Rio Salado (Mexico)
| Río Salado | |
| Country | Mexico |
|---|---|
| States | Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas |
| Source | Sierra Madre Oriental |
| Mouth | Rio Grande |
| - location | Falcon International Reservoir |
| - coordinates | 26°52′N 99°19′W / 26.867°N 99.317°WCoordinates: 26°52′N 99°19′W / 26.867°N 99.317°W [1] |
| Basin | 60,406 km2 (23,323 sq mi) [2] |
| Discharge | for IBWC station 08-4597.00 near Las Tortillas, Tamaulipas |
| - average | 10.02 m3/s (354 cu ft/s) [2] |
| - max | 1,780 m3/s (62,860 cu ft/s) |
| - min | 0 m3/s (0 cu ft/s) |
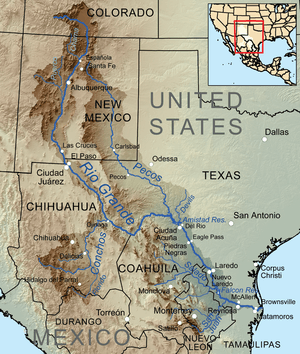 Map of the Rio Grande watershed, showing the Rio Salado joining the Rio Grande south of Laredo. | |
The Río Salado, also Río Salado de los Nadadores,[1] or Salado River, is a river in northern Mexico, a tributary of the Rio Grande (Río Bravo). Its basin extends across the northern portion of Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, and Tamaulipas states.
It originates in the Sierra Madre Oriental in Coahuila and flows east-northeastward. It is joined by the Rio Sabinas in the reservoir created by the Venustiano Carranza Dam. The Salado flows southeast from the reservoir through northern Nuevo León and northwestern Tamaulipas, where it is joined by the Sabinas Hidalgo River, to join the Rio Grande in the Falcón Reservoir, at Rio Grande river kilometer 43.[2]
Economic importance
The river is used mainly for agricultural and mining activity, especially for irrigation of cotton. Fishing has been increasing because some species have been introduced as tent s, gizzard sardine, sardine largemouth bass and white bass, the water lily, among others.
Environmental impact
The river faces a number of problems related to mismanagement. There is no system to regulate the exploitation of resources found there. It is not known what kind of species exist there or that amount, which could be on the verge of a catastrophe, well water is used as a resource for subsidy when there is scarcity of rain in the region.