Eta Geminorum
| |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Gemini |
| A | |
| Right ascension | 06h 14m 52.657s[1] |
| Declination | +22° 30′ 24.48″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.15 - 3.90[2] |
| B | |
| Right ascension | 06h 14m 52.569s[1] |
| Declination | +22° 30′ 24.31″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.04[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2 IIIa[3] + G0 III[4] |
| Variable type | SRa + EA[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −62.46 ± 1.06[5] mas/yr Dec.: −12.12 ± 0.70[5] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 8.48 ± 1.23[5] mas |
| Distance | approx. 380 ly (approx. 120 pc) |
| Orbit[6][7] | |
| Primary | Aa |
| Companion | Ab |
| Period (P) | 8.17 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.077" |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.53 |
| Orbit | |
| Primary | A |
| Companion | B |
| Period (P) | 473.7 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 1.08" |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.54 |
| Details | |
| Aa | |
| Mass | 6.30[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 153[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 3,162[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,548[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.04[9] dex |
| Ab | |
| Mass | 2.06[7] M☉ |
| B | |
| Mass | 1.18[7] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Eta Geminorum (η Geminorum, abbreviated Eta Gem, η Gem), also named Propus,[10] is a triple star system in the constellation of Gemini. It is a naked-eye variable star around 380 light years from the Sun.
Nomenclature
Beta Geminorum is the star's Bayer designation. The traditional names Tejat Prior, Propus (from the Greek, meaning forward foot) and Praepes and Pish Pai (from the Persian Pīshpāy, پیشپای, meaning foreleg). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[12] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[13] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Propus for this star.
This star, along with γ Gem (Alhena), μ Gem (Tejat Posterior), ν Gem and ξ Gem (Alzirr) were Al Han'ah, "the brand" (on the neck of the camel). They also were associated in Al Nuḥātai, the dual form of Al Nuḥāt, "a Camel's Hump".[14]
In Chinese lunar mansion, Tejat Prior is the only member of the lunar mansion 钺 (Pinyin: Yuè, Chinese 'Battle Axe').[15][14]
Surroundings

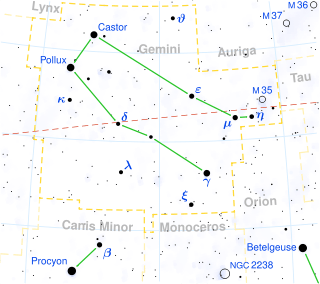
η Geminorum lies at the foot of the Castor side of Gemini, about two degrees west of μ Geminorum and two degrees southeast of the bright open cluster M35. Between the two stars are several faint areas of nebulosity. η Gem just to the west of the supernova remnant shell IC 443. Further east around μ Gem is the emission nebula S249. In between is the small faint emission nebula IC 444 around the 7th magnitude 12 Geminorum.
η Geminorum is near the ecliptic, so it can be occulted by the Moon and, very rarely, by planets. The last occultation by a planet took place on July 27, 1910, by Venus, and the next to last on July 11, 1837, by Mercury.
Variability
In 1865, Julius Schmidt first reported that η Geminorum was a variable star. The light variations were described by Schmidt and other observers as having long maxima of constant brightness, minima of greatly varying size and shape, and a period around 231 days.[16] The star was classified as both a semiregular variable and an eclipsing variable. The eclipse period has been set at about eight years, corresponding to the orbit of an unseen companion. The eclipses have been questioned many times, but special observations are still been made at the times of predicted eclipses.[17][18]
The semi-regular variations have been classified as type SRa, indicating relatively predictable periodicity with some variations in amplitude and light curve shape. These types of variable are considered to be very similar to Mira variables, but with smaller amplitudes.[2] Many long-period variables show long secondary periods, typically ten times longer than the main period, but these changes habe not been detected for η Geminorum. The main period has been refined to an average of 234 days.[19]
System

η Geminorum is a triple system, with the luminous class M star having a close companion known only from radial velocity variations, and a more distant companion resolved visually.
