Myriapoda
| Myriapods Temporal range: Late Silurian–Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Representatives of the four extant myriapod classes. Clockwise from top left: Chilopoda, Diplopoda, Symphyla, and Pauropoda. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Myriapoda Latreille, 1802 |
| Classes [1] | |
Myriapoda is a subphylum of arthropods containing millipedes, centipedes, and others. The group contains over 13,000 species, most of which are terrestrial.[2] Although their name suggests they have myriad (10,000) legs, myriapods range from having over 750 legs (the millipede Illacme plenipes)[3] to having fewer than ten legs.
The fossil record of myriapods reaches back into the late Silurian, although molecular evidence suggests a diversification in the Cambrian Period,[4] and Cambrian fossils exist which resemble myriapods.[2] The oldest unequivocal myriapod fossil is of the millipede Pneumodesmus newmani, from the late Silurian (428 million years ago). P. newmani is also important as the earliest known terrestrial animal.[5][6] The phylogenetic classification of myriapods is still debated.
The scientific study of myriapods is myriapodology, and those who study myriapods are myriapodologists.[7]
Anatomy

Myriapods have a single pair of antennae and, in most cases, simple eyes. The mouthparts lie on the underside of the head, with an "epistome" and labrum forming the upper lip, and a pair of maxillae forming the lower lip. A pair of mandibles lie inside the mouth. Myriapods breathe through spiracles that connect to a tracheal system similar to that of insects. There is a long tubular heart that extends through much of the body, but usually few, if any, blood vessels.[8]
Malpighian tubules excrete nitrogenous waste into the digestive system, which typically consists of a simple tube. Although the ventral nerve cord has a ganglion in each segment, the brain is relatively poorly developed.[8]
During mating, male myriapods produce a packet of sperm, or spermatophore, which they must transfer to the female externally; this process is often complex and highly developed. The female lays eggs which hatch as much shortened versions of the adults, with only a few segments and as few as three pairs of legs. The young add additional segments and limbs as they repeatedly moult to reach the adult form.[8]
Ecology
Myriapods are most abundant in moist forests, where they fulfill an important role in breaking down decaying plant material,[2] although a few live in grasslands, semi-arid habitats or even deserts.[9] A very small percentage of species are littoral (found along the sea shore).[10][11] The majority are detritivorous, with the exception of centipedes, which are chiefly nocturnal predators. Pauropodans and symphylans are small, sometimes microscopic animals that resemble centipedes superficially and live in soils. Millipedes differ from the other groups in having their body segments fused into pairs, giving the appearance that each segment bears two pairs of legs, while the other three groups have a single pair of legs on each body segment.
Although not generally considered dangerous to humans, many millipedes produce noxious secretions (often containing benzoquinones) which in rare cases can cause temporary blistering and discolouration of the skin.[12] Large centipedes, however can bite humans, and although the bite may cause intense pain and discomfort, fatalities are extremely rare.[13]
Classification
There has been much debate as to which arthropod group is most closely related to the Myriapoda.[14] Under the Mandibulata hypothesis, Myriapoda is the sister taxon to Pancrustacea, a group comprising the Crustacea and Hexapoda (insects and their close relatives). Under the Atelocerata hypothesis, Hexapoda is the closest, whereas under the Paradoxopoda hypothesis, Chelicerata is the closest. This last hypothesis, although supported by few, if any, morphological characters, is supported by a number of molecular studies.[15] There are four classes of extant myriapods, Chilopoda (centipedes), Diplopoda, Pauropoda and Symphyla, containing a total of around 12,000 species.[16] While each of these groups of myriapods is believed to be monophyletic, relationships among them are less certain.[17]
Centipedes
Centipedes make up the class Chilopoda. They are fast, predatory and venomous, hunting mostly at night. There are around 3,300 species,[16] ranging from the diminutive Nannarrup hoffmani (less than 12 mm or 1⁄2 in in length)[18] to the giant Scolopendra gigantea, which may exceed 30 centimetres (12 in).
