Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
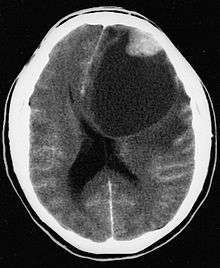
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a brain tumor that occurs most frequently in children and teenagers. At Boston Children's Hospital, the average age at diagnosis is 12 years.[1]
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma usually develops within the supratentorial region (the area of the brain located above the tentorium cerebelli). It is generally located superficially (in the uppermost sections) in the cerebral hemispheres, and involves the leptomeninges. It rarely arises from the spinal cord.
These tumors are formed through the mitosis of astrocytes. They are found in the area of the temples, in the brain's frontal lobe, or on top of the parietal lobe. In about 20% of cases, tumors exist in more than one lobe.
Symptoms
Children with PXA can present with a variety of symptoms. Complaints may vary, and patients may report symptoms that have been occurring for many months and are often linked with more common diseases. (For example, headaches are a common complaint.)
Some children, however, will present with symptoms that start very suddenly, like seizures.
Diagnosis
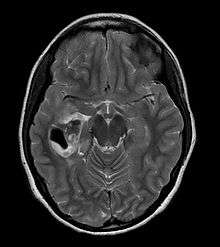
PXA is diagnosed through a combination of diagnostic processes:
- Initially, a doctor will interview the patient and do a clinical exam, which will include a neurological examination.
- A CT scan of the brain, and/or an MRI scan of the brain and spine, will be performed. A special dye may be injected into a vein before these scans to provide contrast and make tumors easier to see.
- For children experiencing seizures, an EEG might be part of the diagnostic process (the goal being to record the brain's electrical activity in order to identify and localize seizure activity).
- Finally, a biopsy of the tumor, taken through a needle during a simple surgical procedure, helps to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
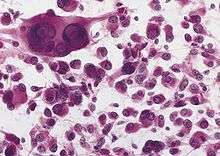
Surgery is often the treatment of choice. Total resection (removal of the tumor) is often possible. However, the best choice of treatment will depend on many individual factors, including:
- The patient's medical history and overall health condition
- The type, location, and size of the tumor
- The patient's age
- How well the patient tolerates specific medications, procedures, or therapy
- How slowly or quickly the tumor is expected to progress
If surgery is performed and the tumor is completely resected, further treatment may not be required. The patient will, however, need repeated MRIs to monitor for tumor re-growth.
For tumors that recur, another surgical resection might be attempted. For tumors that could not be completely removed, radiation therapy may also be recommended. Also called radiotherapy, this treatment uses high-energy radiation to damage or kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Effects of treatment on symptoms
Symptoms of PXA may disappear, or improve progressively, after treatment. For example:
- Symptoms related to increased pressure in the brain often disappear after surgical removal of the tumor.
- Effects like seizures might progressively improve as recovery progresses.
- Steroid treatment is often used to control tissue swelling that may occur before and after surgery.
Side effects of treatment
Brain surgery
Children with PXA may experience seizures as a symptom of their disease. However, any person undergoing brain surgery is at risk of developing epileptic seizures. Medication is administered to minimize or prevent seizure activity. Additionally, after surgery, parents should be informed of the risk of seizures, and educated on what to do in the event of a seizure.
With any brain surgery, there is also a risk of brain damage.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy may cause swelling in the brain, related to tissue inflammation. This inflammation may lead to symptoms like headaches. It may be treated with oral medication.
Prognosis following treatment
With treatment, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas are associated with a high rate of cure.[2]
- Grade II pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas are known to progress towards grade II tumors, which are more likely to recur after surgical removal.
- Grade III anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas may evolve and show signs of anaplasia, according to evidence in the medical literature.[3]
Response to progressive or recurrent disease
If PXA recurs or gets worse, the recommended course of action is to monitor the disease and reattempt a complete surgical removal, according to the medical literature. In cases of progressive or recurrent disease, or when maximal surgical removal has been achieved, the medical team will consider radiation therapy.
Nine medical institutions in the United States have formed a Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium, which "is dedicated to the development of new and innovative treatments for children with progressive/recurrent brain tumors not responsive to standard therapies. Children with pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas would be eligible for a number of experimental therapies available through the consortium.[4]
Mortality
Among people with PXA who were able to have their tumors completely resected during surgery, there is a long-term survival rate of 90%. After incomplete resection, the long-term survival rate is higher than 50%. Morbidity is determined by the type and evolution of the tumor, with high-graded anaplastic tumors causing more fatalities.
References
- ↑ Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma, Boston Children's Hospital website, http://www.childrenshospital.org/health-topics/conditions/pleomorphic-xanthoastrocytoma
- ↑ Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma, Boston Children's Hospital website, http://www.childrenshospital.org/health-topics/conditions/p/pleomorphic-xanthoastrocytoma/treatments
- ↑ Idotsmail H. Tekköka (Mersin University School of Medicine, Mersin, Turkey), Aydin Savb (Marmara University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey) (2004). "Case report : Anaplastic Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytomas Review of the Literature with Reference to Malignancy Potential". Pediatric Neurosurgery. 2004 (40): 171–181. doi:10.1159/000081935.
- ↑ Children's Hospital Boston, http://www.childrenshospital.org/az/Site1454/mainpageS1454P0.html
External links
- Boston Children's Hospital
- ARRS RD Tien, CA Cardenas and S Rajagopalan, American Journal of Roentgenology, Vol 159, 1287–1290, 1992 by American Roentgen Ray Society, Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma of the brain: MR findings in six patients
- MR and CT imaging of 24 pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas (PXA) and a review of the literature Biomedsearch.com PMID 17205313
- neuroconcology Oxford journals
- JNNP journal of neurology neurosurgery and psychiatry
- Path consult DDX-fundamentals
- PLGA Pediatric Lowgrade Astrocytoma's
- Classic PXA MR scans MedPix Database