Temasek Holdings
|
| |
| Investment company / Sovereign wealth fund | |
| Industry | Investment Management |
| Founded | 1974 |
| Headquarters | Singapore |
Key people |
Lim Boom Heng ,[1] Chairman Ho Ching,[1] Executive Director & CEO |
| Revenue |
|
|
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Owner | Government of Singapore |
| Subsidiaries | |
| Website |
www |
Temasek Holdings Private Limited (abbreviated as Temasek) state-owned holding company that can be characterized as a National Wealth Fund owned by the Government of Singapore. Incorporated in 1974, Temasek owns and manages a net portfolio of S$242 billion[3] (US$180 billion; as of 31 March 2016), mainly in Singapore and Asia.[4] It is an active shareholder and investor, and its portfolio covers a broad spectrum of sectors including financial services, telecommunications, media and technology, transportation and industrial, life sciences, consumer, real estate, as well as energy and resources. Temasek has a multinational team of over 580 people, in 11 offices globally including Singapore [5] and New York.[6]
Temasek is commonly referred to as a sovereign wealth fund, particularly by the press and research outlets based outside Singapore.[7] However, it has frequently disputed this terminology, and prefers to be referred to as an investment company, because it invests mostly in equities, is the outright owner of many assets, and pays taxes like other commercial investment firms.[8] However, its sole shareholder (to which it distributes dividends) is Singapore's Ministry of Finance. A spokesman for the Ministry of Finance has previously noted that even though "there is still no universally accepted definition of sovereign wealth funds", Temasek is required to abide by international guidelines for sovereign wealth funds.[9] Beginning in 2015, capital gains from Temasek are included in Singapore's government budget, contributing approximately S$3 billion [10] to the 2015 budget.
Apart from Temasek, the Government of Singapore owns another sovereign wealth fund: GIC Private Limited, which manages an estimated US$330 billion and is funded by Singapore's foreign reserves.
Temasek is one of a few global firms assigned with the highest overall corporate credit ratings of "AAA" by Standard & Poor's[11] and "Aaa" by Moody's.[12] Temasek has also attained perfect quarterly scores[13] on the Linaburg-Maduell Transparency Index, a measure of the openness of government-owned investment funds. However, the purported difficulty in measuring transparency of sovereign wealth funds should mean that the existence of such an index itself is highly questionable.[14]
History
Incorporation
At the point of Singapore's independence in August 1965, the Government of Singapore had ownership or joint ownership of various local companies, such as Malaysia-Singapore Airlines (later split up into Malaysia Airlines and Singapore Airlines) and the Singapore Telephone Board (which became Singapore Telecommunications). As part of its push for local and foreign private investment in sectors such as manufacturing and shipbuilding, the government's Economic Development Board (EDB) also bought minority stakes in a variety of local companies.[15] During the first ten years after independence, the government acquired or established several companies,[16] such as the Keppel Corporation (originally Keppel Shipyard, taken over from the Royal Navy after the British military withdrawal from Singapore), ST Engineering (originally a weapon manufacturer set up to supply the Singapore Armed Forces), and the shipping company Neptune Orient Lines.
In 1974, Temasek was incorporated under the Singapore Companies Act[17] to hold and manage the assets previously held directly by the Singapore government. The goal was for Temasek to own and manage these investments on a commercial basis,[18] allowing the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Trade and Industry to focus on policymaking. Temasek's established mission was to contribute to Singapore's economic development, industrialisation, and financial diversification by nurturing effective and commercially driven strategic investments in and around Singapore.
Status
Temasek is a company incorporated in Singapore, and operates under the provisions of the Singapore Companies Act. It is neither a government agency nor a statutory board. Like any other commercial company, Temasek pays taxes to tax authorities, distributes dividends to its shareholder and has its own board of directors and a professional management team. Its sole shareholder is Singapore's Ministry of Finance.
Temasek is designated a Fifth Schedule[19] entity under the Singapore Constitution, which imposes certain safeguards to protect the government's past reserves. For instance, the approval of the President of Singapore is required for any transaction which is likely to result in a draw-down of Temasek's cash reserves.[20] The President also has the right to appoint, terminate, or renew the members of Temasek's board of directors. In most other respects, however, Temasek operates as an independent commercial investment holding company.
In a 2009 speech,[21] Ho Ching, Temasek's Executive Director and CEO, said that the company had made an effort to instill discipline and professionalism, and to be tested and measured by providing public markers of performance. She noted that Temasek's bonds spreads and credit ratings have been regularly[22] and independently[23] monitored as public markers of Temasek's financial position and credit risks. Temasek had also openly[24] and accurately[25] disclosed its financial information through its annual report (although Ho said that, as a private company, it was not legally obliged to do so).
Initial holdings
Temasek's initial portfolio of S$354 million comprised shares in the following companies, start-ups and joint ventures previously held by the Singapore Government. The companies included a bird park, a hotel, a shoe maker, a detergent producer, naval yards converted into a ship repair business, a start-up airline, and an iron and steel mill. The companies in bold below are still within the Temasek portfolio.
- Acma Electrical Industries
- Cerebos Singapore Pte Ltd
- Chemical Industries (F.E.) Ltd
- Development Bank of Singapore Ltd (Now part of DBS Group Holdings)
- Instant Asia Cultural Shows Pte Ltd
- Insurance Corporation of Singapore Ltd
- International Development and Construction Corporation
- Intraco Ltd
- Jurong Bird Park Pte Ltd (Now part of Wildlife Reserves Singapore)
- Jurong Holdings Pte Ltd (Now part of Sembcorp Industries Ltd.)
- Jurong Shipbuilders Pte Ltd (Now part of SembCorp Marine)
- Jurong Shipyard Pte Ltd
- Keppel Shipyard Pte Ltd
- Metrawood Pte Ltd
- Ming Court Hotel Ltd (Now already part of Far East Orchard)
- Mitsubishi Singapore Heavy Industries Pte Ltd
- National Engineering Services Pte Ltd
- National Grain Elevator Ltd
- National Iron & Steel Mills Ltd
- Neptune Orient Lines
- Primary Industries Enterprises Pte Ltd (Now part of SATS Ltd.)
- Sembawang Holdings Pte Ltd
- Singapore Airlines
- Singapore Airport Duty-Free Emporium Pte Ltd (Now jointly owned by Singapore Airlines Limited and SATS Ltd.)
