hall of Famer and Pulitzer Prize winner. The song "North Country Blues" is about the decline of mining in the Mesabi Range, and its effect on miners and their families.
- Steve Enich, professional football player.
- Roger Enrico, Chairman/CEO of PepsiCo from 1996 to 2001, and Chairman of DreamWorks Animation SKG Inc from 2004 to 2012. board of directors of the National Geographic Society, the Environmental Defense Fund and the American Film Institute.
- Philip Falcone, billionaire Wall Street investor.
- Judy Garland, famous actress (born Frances Gumm).
- Dick Garmaker, professional basketball player.
- Robert Rowe Gilruth, first director of NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center, later renamed the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center.
- Gus Hall, former leader of the Communist Party USA and four-time U.S. presidential candidate.
- Jeff Halper, professor of anthropology, author, lecturer, political activist and co-founder of Israeli Committee Against House Demolitions.
- John Harrington, right wing on 1980 "Miracle on Ice" gold medal olympic team.
- Chi Chi LaRue, American film director
- Roger Maris, professional baseball player, former single-season home run record holder.
- John Mariucci, NHL hockey player, hockey coach for the University of Minnesota, and 1956 US Olympic hockey coach.[14]
- Kevin McHale, professional basketball player, 3 NBA titles with the Boston Celtics, former Minnesota Timberwolves Vice President. Current coach of Houston Rockets.
- Bethany McLean, co-author of Enron: The Smartest Guys in the Room.
- Joe Micheletti, professional hockey player, television Olympics & NHL hockey analyst in NYC.
- Pat Micheletti, professional hockey player.
- Robert Mondavi, American wine entrepreneur.
- Marie Myung-Ok Lee, novelist and essayist.
- Carol J. Oja, music historian at Harvard University.
- Jeno Paulucci, founder of Jeno's Pizza and Chun King Foods brands.
- Mark Pavelich, center on 1980 "Miracle on Ice" gold medal olympic team.
- Rudy Perpich, Minnesota governor, former town dentist.
- John (Jack) Petroske, member of the 1956 men's U.S. Olympic Hockey Team, winning a silver medal.
- Gary Puckett, musician.
- Buzz Schneider, LW on 1980 "Miracle on Ice" gold medal olympic team.Member of 1976 olympic team.
- John P. Sheehy, internationally known architect.
- Carl Wickman, founder and longtime CEO of Greyhound Lines.
Popular culture
Bob Dylan memorialized the Iron Range in the 1963 song North Country Blues, a lament portraying hard times in the region. Presented in his 1964 album The Times They Are a-Changin', it includes such lines as:
- So the mining gates locked and the red iron rotted
- And the room smelled heavy from drinking
- When the sad, silent song made the hour twice as long
- As I waited for the sun to go sinking [15]
The Mesabi Range was brought to public attention by the 2005 film North Country, which depicts a fictionalized version of the events surrounding Jenson v. Eveleth Taconite Co., a sexual harassment, class-action lawsuit that female miners brought against a Mesabi Range mining company.
The range is also featured in the song "Youngstown", by Bruce Springsteen, from his 1995 album The Ghost of Tom Joad:
- From the Monongahela valley, to the Mesabi Iron Range –
- To the coal mines of Appalachia, the story's always the same.
Springsteen lifted the two lines of the above lyric from the opening voice-over by Gregory Peck in the 1945 movie The Valley of Decision set in a Pennsylvania steel town.
"Mesabi" is the title song of a 2011 album by Tom Russell: "Some things never change on the Mesabi Iron Range . . . Bethlehem of the Troubadour Kid" (referring to Bob Dylan – see above).
See also
- Gogebic Range
- Soudan Underground Mine State Park
- Cliffs Shaft Mine Museum
- Cuyuna Range
- Vermilion Range (Minnesota)
- Gunflint Range
- Iron Mountain Central Historic District
- Marquette Iron Range
- Rouchleau Mine
References
- ↑ Duluth News Tribune
- ↑ The Ojibwe peoples dictionary. Minnesota Geographic Names. Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society (Minnesota Historical Society: St. Paul, 1920), page 504. Available in fulltext at Google Book Search Archived May 29, 2016, at the Wayback Machine..
- ↑ John D. Nichols and Earl Nyholm. A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. University of Minnesota Press (University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, 1995) ISBN 0-8166-2427-5
- ↑ "History of the Iron Range". Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- 1 2 Marsden, R.W.; Emanuelson, J.W.; Owens, J.S.; Walker, N.E.; Werner, R.F. (1968). John D. Ridge, ed. The Mesabi Iron Range, Minnesota, in Volume 1 of Ore Deposits of the United States, 1933-1967. The American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, Inc. p. 520-521.
- ↑ Gruner, John (1946). The Mineralogy and Geology of the Taconites and Iron Ores of the Mesabi Range, Minnesota. Office of the Commissioner of the Iron Range Resources and Rehabilitation. p. 8,38.
- 1 2 Mangou, Patrick J. "The Archean Terranes of Minnesota". US Geology and Geomorphology. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ↑ Mesabi Range Archived April 26, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "MyTopo Free Online Topo Maps". MyTopo. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ↑ Iron Range – The Mining Frontier Archived September 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.. Macalester College.
- ↑ Michael G. Karni (1986). Dirk Hoerder, ed. Struggle a Hard Battle. DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois University Press. pp. 210–211.
- ↑ Michael G. Karni (1986). Dirk Hoerder, ed. Struggle a Hard Battle. DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois University Press. pp. 215–216.
- ↑ Michael G. Karni (1986). Dirk Hoerder, ed. Struggle a Hard Battle. DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois University Press. pp. 218–219.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved 2014-01-01.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on April 24, 2016. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- Leith, Charles Kenneth (1903). The Mesabi Iron-bearing District of Minnesota. U.S. Geological Survey Monograph 43. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office.
- Stacy, Francis N. (September 1904). "The Iron Mines That Give Us Leadership: The Most Extraordinary Deposits In The World In The Mesabi Range". The World's Work: A History of Our Time. VIII: 5235–5243. Retrieved 2009-07-10. Includes numerous photos of c. 1904 Mesabi iron works.
Further reading
- Beck, J. Robert. Well, Here We Are! The Hansons and the Becks. Lincoln, Nebraska: iUniverse, 2005.—A history of a Swedish-Finnish immigrant family from the Mesabi Iron Range, which details the social (and socialist) conditions of the area during its heyday.
- George, Harrison. "The Mesaba Iron Range," International Socialist Review, vol. 17, no. 6 (December 1916), pp. 329–332.
- George, Harrison. "Victory on the Mesaba Range," International Socialist Review, vol. 17, no. 7 (January 1917), pp. 429–431.