Renaissance Latin
| Renaissance Latin | |
|---|---|
|
Mural of Dante in the Uffizi Gallery, by Andrea del Castagno, c. 1450. | |
| Native to | The administrations and universities of numerous countries |
| Region | Europe |
| Era | Evolved from Medieval Latin in the 14th century; developed into New Latin by the 16th century |
|
Indo-European
| |
| Latin alphabet | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Most Roman Catholic countries |
| Regulated by | The community of scholars at the earliest universities |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
Renaissance Latin is a name given to the distinctive form of Latin style developed during the European Renaissance of the fourteenth to fifteenth centuries, particularly by the Renaissance humanism movement.
Ad fontes
Ad fontes ("to the sources") was the general cry of the humanists, and as such their Latin style sought to purge Latin of the medieval Latin vocabulary and stylistic accretions that it had acquired in the centuries after the fall of the Roman Empire. They looked to golden age Latin literature, and especially to Cicero in prose and Virgil in poetry, as the arbiters of Latin style. They abandoned the use of the sequence and other accentual forms of metre, and sought instead to revive the Greek formats that were used in Latin poetry during the Roman period. The humanists condemned the large body of medieval Latin literature as "Gothic"—for them, a term of abuse—and believed instead that only ancient Latin from the Roman period was "real Latin".
Some 16th-century Ciceronian humanists also sought to purge written Latin of medieval developments in its orthography. They insisted, for example, that ae be written out in full wherever it occurred in classical Latin; medieval scribes often wrote e instead of ae. They were much more zealous than medieval Latin writers that t and c be distinguished; because the effects of palatalization made them homophones, medieval scribes often wrote, for example, eciam for etiam. Their reforms even affected handwriting; Humanists usually wrote Latin in a humanist minuscule script derived from Carolingian minuscule, the ultimate ancestor of most contemporary lower-case typefaces, avoiding the black-letter scripts used in the Middle Ages. This sort of writing was particularly vigilant in edited works, so that international colleagues could read them more easily, while in their own handwritten documents the Latin is usually written as it is pronounced in the vernacular. Therefore, the first generations of humanists did not dedicate much care to the orthography till the late sixteenth and seventeenth century. Erasmus proposed that the then-traditional pronunciations of Latin be abolished in favour of his reconstructed version of classical Latin pronunciation, even though one can deduce from his works that he himself used the ecclesiastical pronunciation.
The humanist plan to remake Latin was largely successful, at least in education. Schools taught the humanistic spellings, and encouraged the study of the texts selected by the humanists, to the large exclusion of later Latin literature. On the other hand, while humanist Latin was an elegant literary language, it became much harder to write books about law, medicine, science or contemporary politics in Latin while observing all of the Humanists' norms about vocabulary purging and classical usage.
Renaissance Latin gradually developed into the New Latin of the 16th–19th centuries, used as the language of choice for authors discussing subjects considered sufficiently important to merit an international (i.e., pan-European) audience.
Renaissance Latin works and authors
14th century
- 1359. Epistolæ familiares by Petrarch (1304–1374)
- 1360. Genealogia deorum gentilium by Giovanni Boccaccio (1313–1375)
15th century
- 1425. Hermaphroditus by Antonio Beccadelli (1394–1471)
- 1441. De elegantiis Latinæ linguæ by Lorenzo Valla (1406–1457)
- 1442. Historia Florentini populi by Leonardo Bruni (c. 1370–1444)
- 1444. Historia de duobus amantibus by Æneas Sylvius Piccolomini, Pope Pius II (1405–1464)
- 1452. De re ædificatoria by Leone Battista Alberti (1404–1472)
- 1471. Contra amores by Bartolomeo Platina (1421–1481)
- 1479. De inventione dialectica by Rodolphus Agricola (1444–1485)
- 1481. Introductiones Latinæ by Antonio de Nebrija (1441–1522)
- 1486. De hominis dignitate by Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (1463–1494)
- 1491. Nutricia by Poliziano (1454–1494)
- Theologia Platonica de immortalitate animæ by Marsilio Ficino (1433–1499)
- Francesco Filelfo (1398–1481)
References
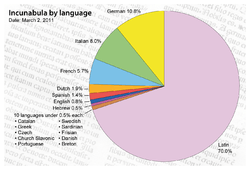
- ↑ "Incunabula Short Title Catalogue". British Library. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
External links
- An Analytic Bibliography of On-line Neo-Latin Titles (also Renaissance Latin).
- Neo-Latin Humanist Texts at DigitalBookIndex.
- René Hoven, Lexique de la prose latine de la Renaissance. Dictionary of Renaissance Latin from prose sources, with the collaboration of Laurent Grailet, Leiden, Brill, 2006 (2nd edition), 683 p.
- The Centre for Neo-Latin Studies, focusing on Irish Renaissance Latin.