- Singapore Cable Car Pte Ltd
- Singapore General Aviation Service Company Pte Ltd
- Singapore National Printers Pte Ltd
- Singapore Offshore Petroleum Services Pte Ltd
- Singapore Textiles Industries Ltd
- Singapore Treasury Building Pte Ltd
- Singapore Zoological Gardens (Now part of Wildlife Reserves Singapore)
- Singmanex Pte Ltd
- Sugar Industry of Singapore Ltd
- United Industrial Corporation Ltd
- United Vegetable Oil Pte Ltd
Financial highlights
2016
Performance
- As at 31 March 2016, Temasek's net portfolio value was S$242 billion, down S$24 billion from last year and with a 60:40 underlying exposure to mature economies and growth regions.[26]
- Temasek invested S$30 billion and divested a record S$28 billion.[27]
- Temasek's one-year Total Shareholder Return (TSR) was negative 9.02% in Singapore dollar terms. Longer term 10-year and 20-year TSRs were both 6%, and TSR since inception in 1974 was 15%.[28]
- Wealth Added, which is Temasek's dollar return above aggregated risk-adjusted hurdle for the year, was negative S$44.7 billion for the year.[29]
- Temasek ended the year in a net cash position. In liquidity terms, Temasek's cash and bank balances, together with short term investments, were three times the S$8 billion debt due over the next decade.[30]
Major investments
The top three sectors for investments in 2016 were Telecommunications, Media & Technology, Financial Services and Life Sciences & Agriculture.[29] During the year, Temasek invested an additional US$500 million in Alibaba shares[31] and invested US$3 billion in Avanda Global Multi-asset Master Fund, a Singapore-based multi-strategy, global asset manager.[32]
Temasek continued to expand their financial services portfolio into non-banking sub-sectors including an investment in PayPal, a digital payment service provider operating in more than 200 markets worldwide.[33]
Temasek has also been investing in smaller but fast-growing technology-enabled companies, such as SoFi and C2FO in the US, Funding Circle in the UK, and BillDesk and Policy Bazaar in India. Within the investment brokerage space, Temasek invested about HK$2 billion in CITIC Securities, a full-service securities firm in China.[34]
In Life Sciences & Agriculture, Temasek invested US$300 million in the management buyout of China-based WuXi PharmaTech, a global provider of laboratory and manufacturing services to biopharma and medical device companies.[33]
The US accounted for Temasek's largest share of new investments during the year. In the US, Temasek increased their position in the logistics sector via a US$450 million investment in Univar, a distributor of commodity and specialty chemicals.[33]
As at 31 March 2016, in terms of geographic exposure by underlying assets, Singapore and China were highest at 29% and 25% respectively. The US is third largest at 10%.[4]
Investments
The top three sectors for investments in 2016 were Telecommunications, Media & Technology, Financial Services and Life Sciences & Agriculture.[29]
In the Telecommunications, Media & Technology space, Temasek invested an additional US$500 million in Alibaba shares[31] and, along with other top sovereign investors, invested a total of $1.5 billion in Cainiao, a data and technology-based logistics platform focused on e-commerce.[35]
In the Financial Services space, Temasek continued to expand into non-banking sub-sectors including an investment in PayPal, a digital payment service provider operating in more than 200 markets worldwide.[36] Temasek also increased their stake in Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and invested in Postal Savings Bank of China, a provider of financial services to rural, small-to-medium enterprises, and retail banking segments.[37]
In line with Temasek's theme of investing in companies with distinct competitive advantages, Temasek invested in Airbnb, a global marketplace for travel accommodation in 190 countries worldwide. Temasek has also invested in Didi Chuxing, a Chinese transportation network company; and Meituan-Dianping, an online-to-offline local service platform in China.[38] In October 2015, Temasek committed to funding Dell's merger with EMC, which, when completed, will result in one of the world's top technology vendors.[33]
As for Life Sciences & Agriculture, Temasek invested in Alvogen, an international generics pharmaceuticals company. Temasek also increased their investment in COFCO International Limited, a holding company which owns the controlling stakes in international supply chain managers Nidera and Noble Agri.[33]
In terms of geography, Asia (excluding Singapore) accounted for about 40% of Temasek's portfolio during the year, followed by Singapore with 29%.[29]
In Asia, Temasek increased their investments in the consumer sector in South Korea by investing in Homeplus, a domestic hypermarket operator with 140 stores. In India, Temasek invested in Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, a global manufacturer and distributor of branded and generic pharmaceuticals; ICICI Prudential, a life insurance company; and CarTrade, an online auto classifieds company.[39]
In Europe, Temasek made a CHF600 million investment in Switzerland-based airport retail operator, Dufry AG, to help finance its merger with World Duty Free to create one of the largest travel retailers worldwide. Temasek also continued their investments in UK real estate by acquiring a stake in Blue Fin Building, a Grade A property located in South Bank, London.[33]
Temasek's key divestments during the year include STATS ChipPAC and Cognizant Technology Solutions, Lloyds Banking Group, and Kweichou Moutai.[40]
Temasek's major investments include:
Telecommunications, Media & Technology
|
Financial Services
|
Transportations & Industrials
|
Consumer & Real Estate
|
Energy & Resources
Life Sciences & Agriculture
|
Summary of financial performance
| Performance measure | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portfolio value | S$186 bn | S$193 bn | S$198 bn | S$215 bn | S$223 bn | S$266 bn | S$242 bn |
| Total Shareholder Return (one year TSR by market value) | 42% | 4.6% | 1.50% | 8.86% | 1.50% | 19.2% | -9.02% |
| Total Shareholder Return (by market value since inception) | 17% | 17% | 17% | 16% | 16% | 16% | 15% |
| Net investments | S$4 bn | S$4 bn | S7 bn | S$7 bn | S$14 bn | S$11 bn | S$2 bn |
| Footnotes |
Timeline of investments
Based on publicly available information, Temasek's investment and divestment activities include, but are not limited to the following:
2016
- In June 2016, Temasek tendered their shares in Neptune Orient Lines (NOL) as part of the Voluntary General Offer made by CMA CGM in December 2015.[41]
- In June 2016, Temasek invested an additional US$500 million in Alibaba shares.[31]
- In January 2016, Temasek set up Mandai Safari Park Holdings to further develop concepts for the rejuvenation of Mandai and seek the appropriate approvals for the project, as well as integrate the operations of Singapore's existing nature-based attractions, under the long-standing ownership of Wildlife Reserves Singapore.[42]
- In March 2016, InnoVen, the first venture debt financing platform for high growth startup companies in India, China, and South East Asia, signed its first financing agreements in South East Asia, with loans totalling US$5 million to Malaysia-based KFit Holdings, an e-commerce health and fitness company; and Thailand-based Pomelo Fashion, an e-commerce fashion company.
- Heliconia Capital, an investment firm that focuses on growth-oriented Singapore companies, continued to deploy capital from its SME Co-Investment Fund and SME Growth Mezzanine Fund.[43]
- In 13 July 2016, ONE Championship, Asia's largest sports media property, received a significant investment from Heliconia Capital Management, a subsidiary of Temasek Holdings [44]
2015
- In February 2015, it was reported that Temasek sold 7.3 million shares in Alibaba Group Holding in the fourth quarter as the Chinese Internet firm's shares rallied following its initial public offering in September.[45]
- In February 2015, the firm entered an agreement with Industrial landlord JTC Corporation to merge four of their subsidiaries into a single platform. worth $5 billion.[46]
- In March 2015, the firm joined Hotel Properties Ltd (HL) and three other partners to buy two prime central London properties for £308 million (S$628.53 million) for a residential and office tower development.[47]
- In April 2015, the firm announced a planned investment of 9.45 billion rupees ($151.39 million) in Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd through its wholly owned subsidiary Aranda Investments.[48]
- In June 2015, it joined European private equity fund CVC to buy a controlling stake in the pharmaceutical firm Alvogen.[49]
- In June 2015, it was reported that the firm is investing $40m in Hello, a three-year-old company founded by James Proud.[50]
- In July 2015, it was reported that the firm joined Facebook co-founder in new venture capital fund, Golden Gate Ventures Fund II LP. id to take stakes in technology companies in Southeast Asia.[51]
- In October 2015, it was announced that the company has committed, as an investment partner, to the Dell acquisition offer for EMC Corporation[52]
2014
- In February 2014, it was reported that Temasek was seeking to sell its US$3.1 billion stake in the Thailand-based telecoms firm Shin Corporation and that it has approached SingTel as a potential buyer.[53] Temasek and SingTel declined comment, noting that it was not their policy to respond to market speculation.[53]
- In March 2014, Ophir Energy reported that Temasek subsidiary Pavilion Energy had acquired a 20% interest in a joint venture to exploit Blocks 1,3 and 4 offshore Tanzania, for the development of LNG resources for a total consideration of US$1.293bn.[54]
- In April 2014, Temasek made a US$5.7 billion investment for a 24.95% stake in A.S. Watson,[55] a global health and beauty retailer with over 11,600 retail outlets in Asia and Europe. Temasek also made an investment of €425 million to NN Group,[55] a Dutch insurance company.
- In May 2014, Temasek raised its stake in Olam, a global supply chain manager and processor of agricultural products and food ingredients, to 58.5% through Temasek's wholly owned subsidiary, Breedens Investments.[56]
2013
- In February 2013, Temasek invested US$300 million for a 26.1% stake of PT Matahari Putra Prima (MPPA),[57] a subsidiary of the PT Multipolar (MLPL)[58] holding company, through its indirect wholly owned subsidiary, Anderson Investments. Temasek also increased its stake in Olam[59] to 21%.
- In March 2013, Temasek bought a 5.04% stake in Repsol SA[60] (16.01 euros per share), making this Singapore's largest investment in Spain. During the same period Temasek invested in Tiger Airways, a budget carrier headquartered in Singapore,[61] in HealthCare Global Enterprises (HCG),[62] a Bangalore-based cancer care provider, and in Evonik Industries AG,[63] a German specialty chemicals company.
- In April 2013, Temasek established Pavilion Energy Pte. Ltd.[64] to invest in clean energy, especially around the LNG supply chain.
- In May 2013, Temasek increased its stake in the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC)[65] and invested in Markit,[66] a leading global financial information services company.
- In June 2013, Temasek invested in Fanatics, Inc.,[67] a US sports apparel online retailer, and in Celltrion,[68] a South Korean biotechnology firm.
- In July 2013, Temasek and Goldman Sachs jointly invested US$110 million through private placements in Chinese online literature platform Cloudary.[69] Temasek also raised its shares in CITIC Securities Co.,[70] China's largest listed brokerage firm, from 8.95% to 9.01%.
