Solitomab
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Bi-specific T-cell engager |
| Source | Mouse |
| Target | EpCAM |
| Clinical data | |
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1005198-65-1 |
| ChemSpider | none |
| UNII |
ZQQ51B5708 |
Solitomab (INN) (MT110) is an artificial bispecific monoclonal antibody that is being investigated as an anti-cancer drug. It is a fusion protein consisting of two single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) of different antibodies on a single peptide chain of about 55 kilodaltons. One of the scFvs binds to T cells via the CD3 receptor, and the other to EpCAM as a tumor antigen against gastrointestinal, lung, and other cancers.[1][2][3]
Mechanism of action
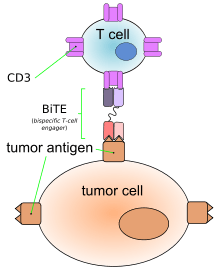
Like other bispecific antibodies, and unlike ordinary monoclonal antibodies, solitumab forms a link between T cells and its target tumor cell antigen. This causes T cells to exert cytotoxic activity on tumor cells by producing proteins like perforin and granzymes, independently of the presence of MHC I or co-stimulatory molecules. These proteins enter tumor cells and initiate the cell's apoptosis.[1][4] This action mimics physiological processes observed during T cell attacks against tumor cells.[4]
References
- 1 2 Helwick, Caroline (1 June 2008). "Novel BiTE antibody mediates contact between T cells and cancer cells". Oncology NEWS International. 17 (6).
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00635596 for "Phase I Study of MT110 in Colorectal Cancer (CRC), Gastrointestinal (GI) and Lung Cancer (MT110-101)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Amann, M.; d'Argouges, S.; Lorenczewski, G.; Brischwein, K.; Kischel, R.; Lutterbuese, R.; Mangold, S.; Rau, D.; Volkland, J.; Pflanz, S.; Raum, T.; Münz, M.; Kufer, P.; Schlereth, B.; Baeuerle, P. A.; Friedrich, M. (2009). "Antitumor Activity of an EpCAM/CD3-bispecific BiTE Antibody During Long-term Treatment of Mice in the Absence of T-cell Anergy and Sustained Cytokine Release". Journal of Immunotherapy. 32 (5): 452–464. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181a1c097. PMID 19609237.
- 1 2 "BiTE Antibody Platform". Micromet Inc.