Sargon II
| Sargon II | |
|---|---|
| King of Assyria, Babylonia, Akkad and Sumer | |
 Sargon II with a dignitary, bas-relief from Khorsabad. | |
| Reign | 722 – 705 BC |
| Predecessor | Shalmaneser V |
| Successor | Sennacherib |
| Born |
ca. 765 BC Kalhu |
| Died |
705 BC lost in battle against the Tabal kingdom in Anatolia |
| Spouse |
Ra'īma Atalyā |
| Issue |
Sennacherib Aḥāt-Abīšā At least 2 other sons |
| Dynasty | Sargonid dynasty |
| Father | Tiglath-Pileser III |
| Mother | Yabā/Banītu |
Sargon II (Assyrian Šarru-ukīn (LUGAL-GI.NA 𒈗𒄀𒈾); Aramaic סרגן ;[1] reigned 722 – 705 BC) was an Assyrian king. A son of Tiglath-Pileser III, he came to power relatively late in life, possibly by usurping the throne from his older brother, Shalmaneser V.
The Neo-Assyrian pronunciation of the name was presumably /sargi:n(u)/ or /sarga:n(u)/; the spelling Sargon is based on the Biblical form of the name (סרגון), mentioned in Isaiah 20:1.[2] The regnal number is modern, applied for disambiguation from the Old Assyrian king Sargon I and the still-older Akkadian ruler Sargon the Elder.
Early reign
Sargon II was a son of Tiglath-Pileser III and appears to have seized the throne from his brother, Shalmaneser V in a violent coup.[3] Sargon was already middle-aged when he came to the throne, and was assisted by his son, the crown prince, Sennacherib.[4] Sargon's brother, Sinahusur, served as his grand vizier.[5]
Military campaigns
Sargon was beset with widespread rebellions by the beginning of his rule. Marduk-apla-iddina II, a chieftain of the Chaldean tribes in the marshes of the south, declared himself king of Babylon and was crowned king in 721 BC. In 720 BC, Sargon and Marduk-apla-iddina met in battle on the plains east of Babylon. Marduk-apla-iddina was supported by Elam. The Elamite troops were able to push back the Assyrian army, and he retained control of the south and the title of king of Babylon.[4]
In 717 BC, the Syro-Hittite city of Carchemish on the Upper Euphrates rebelled. Carchemish was a small kingdom situated at an important Euphrates crossing. Sargon violated existing treaties in attacking the city, but with the wealth seized was able to continue to fund his army.[4]
In 716 BC he moved against the Mannaeans, where the ruler Aza, son of Iranzu, had been deposed by Ullusunu with the help of the Urartuans. Sargon took the capital Izirtu, and stationed troops in Parsuash (the original home of the Persian tribe, on lake Urmia) and Kar-Nergal (Kishesim). He built new bases in Media as well, the main one being Harhar which he renamed Kar-Sharrukin. In 715 BC, others were to follow: Kar-Nabu, Kar-Sin and Kar-Ishtar — all named after Babylonian gods and resettled by Assyrian subjects.
The eighth campaign of Sargon against Urartu in 714 BC is well known from a letter from Sargon to the god Ashur (found in the town of Assur, now in the Louvre) and the bas-reliefs in the palace of Dur-Sharrukin. The reliefs show the difficulties of the terrain: the war-chariots had to be dismantled and carried by soldiers (with the king still in the chariot); the letter describes how paths had to be cut into the intractable forests. The campaign was probably motivated by the fact that the Urartians had been weakened by incursions of the Cimmerians, a nomadic steppe tribe. One Urartian army had been completely annihilated, and the general Qaqqadanu taken prisoner.[6]
After reaching Lake Urmia, he turned east and entered Zikirtu and Andia on the Caspian slopes of the Caucasus. When news reached him that king Rusas I of Urartu was moving against him, he turned back to Lake Urmia in forced marches and defeated a Urartian army in a steep valley of the Uaush (probably the Sahend, east of Lake Urmia, or further to the south, in Mannaea country), a steep mountain that reached the clouds and whose flanks were covered by snow. The battle is described as the usual carnage, but King Rusas managed to escape. The horses of his chariot had been killed by Assyrian spears, forcing him to ride a mare in order to get away, very unbecoming for a king.