2012
- In January 2012, Temasek invested 6.85 billion rupees (US$136.12 million) in Godrej Consumer Products.[71]
- In April 2012, Temasek raised its stake in the Industrial & Commercial Bank of China Ltd. by purchasing US$2.3 billion of its Hong Kong-listed shares from Goldman Sachs Group Inc[72] and purchased almost half of the shares offered by Kunlun Energy[73] for $1.34 billion.
- In May 2012, Temasek, along with Warburg Pincus, Kelso & Company, and The Jordan Company, made an investment of up to $1.125 billion in Venari Resources, an early-stage company focused on deep water oil exploration in the Gulf of Mexico.[74] Temasek also made a S$160 million investment in the eighth largest bank in Mexico, Banco del Bajio[75] and jointly invested $468 million with RRJ Capital in Houston-based liquefied natural gas firm Cheniere Energy Inc.[76]
- In August 2012, Temasek sold its 1.4% stake in Tiger Beer maker Asia Pacific Breweries (APB) to Heineken.[77]
- In September 2012, Temasek sold a 2.5% stake (or 400 million shares) in SingTel, bringing its shares down to 51.9%.[78]
- In November 2012, Temasek raised its stake in Rio Tinto Group's Turquoise Hill Resources Ltd. (TRQ) unit to 3.7%[79] and set up Clifford Capital, a specialist finance company,[80] along with a consortium of shareholders including DBS, Standard Chartered, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corp, Manulife, and Prudential.
- In November 2012, Temasek also increased its H-share stake in China Construction Bank[81] (CCB) to 9.4%.
- In December 2012, Temasek bought a stake in a Turkish government-owned bank, Turkiye Halk Bankasi,[82] and entered into a definitive agreement with Godrej Agrovet, a subsidiary of Godrej Industries, to acquire a 19.99% stake in the company for Rs 572 crore.[83] Temasek also raised its stake in commodity trader Olam International to 19%.[84]
2011
- In January 2011, Temasek acquired a total of 65.126 million new shares (S$90 million) in Asian Citrus Holdings Limited,[85] one of the largest Chinese orange growers and tropical fruit juice suppliers.
- In February 2011, Temasek invested more than S$200 million in ACR Capital, a pan-Asia reinsurer.[86]
- In March 2011, Temasek invested over S$100 million in the first container port business trust listed on the Singapore Exchange, Hutchison Port Holdings Trust.[87]
- In May 2011, Temasek, Pfizer, Guoco Group, and the Bank of China Group Investment bought a total of $550 million shares in Shanghai Pharmaceuticals Holding Co.. Temasek also partnered with RRJ Capital and anchored a consortium that purchased a 70% stake in Frac Tech, a US-based company providing well stimulation services.
- In June 2011, Temasek partnered with Khazanah Nasional Berhad to form a 40:60 joint venture, M+S Pte Ltd, to develop landmark projects in Singapore's Marina South and Ophir-Rochor. Temasek also invested US$55 million in Hoang Anh Gia Lai, a resources and real estate conglomerate with operations in Indochina.[88]
- In September 2011, Temasek invested S$50 million in Alibaba Group,[89] China's largest e-commerce website and bought 4.4 billion shares in China Construction Bank Corp., raising its stake to 8.10%.[90]
2010
- In February 2010, Temasek injected S$210 million into Surbana to support their growth plans and took up a 4% stake in Sobha Developers, a developer in South India.[91]
- In March 2010, Temasek invested nearly $50 million in Amyris Biotechnologies Inc, the US parent of Amyris Brasil, a Brazilian company which produces biofuels and other chemicals from sugarcane.[92] Temasek also invested S$200 million in Platmin, a Canadian-listed platinum producer with assets in South Africa.[93]
- In April 2010, Temasek invested S$687 million in Inmet Mining, a Canadian copper producer with operations in six countries,[94] and invested $257.4 million for a 10% stake in Celltrion, a Korean biopharmaceutical company developing biosimilars (generic biotech drugs) for both emerging and developed markets.[95] Temasek's investment in GMR Energy[96] also gave Temasek a S$280 million exposure to India's growing power sector.
- In May 2010, Temasek invested S$240 million in India's premier multi-asset class exchange, the National Stock Exchange of India.[97] Temasek also invested S$700 million in Chesapeake Energy Corporation, the second-largest producer of natural gas in the USA.[98]
- In July 2010, Temasek partnered with Impulsora Mexicana de Desarrollos Inmobiliarios in Mexico and committed over S$100 million to pursue land banking opportunities through the joint investment Supra Terra.[99]
- In August 2010, Temasek invested S$50 million in Tudou, a Chinese online video site.[100]
- In October 2010, Temasek purchased a 14% stake in Odebrecht Oil & Gas, an upstream services provider for the oil industry, for $400 million.[101]
- In December 2010, Temasek invested in New China Life, a Beijing-based insurer.
2009
- In January 2009, Temasek sold its close to 2% stake in British bank Barclays.[102]
- In February 2009, Temasek offered new shares via the $335 million rights issue by the Indonesian Bank Danamon.[103]
- In March 2009, Temasek sold its 3.8% stake in Bank of America Corp[104] and all of its 3.26% stake in China's Minsheng Bank.[105]
- In June 2009, Temasek re-invested S$438 million in Singapore-based Olam International for a 13.8% stake.[106] Temasek also supported the planned S$1.4 billion ($972 million) rights issue by Neptune Orient Lines (NOL).[107]
- In September 2009, Temasek took up its full pro-rata 27.77% of the S$235.2 million rights issue by CitySpring Infrastructure Trust[108] and sold its stake in Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing Ltd., a maker of customised semiconductors.[109]
- In October 2009, Temasek invested $50 million in Longfor Properties Co Ltd, a real estate developer in Hong Kong,[110] and invested S$21 million (US$15million) in Li & Fung Trinity Limited, a luxury menswear retailer in Hong Kong.[111]
- In November 2009, Temasek invested S$418 million in the convertible debentures of Niko Resources, a Canadian-listed oil and gas company with assets in Asia,[112] and invested S$343 million for a 12% stake in Seoul Semiconductor, a Korean light emitting diode (LED) company.[113]
2008
- In January 2008, Temasek bought 14.5 million shares to raise its stake in Standard Chartered Bank to 19%.[114]
- In February 2008, Temasek lifted its stake in Australia's childcare provider, ABC Learning Centres, from 12.35% to 14.66%.[115]
- In March 2008, Temasek sold 55.7% of its Bank Internasional Indonesia stake to Maybank for $1.5 billion[116] and sold Tuas Power Ltd. to power producer China Huaneng Group for S$4.24 billion.[117]
- In April 2008, Temasek invested S$150 million in Lung Ming, an independent iron ore company that owns and operates the Eruu Gol iron ore mine in Mongolia.[118]
- In August 2008, Temasek sold its 60% stake in Singapore Computer Systems (SCS) for S$140 million to Singapore Telecommunications (Singtel).[119]
- In September 2008, Temasek sold Senoko Power to Marubeni-led Lion Power consortium for S$3.65 billion.[120]
- In December 2008, Temasek sold its 69.68% stake in Singapore Food Industries Limited (SFI) for S$334.5 million to Singapore Airport Terminal Services Limited (SATS).[121]
- In December 2008, Temasek sold PowerSeraya to YTL Power International for an enterprise value of S$3.8 billion.[122]
2007
- In February 2007, Temasek set up and listed the CitySpring Infrastructure Trust,[123] a yield-oriented vehicle for infrastructure investments in Asia and took advantage of the increasing depth of the debt market to introduce different risk-related securities through Astrea,[124] a special purpose vehicle holding a portfolio of investments in private equity funds.
- In May 2007, Temasek raised its stake in STATS ChipPAC[125] from 35% to 83% following a voluntary cash tender offer for the company in March 2007, thus providing greater exposure to the semiconductor sector. Temasek also completed its investment in childcare services with a 12% stake in ABC Learning Centres,[126] which operates childcare centres in Australia, New Zealand, the UK, and USA and invested in MEG Energy, one of the largest Canadian oil sands developers.
- In June 2007, Temasek invested in Russia at the initial public offering of the PIK Group,[127] an important residential real estate developer, and took a 10% stake in Minh Phu Seafood Joint-Stock Company,[128] a shrimp processor and exporter in Vietnam with exports to US, Japan, Canada, EU, and Australia. Temasek also expanded its platform in NIB Bank of Pakistan through the acquisition of the Pakistan Industrial Credit & Investment Corporation Ltd (PICIC).[129]
- In August 2007, Temasek invested in the Pacific Road Resources Fund,[130] an Australia-based specialised resources fund focused on investing in mining projects in Asia Pacific, South America and OECD economies. Temasek also invested in Indochina Capital[131] 's Vietnam-dedicated real estate funds to acquire and develop office, retail, residential, and hotel as well as resort properties.
