Provinces of Rwanda
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Rwanda |
|
Government |
|
Judiciary |
|
United Nations in Rwanda |
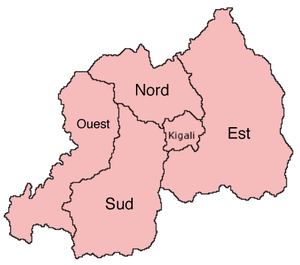

The Provinces of Rwanda, called intara, are divided into districts (akarere) and municipalities (umujyi). Prior to January 1, 2006, Rwanda was composed of 12 provinces, however, the Rwandan Government decided to establish new provinces in an attempt to address issues that arose from the Rwandan Genocide of 1994.
The first goal was to decentralise power. The perception was that Rwanda's centralised governing system had been a contributing factor to the genocide. The new provinces are more multiethnic than the previous twelve which helps to weaken ethnic divisions. Finally, the new provinces do not have the associations that the previous twelve had with events from the genocide.
Until 2002 the provinces were called prefectures (perefegitura).[1]
Provinces
As of January 1, 2006 the five provinces of Rwanda are:
| Province | Kinyarwanda name | Capital | Area (km2) [2] |
Population (2012 census) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kigali | Umujyi wa Kigali | Kigali City | 730 | 1,132,686 |
| Southern | Amajyepfo | Nyanza | 5,963 | 2,589,975 |
| Western | Iburengerazuba | Kibuye | 5,883 | 2,471,239 |
| Northern | Amajyaruguru | Byumba | 3,276 | 1,726,370 |
| Eastern | Iburasirazuba | Rwamagana | 9,458 | 2,595,703 |
Former provinces
Prior to 2006 the provinces were:

- Butare Province
- Byumba Province
- Cyangugu Province
- Gikongoro Province
- Gisenyi Province
- Gitarama Province
- Kibungo Province
- Kibuye Province
- Kigali City
- Kigali-Rural Province (Kigali Ngali)
- Ruhengeri Province
- Umutara Province
See also
References
- ↑ "Provinces of Rwanda". Statoids. Gwillim Law. 27 April 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ↑ Rwanda at GeoHive
External links
- Ministry of Local Government, Community Development and Social Affairs
- Rwanda redrawn to reflect compass, BBC News, 3 January 2006