Millipedes

Millipedes form the class Diplopoda. Most millipedes are slower than centipedes, and feed on leaf litter and detritus. They are distinguished by the fusion of each pair of body segments into a single unit, giving the appearance of having two pairs of legs per segment. Around 8,000 species have been described, which may represent less than a tenth of the true global millipede diversity.[16] The name "millipede" is a compound word formed from the Latin roots millia ("thousand") and pes (gen. pedis) ("foot"), although millipedes typically have between 36 and 400 legs. One species, Illacme plenipes, has the greatest number of legs of any animal, with 750.[3] Pill millipedes are much shorter, and are capable of rolling up into a ball, like pillbugs.
Symphyla
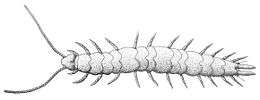
About 200 species of them are known worldwide.[16] They resemble centipedes but are smaller and translucent. Many spend their lives as soil infauna, but some live arboreally. Juveniles have six pairs of legs, but, over a lifetime of several years, add an additional pair at each moult so that the adult instar has twelve pairs of legs.[19]
Pauropoda
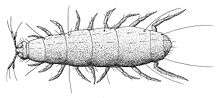
Pauropoda is another small group of small myriapods. They are typically 0.5–2.0 mm long and live in the soil on all continents except Antarctica.[20] Over 700 species have been described.[16] They are believed to be the sister group to millipedes, and have the dorsal tergites fused across pairs of segments, similar to the more complete fusion of segments seen in millipedes.[21]
Arthropleuridea
Arthropleurideans were ancient myriapods that are now extinct, known from the late Silurian to the Permian. The most famous members are from the genus Arthropleura, which was a giant, probably herbivorous, animal that could be up to 3 metres (10 ft) long, but the group also includes species less than 1 cm (0.39 in). Arthropleuridea was historically considered a distinct class of myriapods, but since 2000 scientific consensus has viewed the group as a subset of millipedes, although the relationship of arthropleurideans to other millipedes and to each other is debated.[22][23]
Myriapod relationships
A variety of groupings (clades) of the myriapod classes have been proposed, some of which are mutually exclusive, and all of which represent hypotheses of evolutionary relationships. Traditional relationships supported by morphological similarities (anatomical or developmental similarities) are challenged by newer relationships supported by molecular evidence (including DNA sequence and amino acid similarities).[24][25]
- Dignatha (also called Collifera) is a clade consisting of millipedes and pauropods, and is supported by morphological similarities including the presence of a gnathochilarium (a modified jaw and plate apparatus) and a collum, a legless segment behind the head.
- Trignatha (also called Atelopoda) is a grouping of centipedes and symphylans, united by similarities of mouthparts.
- Progoneata is a group encompassing Dignatha and symphylans while excluding centipedes. Shared features include reproductive openings (gonopores) behind the second body segment, and sensory hairs (trichobothria) with a bulb-like swelling.
- Edafopoda is a grouping of symphylans and pauropodans that is supported by shared genetic sequences, yet conflicts with Dignatha and Trignatha.[26]

See also
- Euthycarcinoidea, a group of enigmatic arthropods that may be ancestral to myriapods
- Colonization of land, major evolutionary stages leading to terrestrial organisms
- Metamerism, the condition of multiple linearly repeated body segments
References
- ↑ "Myriapoda". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- 1 2 3 Ben Waggoner (February 21, 1996). "Introduction to the Myriapoda". University of California, Berkeley.
- 1 2 Paul E. Marek & Jason E. Bond (June 8, 2006). "Biodiversity hotspots: rediscovery of the world's leggiest animal". Nature. 441 (7094): 707. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..707M. doi:10.1038/441707a. PMID 16760967.
- ↑ Markus Friedrich & Diethard Tautz (2002). "Ribosomal DNA phylogeny of the major extant arthropod classes and the evolution of myriapods". Nature. 376 (6536): 165–167. Bibcode:1995Natur.376..165F. doi:10.1038/376165a0. PMID 7603566.
- ↑ Rowland Shelley & Paul Marek (March 1, 2005). "Millipede Fossils". East Carolina University.
- ↑ Garwood, Russell J.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (September 2011). "Early Terrestrial Animals, Evolution, and Uncertainty". Evolution: Education and Outreach. New York: Springer Science+Business Media. 4 (3): 489–501. doi:10.1007/s12052-011-0357-y. ISSN 1936-6426. Retrieved 2015-07-21.