- In China, Temasek invested over S$1.6 billion to back emerging champions such as Country Garden,[132] a property developer, Xingyu Hengdeli,[133] a luxury watch retail chain, and Yingli Green Energy,[133] a solar equipment producer. Temasek also invested in Lian Lian Holdings Ltd, a provider of low-cost platform for mobile micro-payments, and in Great Wall Airlines,[134] A 3-way joint venture between Beijing Aerospace Satellite Applications Corporation, Singapore Airlines, and Temasek.
- In India, Temasek's investments in emerging champions such as ICICI Bank[135] and BPO company Firstsource Solutions[136] complemented newer investment commitments in Tata Sky,[137] a provider of Direct-to-Home digital satellite TV services, and INX Media,[138] a new television broadcaster. Temasek also made a commitment to invest in GVK Power and Infrastructure Limited,[139] both infrastructure development companies.
2006
- In January 2006, Temasek joined a consortium of Thai investors to invest in Shin Corp[140] and co-invested with Istithmar PJSC of Dubai in Thailand's healthcare sector, each taking about 6% in Bumrungrad Hospital,[141] one of the largest hospitals in Southeast Asia.
- In March 2006, Temasek placed out 770 million SingTel ordinary shares worth over S$2 billion[142] and completed its purchase of an 11.5% stake in Standard Chartered from the Tan Sri Khoo Teck Puat Estate.[143] Temasek also participated in the restructuring of China Aviation Oil with a minority co-investment stake alongside oil major BP[144] and invested in Tata Teleservices, one of India's telecom service providers.[145]
- In March 2006, Temasek also invested some US$400 million in the E.Sun Financial Holding Company, the holding company of Taiwan's E.Sun Commercial Bank,[146] and acquired a 9.95% Stake in i-Logistics,[147] a Japanese logistics firm with core capabilities in international and multi-modal distribution services.
- In April 2006, Temasek made a follow-on investment in ICICI OneSource, one of India's leading BPO providers and expanded its exposure to infrastructure in India by partnering Reliance Energy for a 50% stake in the US$200 million Reliance India Power Fund.[148] Temasek also made a minority investment in Aptuit,[149] a contract research company providing pre-clinical development services and clinical trial materials.
- In May 2006, Temasek invested US$106 million in eMobile,[150] a Japanese wireless services provider, and completed its investment in Neumayer Tekfor, a global producer of precision automotive parts.
- In August 2006, Temasek acquired 30% of PT Chandra Asri,[151] an Indonesian producer of ethylene, a key feedstock for petrochemical products.
- In October 2006, Temasek invested in Intercell AG[152] of Austria and Vical Inc[153] of USA, both of which have platform technologies for the development of vaccines.
- In December 2006, Temasek made a substantial investment in food and beverage with a 15% stake in Fraser and Neave,[154] a Singapore-based food and beverage enterprise with significant reach in the region. Temasek also took a 9% stake in the first Vietnam-focused infrastructure fund, Vietnam Infrastructure Limited, a closed-end AIM-listed fund managed by VinaCapital.
2005
- In January 2005, Asia Financial Holdings, a wholly owned subsidiary of Temasek, acquired a 5% stake in China Minsheng Banking Corporation (Minsheng), China's first privately owned bank.
- In March 2005, Temasek's Aranda Investments acquired 5.5 million shares in Mahindra & Mahindra,[155] a utility vehicle and tractor manufacturer in India. Temasek's AFH also completed its first investment in Malaysia's banking sector, partnering Langkah Bahagia to jointly purchase a 30% stake in Malaysian Plantations,[156] the 100% shareholder of Alliance Bank Berhad. Also in March 2005, AFH made its first direct investment in Pakistan, with a 25% stake in the listed NDLC-IFIC Bank (NIB).[157]
- In April 2005, Temasek joined a US$100 million consortium led by Rolls-Royce to develop high temperature solid oxide fuel cells for one to two megawatt power systems.[158]
- In May 2005, Temasek took a 24% stake in Great Wall Airline Co.,[159] a cargo airline venture with SIA Cargo (25%) and China Great Wall Industry Corp (51%).
- In June 2005, Temasek invested $7.5 million in Apollo Healthstreet,[160] a medical business process outsourcing and IT services company that specialises in servicing US-based clients, and partnered Zuellig and Quintiles to form a pharmaceutical sales and commercialisation joint-venture, Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Holdings (APPH).[161]
- In July 2005, AFH increased its stake in NIB to 73% through a general offer to minority shareholders[162] and signed a definitive agreement with the China Construction Bank (CCB)[163] to invest US$1 billion in its upcoming Initial Public Offering (IPO).
- In August 2005, AFH purchased a 5.1% stake in CCB from the majority owner, China SAFE Investments Ltd., and announced its agreement to acquire a 10% interest in Bank of China. Temasek also invested US$1.5 billion for a 5% stake in China Construction Bank[163] and acquired an 8.3% stake in Hopson Development Holdings,[164] a developer of residential properties.
- In September 2005, Temasek took a 50% stake in SingSpring Pte Ltd,[165] a desalination facility in Singapore, and took a 5% in Kinh Do,[166] a Vietnamese confectionery maker with a 50% market share who also distributes its products into Cambodia.
- In October 2005, Temasek acquired 25% of Medreich,[167] a pharmaceutical firm which provides drug formulation and manufacturing services for a wide range of generic products to global pharmaceutical companies. Temasek also co-invested with J. W. Childs, an American private equity firm, in an investment consortium led by Osim to acquire Brookstone,[168] a specialty retailer across the USA.
- In November 2005, Temasek co-invested with Cargill in oil palm plantations in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea through a joint-venture company, CTP Holdings,[169] and committed US$10million in a venture capital fund, GSR Ventures, to fund wireless, Internet, new media, semiconductor, and other technology-rich companies in China.
- In December 2005, Temasek partnered Troika Dialog Asset Management with an initial total commitment of US$150 million to establish the Russia New Growth Fund LP to seek out investments in Russia and in countries of the former Soviet Union.[170] Temasek also participated as a cornerstone investor in the initial public offering of China's Dongfeng Motor Group.
- Also in December 2005, Temasek co-invested with Silver Lake Partners and KKR, two American private equity firms, in the US$2.7 billion carve-out of the Semiconductor Products Group of Agilent Technologies to form Avago Technologies, which manufactures analogue and optoelectronic components. Temasek also invested US$1.5 billion for a 5% stake in Bank of China.[171]
2004
- Temasek made its maiden investment in Russia, with a 3% stake in London-listed company Mobile Telesystems.[172]
- Temasek also acquired a number of small pre-IPO and IPO stakes in various emerging players, particularly in the on-line and technology space such as SOMA Networks,[173] a US-based provider of wireless broadband equipment, and Harbour Networks, a Chinese manufacturer of Internet Protocol-based next generation network equipment.
- In March 2004, Temasek made its first major direct investment in Malaysia with a 5% stake in Telekom Malaysia,[174] the country's pioneer telecommunications provider, and made its first investment in airports in the Airport Authority of Thailand.
- In April 2004, Temasek took a 19% stake in Jetstar Asia Airways, a Singapore-based low-cost carrier in partnership with Australia's Qantas Airways and two other Singapore investors.[175]
- In August 2004, Temasek increased its stake in NOL to above 30%,[176] triggering a mandatory general offer under the Singapore Code on Takeovers and Mergers. At the close of the offer on 29 September 2004, Temasek's stake in NOL was above 68%.
- At the end of September 2004, Temasek increased its stake in NOL[176] from approximately 29% to over 67% through a mandatory general offer.
- ST Telemedia, a private investment holding company part of Temasek Holdings, acquired a 62% stake in US submarine cable operator Global Crossing[177] and a 33% stake in India's Idea Cellular[178] jointly with Telekom Malaysia, and became a significant shareholder in US-listed Equinix.[179]
- In the power, energy, and natural resources fields, Temasek invested in companies such as Hyflux[180] (membrane technology for water purification) and Olam International[181] (agricultural commodity supply chain management), as part of this theme.
- In September 2003, Temasek invested US$90 million for a 16% stake in Quintiles,[182] a provider of clinical trial and commercialisation services to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Temasek also acquired a 14% stake in Matrix Laboratories[183] of India and an 8% stake in Apollo Hospital Enterprise Limited,[184] a fully integrated private healthcare services provider in India.
