Cuban dogfish
| Cuban dogfish | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Order: | Squaliformes |
| Family: | Squalidae |
| Genus: | Squalus |
| Species: | S. cubensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Squalus cubensis Howell-Rivero, 1936 | |
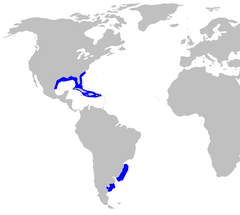 | |
| Range of the Cuban dogfish (in blue) | |
The Cuban dogfish (Squalus cubensis) is a dogfish, a member of the family Squalidae in the order Squaliformes. It is found in the Western Atlantic from North Carolina to Florida, in the Gulf of Mexico, around Cuba, Hispaniola, southern Brazil, and Argentina. It inhabits continental shelves and uppermost slopes at depths from 60 to 380 m. Its length may reach 110 cm.[1]
It is a slim, gray shark with black tips to its dorsal fins black and at the edges of its pectoral fins, its pelvic and caudal fins are white; It possess a spine at front edge of each of its two dorsal fans. It probably feeds on bottom fishes and invertebrates. The isopod parasites which commonly infest the mouth and gills of marine fish are unusually large in the Cuban dogfish. Its reproduction is ovoviviparous, with 10 pups in a litter. It is not generally used for food, but taken commercially for the oil and vitamins extracted from its liver.[1][2]
 Body
Body Head
Head Jaws
Jaws Upper teeth
Upper teeth Lower teeth
Lower teeth
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Squalus cubensis. |
- 1 2 3 Monzini, J. (2006). Squalus cubensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2006.RLTS.T61416A12476876.en
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2006). "Squalus cubensis" in FishBase. Sept 2006 version.