In 1881, Burnham observed that η Geminorum had a close companion. At that time the separation was measured to be 1.08".[20] This has now increased to 1.65" and an orbit has been calculated to be 474 years long and rather eccentric.[16] Little is known about the companion, although it is 6th magnitude. It is given a G0 spectral type and is assumed to be a giant on the basis of its brightness.[4]
In 1902, William Wallace Campbell reported that η Geminorum showed radial velocity variations. The assumption was that the star was a spectroscopic binary, although no period or other orbital parameters were determined.[21] An orbit calculated in 1944 is essentially unchanged today, with a period of 2,983 days and an eccentricity of 0.53. Observations were made looking for sign of eclipses corresponding to the derived orbit, but the evidence was regarded as inconclusive.[22]
Evolution
The luminous main component of η Geminorum is an asymptotic giant branch star, a highly evolved cool luminous star that was originally 2-8 M☉ on the main sequence.[23]
Namesakes
USS Propus (AK-132) was a United States Navy Crater class cargo ship named after the star.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- 1 2 3 Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs. Originally published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989). "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 71: 245. Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K. doi:10.1086/191373.
- 1 2 Hunsch, Matthias; Schmitt, Jurgen H. M. M.; Schroder, Klaus-Peter; Zickgraf, Franz-Josef (1998). "On the X-ray emission from M-type giants". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 330: 225. Bibcode:1998A&A...330..225H.
- 1 2 3 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ↑ Malkov, O. Yu.; Tamazian, V. S.; Docobo, J. A.; Chulkov, D. A. (2012). "Dynamical masses of a selected sample of orbital binaries". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 546: A69. Bibcode:2012A&A...546A..69M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219774.
- 1 2 3 4 Tokovinin, A. A. (1997). "MSC - a catalogue of physical multiple stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement series. 124: 75. Bibcode:1997A&AS..124...75T. doi:10.1051/aas:1997181.
- 1 2 3 Jorissen, A.; Frankowski, A.; Famaey, B.; Van Eck, S. (2009). "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants. III. The eccentricity - period diagram and mass-transfer signatures". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 498 (2): 489. arXiv:0901.0938
 . Bibcode:2009A&A...498..489J. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810703.
. Bibcode:2009A&A...498..489J. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810703. - ↑ Huang, Y.; Liu, X.-W.; Yuan, H.-B.; Xiang, M.-S.; Chen, B.-Q.; Zhang, H.-W. (2015). "Empirical metallicity-dependent calibrations of effective temperature against colours for dwarfs and giants based on interferometric data". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 454 (3): 2863. arXiv:1508.06080
 . Bibcode:2015MNRAS.454.2863H. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1991.
. Bibcode:2015MNRAS.454.2863H. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1991. - 1 2 "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ p. 235, Star-names and Their Meanings, Richard Hinckley Allen, G. E. Stechert, 1899.
- ↑ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1" (PDF). Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- 1 2 Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc. p. 234. ISBN 0-486-21079-0. Retrieved 2010-12-12.
- ↑ (Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 5 月 26 日
- 1 2 Hassforther, B. (2007). "Eta Geminorum - wirklich ein Bedeckungsveraenderlicher?". BAV Rundbrief. 56: 205. Bibcode:2007BAVSR..56..205H.
- ↑ "The 2004 eclipse of Eta Geminorum" (PDF). Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ↑ "The 2004 eclipse of Eta Geminorum" (PDF). Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ↑ Percy, J. R.; Nasui, C. O.; Henry, G. W. (2008). "Long-Term Photometric Variability of 13 Bright Pulsating Red Giants". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. 36: 139. Bibcode:2008JAVSO..36..139P.
- ↑ Clerke, A. M. (1902). "The system of eta Geminorum". The Observatory. 25: 389. Bibcode:1902Obs....25..389C.
- ↑ Campbell, W. W. (1902). "Six stars whose velocities in the line of sight are variable". Astrophysical Journal. 16: 114. Bibcode:1902ApJ....16..114C. doi:10.1086/140954.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Dean B.; Van Dijke, Suzanne E. A. (1944). "The Spectrographic Orbit and Light-Variations of η Geminorum". Astrophysical Journal. 100: 63. Bibcode:1944ApJ...100...63M. doi:10.1086/144637.
- ↑ Eggen, Olin J. (1992). "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun". Astronomical Journal. 104: 275. Bibcode:1992AJ....104..275E. doi:10.1086/116239.