- In the IT sector, Temasek acquired a minority stake in ICICI OneSource,[185] a business process outsourcing company focused on the financial sector, and made an investment in Tata Consultancy Services, an IT services company.
- Temasek acquired a 3% stake in China Power International[186] at its IPO at the end of 2004.
2003
- In June 2003, Temasek used Asia Financial (Indonesia) Pte. Ltd as proxy acquired 51% of Bank Danamon[187] shares from Indonesian Bank Restructuring Agency(IBRA), during 2003 IBRA sold another 10.88% to AFI.
Governance framework
Temasek Charter
As an institution, Temasek is guided by the Temasek Charter,[188] a set of principles that guides the company's actions.
The Charter has three main principles:
1. Temasek is an active investor and shareholder.
2. Temasek is a forward looking institution.
3. Temasek is a trusted steward.
According to the first principle, Temasek "owns and manages its assets and makes investment and divestment decisions based on commercial principles with the aim of delivering sustainable value over the long term".
According to the second principle, Temasek is a "forward looking institution with a long term perspective. Through its "MERITT values" (meritocracy, excellence, respect, integrity, teamwork, and trust),[189] Temasek aims to "foster an ownership culture which aligns employee and shareholder interests".
According to the third principle, Temasek acts as "a responsible corporate citizen that safeguards its past reserves and engages people and communities based on the principles of sustainability and good governance".
Rights and obligations
As an investment company incorporated under the Singapore Companies Act, Temasek owns and manages its assets. This means that it can make business decisions relating to its portfolio with full commercial discretion under the guidance of its Board, such as increasing, holding, or decreasing its investment holdings to achieve maximum risk-adjusted returns over the long term.
Under the Singapore Constitution, Temasek is one of the key Singapore entities with constitutional safeguards to protect its past reserves.
Key companies designated under the Singapore Constitution include the Government of Singapore Investment Corporation Pte Ltd, which manages the reserves of the Singapore Government. Other designated entities with constitutional safeguards for their respective past reserves under the Singapore Constitution are statutory Boards such as the Central Provident Fund Board and the Monetary Authority of Singapore.
Owner and shareholder
Guided by business tenets, Temasek operates with full flexibility without the involvement of its shareholders, Singapore's Ministry of Finance and the President of Singapore.
Temasek is wholly owned by the Minister for Finance, who under the Singapore Minister for Finance (Incorporation) Act (Chapter 183) is a body corporate.
As such, Temasek provides annual statutory financial statements audited by an international audit firm, as well as periodic updates to its shareholder.
Temasek is a Singapore exempt private company exempted from disclosing any financial information publicly, but chooses to publish its Group Financial Summary and portfolio performance in its annual report, the Temasek Review.
Temasek also declares dividends annually, once they are deliberated and recommended by its Board for its shareholder's consideration at the annual general meeting. Temasek contributes to the Singapore Government budget via the dividends it pays to its shareholder and the tax on its profits.
The shareholder's right to appoint, reappoint, or remove Board members is subject to the President's approval, a measure put in place to safeguard the integrity of the Board and to protect the company's past reserves.
The appointment or removal of the CEO by the Board is also subject to the concurrence of the President.
Further to its normal fiduciary duties to the Company, the Board is also accountable to the President to ensure that every disposal of investment is transacted at fair market value.
Protection of Temasek's past reserves
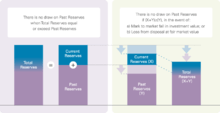
According to the Singapore Constitution, Temasek's past reserves are those accumulated before the current term of Government while its current reserves are those accumulated during the current term of Government.
This means that on the eve of the first day of each term of Government, Temasek's total reserves – comprising past reserves and current reserves as at the changeover – are locked up as past reserves for the next term of Government. This cycle repeats every time there is a change in the term of Government.
The President of the Republic of Singapore has an independent custodial role to safeguard Singapore's critical assets and past reserves. As a key institution under the Singapore Constitution, Temasek is therefore required to seek the President's approval before a draw occurs on Temasek's past reserves.
Temasek's Chairman and CEO also certify the company's Statement of Reserves and Statement of Past Reserves to the President at prescribed intervals, as part of their responsibility to protect its past reserves.
Portfolio companies
Temasek is an active investor and rebalances its portfolio from time to time. Decisions to invest, divest, or hold portfolio companies are based on Temasek's intrinsic value test.
Temasek's portfolio companies are guided and managed by their respective Boards and management, which means Temasek does not direct their business decisions or operations.
As Board directors have a fiduciary duty to safeguard the interests of their respective companies, Temasek advocates that Boards be independent of management in order to provide effective oversight and supervision of management. This includes having mostly non-executive members on Boards with the strength and experience to oversee management.
Temasek also advocates that the Chairman and CEO roles be held by separate persons, independent of each other, to ensure a balance of power for independent decision-making, and a greater capacity for management supervision by the Board.
Temasek protects its interests by exercising its shareholder rights, including voting at shareholders’ meetings when needed.
Board
Temasek's Board provides overall guidance and policy directions to its management. As at 31 August 2013, the Board comprises 10 members, the majority of whom are non-executive independent private sector business leaders.
Community engagement
Since its inception in 1974, Temasek has established 17 endowments focusing on building people, building communities, building capabilities and rebuilding lives.
The Temasek Philanthropic Platform was established in 2016 and its establishment restructured Temasek's 17 endowments into Temsaek Trust, Temasek Foundation Management Services and Temasek's six foundations.[190]
As at 2016:
More than 300,000 lives in Singapore and across Asia have been touched and more than S$2 billion has been committed to Temasek's philanthropic efforts through its six foundations.
Temasek Trust
Established in 2007, with an initial endowment of S$500 million, Temasek Trust provides financial oversight and governance of Temasek's endowment gifts as an independent trustee.[191]
Temasek Trust is responsible for ensuring disciplined and sustainable disbursements of the endowments and gifts to Temasek's six foundations. The Trust may appoint third party fund managers approved by Temasek.[192]
T-Touch
T-Touch is a volunteer initiative driven by Temasek employees to support various communities in the Singapore and globally. It is supported and supplemented by company-side programmes and initiatives, including the Temasek Community Day, which falls on the anniversary of the company's incorporation. Donations by the employees for are matched by the company.
Sponsored initiatives & events
Temasek has also seeded a number of purpose built institutions to help develop and strengthen capabilities in the financial and corporate sectors in Singapore and the rest of Asia, including the Wealth Management Institute, founded in 2003,[193] Sim Kee Boon Institute for Financial Economics. established in 2008, which focuses on education and research in the financial sector.,[194] and the Stewardship and Corporate Governance Centre, launched in 2011, which helpz companies develop succeeding generations of corporate directors .[195]
Temasek Foundation Management Services
A new entity that was established in 2016 as part of Temasek's restructuring of its philanthropic platforms, Temasek Foundation Management Services serves to drive collaboration among the foundations and provide support services for all of Temasek's foundations.[196]
Temasek Family of Six Foundations
Under the Temasek Philanthropic Platform, Temasek's Family of Six Foundations includes the following non-profit organisations (NPPOs):
Temasek Foundation International
Temasek Foundation International, formerly known as Temasek Foundation, is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and supports programmes that aim to build capabilities with programme partners in and beyond Asia. These programmes enable human and social capital development.[197]
Its areas of work are:
- Health Care, which involves the training of healthcare professionals, educators, nurses and specialists, and the upgrading of nursing curriculum, pedagogy and standards.
- Education, which involves helping communities to develop and grow by opening doors to knowledge and skills that lead to better opportunities, higher levels of employability and sustained development.
- Building Bridges, which supports networking platforms for students, leaders and opinion shapers from different countries to come together as one community to learn, share and build upon diversity of cultures.
- Building Institutions, which lends its support to regional public sector leaders through programmes that moot the exchange of ideas that shape economic development, urban development and public administration policies, regulations and systems in their respective communities.
- Rebuilding Lives, which rebuilds communities struck by disaster, mitigating the physical, mental, emotional and economic damage that follows disasters through disaster-preparedness capability programmes and post-disaster rehabilitation efforts.
- Singapore Technologies Endowment Programme (STEP) is a charity and IPC set up in 1997 that focuses on social and cultural activities, leadership, environment and innovation to build bridges and friendship, goodwill and understanding amongst youth in Asia.[198]
Temasek Foundation Cares
Temasek Foundation Cares is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and supports meaningful and innovative community-based programmes for the benefit of Singaporeans. It aims to contribute to the well-being, dignity and livelihood of needy individuals, families and communities by building people, building communities, building capabilities and rebuilding lives.[199]
Some of its featured programmes include:
- An Inclusive Future of Us, which is Temasek Cares’ signature SG50 event that engages special needs persons in building an inclusive Singapore community.