Sargon plundered the fertile lands at the southern and western shore of Lake Urmia, felling orchards and burning the harvest. In the royal resort of Ulhu, the wine-cellar of the Urartian kings was plundered; wine was scooped up like water. The Assyrian army then plundered Sangibuti and marched north to Van without meeting resistance, the people having retreated to their castles or fled into the mountains, having been warned by fire-signals. Sargon claims to have destroyed 430 empty villages.
After reaching Lake Van, Sargon left Urartu via Uaiaish. In Hubushkia he received the tribute of the "Nairi" lands. While most of the army returned to Assyria, Sargon went on to sack the Urartian temple of the god Haldi and his wife Bagbartu at Musasir (Ardini). The loot must have been impressive; its description takes up fifty columns in the letter to Ashur. More than one ton of gold and five tons of silver fell into the hands of the Assyrians; 334,000 objects in total. A relief from Dur-Sharrukin depicted the sack of Musasir as well (which fell into the Tigris in 1846 when the archaeologist Paul-Émile Botta was transporting his artifacts to Paris). Musasir was annexed. Sargon claims to have lost only one charioteer, two horsemen and three couriers on this occasion. King Rusa was said to be despondent when he heard of the loss of Musasir, and fell ill. According to the imperial annals, he took his own life with his own iron sword.
In 713 BC, Sargon stayed at home; his troops took, among others, Karalla, Tabal and Cilicia. Persian and Mede rulers offered tribute. In 711 BC, Gurgum was conquered. An uprising in the Philistine city of Ashdod, supported by Judah, Moab, Edom and Egypt, was suppressed, and Philistia became an Assyrian province.
Conquest of Israel
Under his rule, the Assyrians completed the defeat of the Kingdom of Israel, capturing Samaria after a siege of three years and exiling the inhabitants. This became the basis of the legends of the Lost Ten Tribes. According to the Bible, other people were brought to Samaria, the Samaritans, under his predecessor Shalmaneser V (2 Kings 18). Sargon's name actually appears in the Bible only once, in the Book of Isaiah,[7] which records the Assyrian capture of Ashdod in 711 BC.
Campaign against Babylonia
In 710 BC Sargon felt safe enough in his rule to move against his Babylonian arch-enemy Marduk-apla-iddina II. One army moved against Elam and its new king Shutur-Nahhunte II to prevent them from supplying aid to Marduk-apla-iddina; the other, under Sargon himself, proceeded against Babylon. Sargon first moved against Dūr-Athara which he renamed Dūr-Nabû and made the capital of the new province of Gambalu. He then laid siege to Babylon, and Marduk-apla-iddina II fled. Sargon claimed that he entered Babylon at the request of the priests and civil servants.[8] Babylon yielded to Sargon and he was proclaimed king of Babylonia in 710, thus restoring the dual monarchy of Babylonia and Assyria. He remained in Babylon for three years; in 709 BC, he led the new-year procession as king of Babylon.
Marduk-apla-iddina attempted to flee to Elam but the king forbade him entry. Taking hostages from Ur, Uruk, and other towns, he went to his ancestral city of Dūr-Jakin which he further fortified by adding to the walls and digging a canal from the Euphrates to flood the surrounding area. In 709 BC Sargon's troops gained a victory outside the city but could not take Dūr-Jakin, where Marduk-apla-iddina had fled. A negotiated settlement was reached whereby Sargon would spare Marduk-apla-iddina's life provided the city walls were demolished. It is not clear whether they were, since two years later, Sargon returned to take them down himself.[8]
Sargon had his son, crown-prince Sennacherib, married to the Aramean noblewoman Naqi'a, and stayed in the south to pacify the Aramaic and Chaldean tribes of the lower Euphrates as well as the Suti nomads. Some areas in Elam were occupied as well.
Later reign
In 710 BC, the seven Greek kings of Ia' (Cyprus) had accepted Assyrian sovereignty; in 709, Midas, king of Phrygia, beset by the nomadic Cimmerians, submitted to Assyrian rule and in 708 BC, Kummuhu (Commagene) became an Assyrian province. Assyria was at the apogee of its power. Urartu had almost succumbed to the Cimmerians, Elam was weakened, Marduk-apla-iddina II was powerless, and the Egyptian influence in the Levant had been thwarted.
