Tiber Creek
 Tiber/Goose Creek around 1800, and the modern shorelines of the Potomac River. |
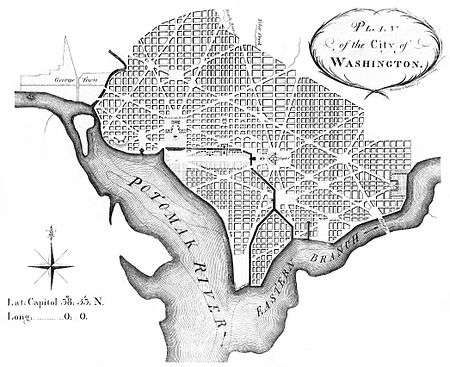 Andrew Ellicott's revision of L'Enfant's Plan, showing Washington City Canal |
Tiber Creek or Tyber Creek is a tributary of the Potomac River in Washington, D.C. In the 19th century it was modified to become part of the Washington City Canal, and subsequently was enclosed in a tunnel.
Naming and course
Originally called 'Goose Creek', it was renamed by settler Francis Pope. Pope owned a 400-acre (1.6 km2) farmstead along the banks of the creek which, in a play on his surname, he named "Rome" after the Italian city, and he renamed the creek in honor of the river which flows through that city. It was southeast of then Georgetown, Maryland, amid lands that were selected for the City of Washington, the new capital of the United States.[1] It flowed south toward the base of Capitol Hill, then west meeting the Potomac near Jefferson Pier.
History
Using the original Tiber Creek for commercial purposes was part of Pierre (Peter) Charles L'Enfant's 1791 "Plan of the city intended for the permanent seat of the government of the United States . . .".[2] The idea was that the creek could be widened and channeled into a canal to the Potomac. By 1815 the western portion of the creek became part of the Washington City Canal, running along what is now Constitution Avenue.[3] By the 1870s, however, because Washington had no separate storm drain and sewer system, the Washington City Canal was notoriously stinky. It had become an open sewer. When Alexander "Boss" Shepherd joined the Board of Public Works in 1871, he and the Board engaged in a massive, albeit uneven, series of infrastructure improvements, including grading and paving streets, planting trees, installing sewers and laying out parks. One of these projects was to enclose Tiber Creek/Washington City Canal. A German immigrant engineer named Adolf Cluss, also on the Board, is credited with constructing a tunnel from Capitol Hill to the Potomac "wide enough for a bus to drive through to put Tiber Creek underground."[4][5]
Many of the buildings on the north side of Constitution Avenue apparently are built on top of the creek, including the Internal Revenue Service Building, part of which is built on wooden piers sunk into the wet ground along the creek course. The low-lying topography there contributed to the flooding of the National Archives Building (Archives I in Washington, DC), IRS, and Ariel Rios buildings that forced their temporary closure beginning in late June 2006. In fact, until the mid-1990s, that part of Washington around the intersection of 14th Street and Constitution Avenue was an open parking lot because the underground water was too difficult to deal with. During construction of the Ronald Reagan Building (1990–98), the engineers figured out how to divert the water. But that dewatering then reduced the water level underneath the IRS building which caused the wooden piers to lose stability and part of the IRS building foundation to sink.
A pub near Tiber Creek's historic course north of Capitol Hill was named after it. The Bistro Bis restaurant now occupies the Tiber Creek Pub's former location.[6] A lock keeper's house from the Washington branch of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal remains at the southwest corner of Constitution Avenue and 17th Street, NW, near the former mouth of Tiber Creek, and the western end of the Washington City Canal.[7][8][9]
References and notes
- ↑ Source: Vlach, John Michael (Spring 2004). "The Mysterious Mr. Jenkins of Jenkins Hill: The Early History of the Capitol Site". The Capitol Dome (newsletter). Retrieved 2009-09-17. External link in
|journal=(help) - ↑ "Original Plan of Washington, D.C." U.S. Library of Congress. Accessed 2009-09-16.
- ↑ Cornelius W. Heine (1953). "The Washington City Canal." Records of the Columbia Historical Society of Washington, D.C. 53-56 (1953-56) 1-27. Now called Historical Society of Washington, DC.
- ↑ German-American Heritage Society of Washington, D.C. Accessed 2009-09-16.
- ↑ "The Tiber Creek Sewer Flush Gates, Washington, D.C.", Engineering News and American Railway Journal, February 8, 1894.
- ↑ Goldreich, Samuel (1998). "Bistro Bis succeeds Capitol Hill pub as welcoming lunch option." Washington Times. 1998-10-12.
- ↑ dcMemorials.com. Plaque beside the Lockkeeper's House marking the former location in Washington, D.C. Accessed 2009-09-16.
- ↑ HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. "Lock Keeper’s House Marker." Accessed 2009-09-16.
- ↑ Coordinates of lock keeper's house: 38°53′31″N 77°02′23″W / 38.8919305°N 77.0397498°W