- Stay Prepared – Trauma Network for Children, which aims to enhance community-based resources to adequately provide psychosocial trauma support for children and families within the community.
- Balaji Sadasivan – Healthcare Building Capability Project, which aims to build manpower capability in the Intermediate and Long-Term Care sector to meet the needs of Singapore's ageing population.
- Ee Peng Liang – Special Needs Building Capability Project, which serves individuals with developmental, intellectual, physical, sensory or multiple disabilities.[200]
Temasek Foundation Connects
Temasek Foundation Connects is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and supports programmes which seek to build bridges and partnerships and promote dialogue and mutual understanding across international communities and markets. Its programmes promote dialogue and advance collective knowledge and mutual understanding in key areas that are important to Singapore and on a global front. The issues addressed include security, geopolitics and economic imperatives as well as best practices in areas such as corporate governance and stewardship.[201]
Under it are two endowments:
- The S Rajaratnam Endowment, which promotes development, peace and stability in Asia through programmes and partnerships targeted at business and political leaders.[202]
- Hon Sui Sen Endowment, which develops future public leaders in the financial industry in Singapore and Asia and fosters fellowship and exchange among them.[203]
Temasek Foundation Nurtures
Temasek Foundation Nurtures is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and supports programmes focused on education and professional development. Its aims are to develop talent and foster learning and growth, particularly for youths to make the leap in areas such as music, arts, sports, math and science, engineering and technology. At the core of this foundation is the belief that education is a key building block of sustainable national development and can improve the quality of lives.[204]
It oversees five endowments:
- The David Marshall Endowment seeks to cultivate talented students with the passion and gift for the arts by providing grants to institutions with a focus in the arts.
- The EW Barker Endowment provides scholarships for high-performing student athletes, overseas training and competitions that offer these students experience and exposure. It is also responsible for the School-within-a-School Programme that accommodates academic needs into a prioritised sport training programme.
- The Tay Eng Soon Endowment seeks to advance young individuals gifted in the field of science and mathematics by providing grants to institutions with a focus in mathematics and science.[205]
- The Music Endowments seek to advance music in Singapore, working with the Singapore Symphony Orchestra and the Singapore Chinese Orchestra.
- The Sunburst Scholarship offers bond-free full-time Diploma or Basic Degree scholarships to Singaporean and youth from Asia who demonstrate academic excellence, a good track record in co-curricular activities, leadership skills and participation in community/social work. These scholarships are available at Singapore polytechnics and universities.[206]
Temasek Foundation Innovates
Temasek Foundation Innovates is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and support programmes focusing on developing practical solutions for a better life through research and innovation. Its aims are to strengthen research capabilities by nurturing talents as well as encouraging multi-disciplinary programmes and inter-agency collaboration for collective capabilities.[207]
It oversees two endowments:
- The Singapore Millennium Foundation, which promotes research through the awarding of post graduate research scholarships and funding of research programmes.[208]
- The Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory, which is a research institute undertaking bio-molecular science research and applications for the benefit of people.[209]
Temasek Foundation Ecosperity
Temasek Foundation Ecosperity is a Singapore-based NPPO that funds and supports strategic and impact-driven programmes focused on championing the sustainability of the global ecosystem and the development of innovative solutions to improve liveability. Its aims are to develop enduring solutions, systems and capabilities against environmental, biological and other adversities in and beyond Singapore. It also strives to develop and nurture a vibrant ecosystem for innovation and entrepreneurship, as well as promote sustainable best practices and standards.[210]
It has piloted and developed two released projects:
- Air+ Smart Mask, released in 2013, was developed to provide N95 protection to Singapore communities, in particular children, from the harmful effects of the haze.[211]
- Airbitat Smart Cooler, unveiled in 2016, was developed as an eco-friendly cooler that uses 80% less energy than an average air conditioning unit and does not produce heat.[212]
Controversy
Shin Corp
Temasek is fully owned by Singapore's Ministry of Finance, and these close links to the government have on several occasions caused protests in foreign countries.
Temasek's 2006 acquisition of Shin Corporation, owned by the family of then Thai prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra, was particularly controversial, with protestors burning effigies of Lee and Ho on the streets of Bangkok.[213] The deal was a factor in exacerbating the Thai political crisis, which eventually led to the downfall of Thaksin and a review of the transaction's legality. The military junta that overthrew Thaksin, later tried unsuccessfully to force Temasek to divest a large part of its investment in Shin Corp.[214] As of 2015, Temasek's stake in Intouch Corporation (as Shin Corporation was renamed) had reduced to 42%.[215]
Fortune Magazine described the investment in Shin Corp as a "spectacular misjudgment"[216]
Nepotism
In 2012, Singaporean blog TR Emeritus alleged that the appointment of Ho Ching, Singapore Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong's wife, as CEO of Temasek Holdings was a case of cronyism and nepotism, which was subsequently deleted and for which they apologised.[216]
See also
References
- 1 2 "Management Team - About Temasek - Temasek". Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek Review 2016 - 404". Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek Portfolio Highlights". 7 July 2016. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- 1 2 "Temasek Review 2016 - Portfolio Highlights". www.temasekreview.com.sg. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Temasek Review 2016 Contact Us". Temasek Review 2016. 29 March 2014. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings Opens New York Office". Sovereign Wealth Fund Institute. 27 June 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ↑ "Company Overview of Temasek Holdings (Private) Limited". Bloomberg Business.
- ↑ "Temasek is different from other sovereign wealth funds and pays tax - Chairman". Venture Capital Post.
- ↑ "Guidelines for wealth funds apply to Temasek, says ministry". AsiaOne News.
- ↑ Wille, Klaus (1 March 2015). "Temasek Faces New Normal With Singapore Eying Its Funds". Bloomberg Business.
- ↑ "Standard & Poor's RatingsDirect(R)" (PDF).
- ↑ "Moody's affirms Temasek's Aaa rating".
- ↑ "Temasek hits perfect score on transparency index".
- ↑ "Singapore sovereign wealth funds – Part 1: The transparency problem".
- ↑ "About Singapore - Our History - The Sixties".
- ↑ Government-owned corporation#Singapore
- ↑ "Singapore Statues Online - 50 - Companies Act".
- ↑ "Speeches by Ho Ching, Executive Director & CEO, at the Institute of Policy Studies".
- ↑ "Singapore Statues Online - 36 - Constitution of the Republic of Singapore (Amendment No. 2) Act 1998".
- ↑ "Temasek FAQs".
- ↑ "Speeches - Media Centre - Temasek".
- ↑ "Moody's affirms Temasek's Aaa rating".
- ↑ "S&P CONFIRMS AAA RATING AS TEMASEK UPSIZES GLOBAL NOTES TO US$15 BILLION". 15 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "Tougher challenges for Temasek ahead". 17 Jul 2012.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings responds to NSP's claims". 23 August 2011.
- ↑ "Temasek reports S$24b drop in net portfolio value as of end-March". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Temasek's portfolio value declines to S$242 billion - Asia Asset Management - The Journal of Investments & Pensions". www.asiaasset.com. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Temasek assets fall first time since 2008". DealStreetAsia. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- 1 2 3 4 "Temasek Review 2016" (PDF). 7 July 2016. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek portfolio value drops 9%; first slide in 7 years". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- 1 2 3 "Temasek, GIC buy $1 billion in Alibaba stock in SoftBank sale". Reuters. 2016-06-02. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ hermesauto (2016-07-08). "Temasek puts US$3b in Avanda's hedge fund-like vehicle". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Wille, Joyce Koh Klaus. "Temasek's S$30 Billion in Deals Span Tire Makers to Pharma Firms". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Temasek to open San Francisco office as it seeks more U.S. tech investments - DealStreetAsia". DealStreetAsia. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "GIC, Temasek Lead $1.5B Funding Round In Alibaba's Cainiao Logistics - China Money Network - Daily News on China's Private Equity, Hedge Funds, and Venture Capital Industry". China Money Network. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ Lim, Kenneth. "Temasek portfolio shrinks 9% in 2016; first negative return since 2009". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ Koh, Klaus Wille Joyce. "Temasek Assets Drop First Time in Seven Years on China Rout". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ hermes (2016-07-07). "Temasek seeks 'emerging champions' in tech sector". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Singapore's Temasek remains upbeat on India even in the middle of global rough ride - The Economic Times". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ Koh, Klaus Wille Joyce. "Temasek Reshapes Holdings in New Era of Subdued Market Returns". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ hermesauto (2016-06-10). "CMA CGM offer for NOL goes unconditional as Temasek tenders its shares". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ migration (2015-01-14). "Major makeover of Mandai zoo precinct to be led by Temasek Holdings and STB". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ hermes (2016-04-08). "SMEs 'can tap expertise of private equity firms'". Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ↑ "Chatri Sityodtong: ONE Championship's Temasek Investment 'Biggest Moment In Company's History'".