Building projects


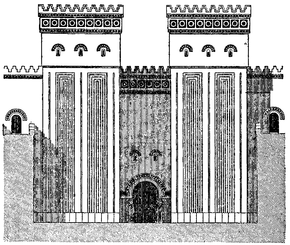
Dur-Sharrukin ("Fort Sargon") was constructed as a new capital city by Sargon II shortly after he came to the throne in 721 B.C.[5] The city measured about a square mile in area. It was enclosed within a great wall of unbaked brick pierced by seven gates. Protective genies were placed on either side of these entrances to act as guardians.[9] The palace was richly decorated with relief-carved stone slabs.
The land in the environs of the town was taken under cultivation, and olive groves were planted to increase Assyria's deficient oil production. The town was of rectangular layout and measured 1760 by 1635 m. The length of the walls was 16,283 Assyrian units, corresponding to the numerical value of Sargon's name. The town was partly settled by prisoners of war and deportees under the control of Assyrian officials, who had to ensure they were paying sufficient respect to the gods and the king. The court moved to Dur-Sharrukin in 706 BC, although it was not completely finished.
Death
In 705 BC, Sargon fell while driving the Cimmerians from Ancient Iran, where they were attacking Sargon's Persian and Median vassals. They later ravaged the kingdoms of Urartu and Phrygia, before being finally subdued by the Assyrians. Sargon was succeeded by his son Sennacherib (Sin-ahhe-eriba).[3]
See also
References
- ↑ References to Sargon II are mostly spelled logographically, as LUGAL-GI.NA or LUGAL-GIN, but occasional phonetic spelling in ú-kin appears to support the form Šarru-ukīn over Šarru-kēn(u) (based on a single spelling in -ke-e-nu found in Khorsabad). The name of the Old Assyrian king Sargon I is spelled as LUGAL-ke-en or LUGAL-ki-in in king lists. In addition to the Biblical form (סרגון), the Hebrew spelling סרגן has been found in an inscription in Khorsabad, suggesting that the name in the Neo-Assyrian period might have been pronounced Sar(ru)gīn, the voicing representing a regular development in Neo-Assyrian. Eckart Frahm, "Observations on the Name and Age of Sargon II and on Some Patterns of Assyrian Royal Onomastics", NABU 2005.2, 46–50.
- ↑ 5623. Sargon, Strong's Concordance.
- 1 2 "Sargon II, King of Assyria (721-705 BC)", The British Museum
- 1 2 3 Radner, Karen "Sargon II, king of Assyria (721-705 BC)", Assyrian empire builders, University College London, 2012
- 1 2 "Excavations At Khorsabad", The Oriental Institute, University of Chicago
- ↑ The Cimmerians were mentioned a number of times in letters by the crown-prince Sennacherib, who ran his father's intelligence service. They cannot be dated exactly, but are believed to have been composed before 713 BC. The letters relate how Sargon crossed the Great Zab and the Little Zab and moved over the mountains of Kullar in the direction of Lake Urmia, crossing the country of Zikirtu, whose ruler Metatti had fled to Uishdish, the provinces of Surikash, Allabria and parts of Parsuash.
- ↑ Isaiah 20:1
- 1 2 Van Der Spek, R., "The Struggle of King Sargon II of Assyria Against the Chaldaean Meradoch-Baladan (710-707 BC)", Jaarberecht, No.25, Leiden (1977-78)
- ↑ "Winged human-headed bull", Department of Near Eastern Antiquities: Mesopotamia, Louvre
Bibliography
- Victor Avigdor Hurowitz, ""Shutting Up" the Enemy: Literary Gleanings from Sargon's Eighth Campaign," in Mordechai Cogan and Dan'el Kahn (eds), Treasures on Camels' Humps: Historical and Literary Studies from the Ancient Near East Presented to Israel Eph'al (Jerusalem, Magnes Press, 2008),
- Albert Ten Eyck Olmstead (1906). Western Asia in the days of Sargon of Assyria.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sargon II. |
| Preceded by Shalmaneser V |
King of Assyria 722 – 705 BC |
Succeeded by Sennacherib |
| Preceded by Marduk-apal-iddina II |
King of Babylon 710 – 705 BC su |