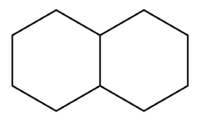
Decalin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Decahydronaphthalene[1] | |
| Other names
Bicyclo[4.4.0]decane[1] Decalin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 91-17-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38853 |
| ChemSpider | 6777 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H18 | |
| Molar mass | 138.25 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.896 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | trans: −30.4 °C (−22.7 °F, 242.7 K) cis: −42.9 °C (−45.2 °F, 230.3 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | trans: 187 °C (369 °F) cis: 196 °C (384 °F) |
| Insoluble | |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.481 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Decalin MSDS |
| Flash point | 57 °C (135 °F; 330 K) |
| 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) | |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Naphthalene; Tetralin |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Decalin (decahydronaphthalene, also known as bicyclo[4.4.0]decane),[3] a bicyclic organic compound, is an industrial solvent. A colorless liquid with an aromatic odor, it is used as a solvent for many resins or fuel additives.[4] It is the saturated analog of naphthalene and can be prepared from it by hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst. Decahydronaphthalene easily forms explosive[5] organic peroxides upon storage in the presence of air.[6][7]
Isomers
Decahydronaphthalene occurs in cis and trans forms. The trans form is energetically more stable because of fewer steric interactions. cis-Decalin is a chiral molecule without a chiral center; it has a two-fold rotational symmetry axis going through the center of the 9–10 bond, but no reflective symmetry. However, the chirality is canceled through a chair-flipping process that turns the molecule into its mirror image.
-

1: trans (left) and cis (right) isomers -
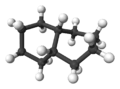 2:
2:ball-and-stick model of cis-decalin -
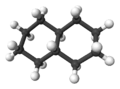 3:
3:trans-decalin -
 4:
4:cis-decalin ring-flip
trans-Decalin
-
4: Half a decalin molecule: cyclohexane in chair conformation. Axial positions are shown in red, while those in equatorial positions are in blue. -
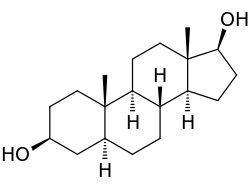
5: Androstanediol, a biomolecule with three trans fused six membered rings (and an also trans fused five membered one)
As can be seen on the model of cyclohexane, the trans configuration comes with a price: the only possible way to join the two six-membered rings in the trans position means the second ring needs to start from the two equatorial bonds of the first ring. A six-membered ring does not offer sufficient space to start out on an axial position (upwards), and reach the axial position of the neighboring carbon atom, which then will be on the downwards side of the molecule.
A second price to be paid is the effective freezing of the rings in a fixed conformation. In biology this fixation is widely used in the steroid skeleton to construct molecules that play a key role in the signaling between distantly separated cells.
See also
References
- 1 2 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 33, 394, 601. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Haynes, William M. (2010). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (91 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 3-134. ISBN 978-1439820773.
- ↑ "Dictionary.com".
- ↑ "Fuel Additive Product".
- ↑ "PDF – Surrogate JP-8 Aviation Fuel Study – Alessandro Agosta Thesis Drexel University" (PDF).
- ↑ "Inchem.org Data".
- ↑ "MSDS Sheet – JT Baker".
- ↑ "ISFuel.com Animation".