- ↑ "Temasek sold 7.3 million shares in Alibaba during rally". Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "JTC, Temasek seal deal to merge four subsidiaries". Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Temasek in joint venture with Hotel Properties, other partners to buy London properties". Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Temasek to invest $150 mln in India's Glenmark Pharma". Reuters. 2015-04-17. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "CVC and Temasek to buy US$2b generic drugs firm Alvogen.". Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ Bradshaw, Tim (2015-06-15). "Tech prodigy eyes $40m in drive for sleep sensor start-up". Financial Times. ISSN 0307-1766. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Facebook co-founder, Temasek invest in Asian tech startup". Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Dell to Buy EMC in Deal Valued at About $67 Billion". Retrieved 2015-10-12.
- 1 2 Azhar, Saeed (18 Feb 2014). "Exclusive: "Temasek seeks to sell $3.1 billion stake in Thailand's Shin Corp to SingTel - sources"". Reuters. Asia. Retrieved 18 Feb 2014.
- ↑ "Completion of sale of 20% interest in Blocks 1, 3 and 4 to Pavilion Energy". Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- 1 2 "Temasek Review 2014" (PDF).
- ↑ "Temasek Review" (PDF).
- ↑ Sentana, I Made (5 February 2013). "Temasek Unit to Buy Stake in Indonesia Retailer". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Temasek subsidiary to buy 26.1% stake of Matahari". 6 February 2013.
- ↑ "Temasek now tops Olam shareholders" (PDF). 16 February 2013.
- ↑ Laya, Patricia (5 March 2013). "Repsol Sells $1.3 Billion Stake to Singapore's Temasek". Bloomberg.
- ↑ Park, Kyunghee (5 March 2013). "Tiger Air to Raise S$293.5 Million for Expansion, Repay Debt". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings invests Rs 140 crore in HealthCare Global Enterprises". The Times Of India. 11 March 2013.
- ↑ Matthews, Sheenagh (11 March 2013). "Evonik Owners Sell 4.6% Stake to Temasek Ahead of Fourth IPO Try". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Singapore sets up LNG investment firm". 6 April 2013.
- ↑ Ho, Prudence; Venkat, P.R. (21 May 2013). "Temasek Adds to ICBC Stake". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Markit Press Release".
- ↑ Bensinger, Greg (6 June 2013). "Web Sports Retailer Fanatics Inc. Tops $3 Billion Valuation". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Celltrion Media Release".
- ↑ "China's Cloudary raises $110m via private placements from Goldman Sachs and Temasek Holdings". 9 July 2013.
- ↑ "Temasek raises stake in CITIC Securities to 9.01%". 15 July 2013.
- ↑ "Temasek to invest $136 mln in Godrej Consumer Products". Reuters. 21 Jan 2012.
- ↑ Venkat, P.R.; Holmes, Sam; Steger, Isabella (16 April 2012). "Temasek Buys ICBC Stake From Goldman". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Temasek, rrj buy half of $1.3b Kunlun energy offering". April 2012.
- ↑ "Venari Resources Announces Investment. 17 August 2016" (PDF).
- ↑ "Banco de Sabadell SA Sells 20% Stake In Banco del Bajio.". 5 July 2012.
- ↑ Holmes, Sam (7 May 2012). "Temasek, RRJ Capital to Invest in Cheniere Energy". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Temasek sells APB stake to Heineken in married deal".
- ↑ "Temasek raises $1bn from SingTel stake sale". 26 September 2012.
- ↑ Donville, Christopher (14 November 2012). "Temasek Raises Stake in Copper Producer Turquoise Hill to 3.7%". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Clifford Capital to capture project finance opportunities with official launch of operations" (PDF) (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek confirms $2.8 billion CCB investment. 7 September 2102".
- ↑ Venkat, P.R.; Peker, Emre (5 December 2012). "Temasek Buys Stake in Turkish Bank". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Temasek to buy 20% stake in Godrej Agrovet". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Temasek now owns 19% stake in Olam". 3 January 2013.
- ↑ "Temasek Subscribed 5.37% of Asian Citrus. 6 January 2012.". 6 January 2012.
- ↑ "ACR Welcomes Temasek as New Shareholder" (PDF) (Press release).
- ↑ "Hutchison port holdings aims fir %5.8bn in singapore". March 2011.
- ↑ "Temasek to Invest in Hoang Anh Gia Lai's Rubber Corp. 8 June 2011.". 8 June 2011.
- ↑ Chon, Gina (23 September 2011). "Alibaba Gets $1.6 Billion Investment". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ Koh, Joyce (6 September 2011). "Temasek Holdings Spends $2.8 Billion for Shares in China Construction Bank". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Sobha says promoter sells 4 pct to Temasek Holdings". Reuters. 8 February 2010.
- ↑ "AMYRIS SECURES INVESTMENT FROM TEMASEK HOLDINGS" (press release)
- ↑ "Temasek Invests in Chesapeake, Spends $1.2 Billion on Resources.". 12 May 2010.
- ↑ "Temasek invests heavily in Inmet Mining to fund big Panama copper project". 1 April 2010.
- ↑ "Temasek acquires 10% stake in celltrion.". 22 April 2010.
- ↑ "Temasek to invest $200 mn in GMR Energy". 9 April 2010.
- ↑ "Temasek buys NYSE's stake in Mumbai bourse".
- ↑ "Temasek Invests in Chesapeake as Part of $1.2 Billion Spent on Resources". Bloomberg. 12 May 2010.
- ↑ Klemming, Lars (28 July 2010). "Temasek, IMDI Form $200 Million Venture to Invest in Real Estate in Mexico". Bloomberg.
- ↑ Chao, Loretta (5 August 2010). "China's Tudou.com raises $50 million". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ Millard, Peter (20 October 2010). "Temasek Buys Stake in Odebrecht Unit in Emerging Markets Plan". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Temasek sold Barclays stake at loss". Reuters. 3 June 2009.
- ↑ "Bank Danamon outlines$335 million rights issue". 20 February 2009.
- ↑ "Temasek Counts the Cost of Merrill Stake.". 18 May 2009.
- ↑ "Temasek Said to Have Sold Entire Stake in China Minsheng Bank". Bloomberg. 9 March 2009. Archived from the original on 16 February 2012.
- ↑ "Temasek invests in commodity firm Olam" (PDF). 2 June 2009.
- ↑ "NOL plans $972 million rights to cut debt, build warchest.". 1 June 2009.
- ↑ "CitySpring Infrastructure Trust: Finally calls for cash".
- ↑ "Temasek profit falls record 66% as bank values drop.". 17 September 2009.
- ↑ "Longfor Properties IPO raises HK$7.07b". 13 November 2009.
- ↑ "Big names back small Trinity listing.". 10 October 2009.
- ↑ "Niko Closes Black Gold Acquisition" (PDF) (Press release).
- ↑ "UPDATE 1-Temasek to buy $242 mln stake in S.Korea LED firms". Reuters. 3 November 2009.
- ↑ "Temasek raises Standard Charted stake to 19%. Asiaone.". 29 January 2008.
- ↑ "Sinagpore's Temasek lifts its stake in ABC Learning". AAP. 28 February 2008.
- ↑ "Maybank Bids $1.5B For Majority In Bank Internasional Indonesia". Forbes. 26 March 2009.
- ↑ "Huaneng buys Singapore's Tuas Power for $3 billion". Reuters. 14 March 2008.
- ↑ "Goldman's Fang makes first private equity investment 2008.". 30 April 2008. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- ↑ "SingTel invests $99 mln in Singapore Computer Systems". Reuters. 24 August 2008.
- ↑ "Consortium led by Marubeni to buy Senoko Power of Singapore". The New York Times. September 2008.
- ↑ "SATS ANNOUNCES CONDITIONAL ACQUISITION OF SFI" (PDF) (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek Shelves PowerSeraya Auction". The New York Times. 26 November 2008.