- ↑ Sue Hubbell (2000). Waiting for Aphrodite: Journeys Into the Time Before Bones. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-618-05684-2.
- 1 2 3 Robert D. Barnes (1982). Invertebrate Zoology. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 810–827. ISBN 0-03-056747-5.
- ↑ "Myriapod". Britannica Concise Encyclopedia.
- ↑ Barber, A.D. (2009). "Littoral myriapods: a review" (PDF). Soil Organisms. 81 (3): 735–760.
- ↑ Barber, A.D. (Ed) (2013). "World Database of Littoral Myriapoda". World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 25 October 2013.
- ↑ "Strange and Unusual Millipedes". herper.com. Retrieved July 2, 2007.
- ↑ Sean P. Bush, Bradley O. King, Robert L. Norris & Scott A. Stockwell (2001). "Centipede envenomation". Wilderness & Environmental Medicine. 12 (2): 93–99. doi:10.1580/1080-6032(2001)012[0093:CE]2.0.CO;2. PMID 11434497.
- ↑ Gregory D. Edgecombe (2004). "Morphological data, extant Myriapoda, and the myriapod stem-group". Contributions to Zoology. 73 (3): 207–252.
- ↑ Alexandre Hassanin (2006). "Phylogeny of Arthropoda inferred from mitochondrial sequences: strategies for limiting the misleading effects of multiple changes in pattern and rates of substitution". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 38 (1): 100–116. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.09.012. PMID 16290034.
- 1 2 3 4 5 A. D. Chapman (2005). Numbers of Living Species in Australia and the World (PDF). Department of the Environment and Heritage. p. 23. ISBN 0-642-56850-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ↑ Jerome C. Regier, Heather M. Wilson & Jeffrey W. Shultz (2005). "Phylogenetic analysis of Myriapoda using three nuclear protein-coding genes". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 34 (1): 147–158. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2004.09.005. PMID 15579388.
- ↑ "Central Park survey finds new centipede". American Museum of Natural History. January 29, 2003.
- ↑ "Garden Symphylans". Integrated Pest Management on Peppermint-IPMP3.0. Oregon State University. Retrieved July 2, 2007.
- ↑ "Pauropods: Pauropoda". Insects and Spiders Scientific Reference. Retrieved July 2, 2007.
- ↑ David Kendall (June 6, 2005). "Pauropods & Symphylids". Kendall Bioresearch.
- ↑ Wilson, Heather M.; Shear, William A. (2000). "Microdecemplicida, a new order of minute arthropleurideans (Arthropoda: Myriapoda) from the Devonian of New York State, U.S.A.". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 90 (4): 351–375. doi:10.1017/S0263593300002674.
- ↑ Shear, William A.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (2010). "The geological record and phylogeny of the Myriapoda". Arthropod Structure & Development. 39 (2-3): 174–190. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2009.11.002. PMID 19944188.
- ↑ Edgecombe GD, Giribet G. (2002). "Myriapod phylogeny and the relationships of Chilopoda". In J Llorente Bousquets, JJ Morrone, HP Ulloa. Biodiversidad, Taxonomia y Biogeografia de Artropodos de Mexico: Hacia una S´ıntesis de su Conocimiento (PDF). Univ. Nac. Aut´on .M´exico: Prensas Ciencias. pp. 143–168.
- ↑ Miyazawa, Hideyuki; Ueda, Chiaki; Yahata, Kensuke; Su, Zhi-Hui (2014). "Molecular phylogeny of Myriapoda provides insights into evolutionary patterns of the mode in post-embryonic development". Scientific Reports. 4 (4127). doi:10.1038/srep04127.
- ↑ Zwick, Andreas; Regier, Jerome C.; Zwickl, Derrick J.; Gadagkar, Sudhindra R. (2012). "Resolving Discrepancy between Nucleotides and Amino Acids in Deep-Level Arthropod Phylogenomics: Differentiating Serine Codons in 21-Amino-Acid Models". PLoS ONE. 7 (11): e47450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047450.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to: Myriapoda |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Myriapoda. |
- Myriapod Fossil Record - University of Bristol
- International Journal of Myriapodology
- International Society of Myriapodology
- British Myriapod and Isopod Group
- Myriapods, the World's Leggiest Animals - North America