- ↑ "Singapore's new taste for infrastructure funds". 23 October 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek review 2007 – Creating Value." (PDF). 5 February 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- ↑ De Clercq, Geert (18 May 2007). "STATS ChipPAC says Temasek acquired 83 pct of firm". Reuters.
- ↑ "Temasek buys 12% of ABC". The Sydney Morning Herald. 30 May 2007.
- ↑ "Wall Street Folly Headline Roundup - 8/27/07 - $1.8B hair cut for HD; Nasdaq's LSE suitors; Merrill pointing Russian listings to LSE; Google economist on economic slowdown; Acer buying Gateway; Goldman buying Tokyo Tiffany RE; US Steel buying Stelco". 27 August 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings Acquires 10 Per Cent Stake in Minh Phu Seafood Joint-Stock Company" (Press release).
- ↑ "NIB Bank acquires PICIC for Rs20.5bn". 1 July 2007.
- ↑ "Pacific Road Resources boss shows no signs of slowing". The Australian. 1 October 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek review 2007 – Creating Value." (PDF). 17 August 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek review 2007 – Creating Value." (PDF). 11 December 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- 1 2 "Temasek eyes residential real estate, renewable energy sectors". 7 August 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek to boost returns in China". 5 September 2006.
- ↑ "ICICI Bank - Shareholding Details after FPO".
- ↑ "First Source makes pre-IPO placement to two US firms". The Times Of India. 5 January 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek buys 10% in Tata Sky". The Times Of India. 6 January 2007.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings invests in Indian TV venture". The Times Of India. 15 March 2007.
- ↑ "GVK plans to merge group firms into umbrella company". The Times Of India. 7 August 2006.
- ↑ "Temasek-SCB led investor group acquires Shinawatra and Damapong Families' stakes in Shin Corp" (Press release).
- ↑ "Istithmar and Temasek Invest in Bumrungrad" (Press release).
- ↑ "Liquidity of SingTel Stock Further Enhanced Temasek offer of SingTel shares" (Press release).
- ↑ Olson, Parmy (28 March 2006). "Ho Ching's Temasek Buys Standard Chartered Stake". Forbes.
- ↑ "China Aviation rescue plan agreed". BBC News. 3 March 2006.
- ↑ "Singapore's Temasek buys stake in Tata Teleservices". 8 March 2006.
- ↑ "E.Sun partners with Temasek Holdings". 15 March 2006.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings Acquires a 9.95% Stake in i-Logistics" (Press release).
- ↑ "Reliance, Temasek to launch India power fund". 26 July 2004.
- ↑ "Aptuit Secures Additional Private Equity Funding, Bringing Potential Capital Available to More Than $750 Million"(press release)
- ↑ "eMobile completed 27.3 billion yen additional equity financing to reach a total of 143.2 billion yen and secured over 360 billion yen capital through equity and debt financing; Temasek Holdings to become the third largest shareholder of eMobile" (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek review 2006 – Managing for Value." (PDF). 14 August 2006. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Temasek portfolio crosses US$100 billion mark" (Press release).
- ↑ "Vical Scores $25M". 19 October 2006.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings (Private) Limited announces investments in Fraser & Neave Limited". 18 March 2016 revisited.
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings' Subsidiary Acquires 5.5 million M&M Shares" (Press release).
- ↑ "Langkah Bahagia and Duxton Investments Invest in MPlant" (Press release).
- ↑ "NIB Bank Announced AFH has acquired 25% of the shareholding of NIB" (Press release).
- ↑ "Rolls-Royce and Singapore Partners to Invest in Fuel Cells" (Press release).
- ↑ "China Great Wall Industry Corporation, Singapore Airlines Cargo and Dahlia Investments to Form Joint Venture Cargo Airline in China" (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek arm, One Equity to invest $7.5m in Apollo Health Street". 2 May 2005.
- ↑ "Interpharma, Quintiles and Temasek to Form Pharma Commercialization Joint Venture in Asia Pacific With US$112 Million Investment Fund" (Press release).
- ↑ "Singapore Equity Raises Stake in NIB to 72.6%" (Press release).
- 1 2 "China Construction Bank and Temasek Established Strategic Partnership in Beijing" (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek Holdings (Private) Limited announces investments in Fraser & Neave Limited.". Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Divestment of 50% Equity in SingSpring Pte Ltd" (Press release).
- ↑ "Kinh Do stocks begin trading". 13 December 2005.
- ↑ "Temasek buys 25% in Medreich for Rs 109 cr". The Times Of India. 15 October 2005.
- ↑ "This Chairmaker Sure Isn't Sitting Back". 16 October 2005.
- ↑ "Cargill and Temasek Holdings Invest in Palm Plantations in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea" (Press release).
- ↑ "Troika Dialog and Temasek Holdings Announce Launch of New Private Equity Fund for Russia and CIS" (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek to buy 5% of Bank of China - report". 26 December 2005.
- ↑ "Amtel Holland Holdings N.V. Is Pleased to Announce That It Has Closed A Round of Private Equity Capital Totaling US$ 70 million" (Press release). 30 June 2005.
- ↑ "SOMA Networks Raises $50 Million in Financing Led by Temasek Holdings and Morgan Stanley Venture Partners" (Press release).
- ↑ "Telekom Malaysia looks east". 18 December 2004.
- ↑ "Temasek media centre" (Press release). Temasek.
- 1 2 "Close of Temasek's offer for NOL" (Press release).
- ↑ "Global Crossing Emerges From Chapter 11; ST Telemedia and Global Crossing Complete Investment" (Press release).
- ↑ "IDEA, STT-TM deal finalised" (Press release).
- ↑ "Wall Street Drought Ends for Hosting Companies". 24 November 2003.
- ↑ "Divestment of 50% Equity in SingSpring Pte Ltd.". 11 January 2003. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Investing in Value – Temasek Review". 18 March 2016 revisited.
- ↑ "Temasek Invests US$90 Million in Quintiles" (Press release).
- ↑ "Matrix Laboratories Limited today signed definitive agreements with India Newbridge Investments Limited and Maxwell (Mauritius) Pte Limited" (Press release).
- ↑ "Temasek picks up stake in Apollo Hospitals". The Times Of India. 30 July 2004.
- ↑ "ICICI OneSource Raises Fresh Capital" (Press release).
- ↑ "China Power makes sharp IPO trading debut". 16 October 2004.
- ↑ "Bank Danamon Annual report(2003)"
- ↑ "Temasek Charter: Context". 18 March 2016 revisited.
- ↑ Temasek MERITT Values, accessed October 2013.
- ↑ "Temasek reorganizes philanthropic efforts into six new foundations". www.dealstreetasia.com. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek launches new philanthropic platform". Channel NewsAsia. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Trust". www.temasektrust.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Wealth Management Institute - About Us". accessed 18 March 2016
- ↑ Sim Kee Boon Institute for Financial Economics, Vision and Mission, accessed October 2013.
- ↑ "Stewardship Asia – About". Accessed 18 March 2016.
- ↑ hermesauto (2016-09-06). "Temasek reorganises its philanthropic organisations to better serve community". The Straits Times. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation International". www.temasekfoundation-international.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation International". temasekfoundation-international.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Cares". www.temasekfoundation-cares.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Cares - Building Community". www.temasekfoundation-cares.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Connects". www.temasekfoundation-connects.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "S Rajaratnam Endowment". www.srajaratnamendowment.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Review 2016 - Community Stewardship". www.temasekreview.com.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Nurtures". www.temasekfoundation-nurtures.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "News Releases - Media Centre - Temasek". www.temasek.com.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Nurtures Sunburst Scholarships |". www.tefsunburstscholarship.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Innovates". www.temasekfoundation-innovates.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Singapore Millennium Foundation Ltd – Singapore Millennium Foundation Ltd". www.singaporemillenniumfoundation.com.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "TLL Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory". www.tll.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Temasek Foundation Ecosperity". www.temasekfoundation-ecosperity.org.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ "Airplus". airplus-asia.com. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ hermes (2016-08-26). "Outdoor cooling system on trial at zoo". The Straits Times. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- ↑ Thailand: Protesters burn images of Lee, wife. Bangkok Post, 18 March 2006.
- ↑ Thailand Moves Against Foreign Firms, Asia Sentinel, 10 January 2007
- ↑ "Temasek Review". Temasek. 2015-07-04. Retrieved 2015-10-21.
- 1 2 "Singapore's Lee Family and Nepotism - Asia Sentinel". 24 February 2012. Retrieved 2 December 2016.