Turpan water system

The Turpan water system or Turfan water system (locally called karez water system, Uyghur: كارىز, кариз, ULY: kariz) in Turpan, located in the Turpan Hollow, Xinjiang, China, is a vertical tunnel system adapted by the Turpan people. The word karez means "well" in the local Uyghur language.[1] Turpan has the Turpan Water Museum (a Protected Area of the People's Republic of China) dedicated to demonstrating its karez water system, as well as exhibiting other historical artifacts.
Turpan's well system was crucial in Turpan's development as an important oasis stopover on the ancient Silk Road skirting the barren and hostile Taklamakan Desert. Turpan owes its prosperity to the water provided by its karez well system.[2]
Description
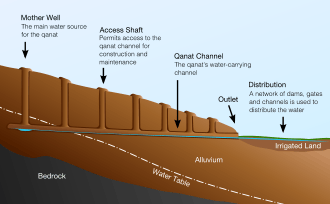
Turpan's karez water system is made up of a horizontal series of vertically dug wells that are then linked by underground water canals to collect water from the watershed surface runoff from the base of the Tian Shan Mountains and the nearby Flaming Mountains. The canals channel the water to the surface, taking advantage of the current provided by the gravity of the downward slope of the Turpan Depression. The canals are mostly underground to reduce water evaporation.[3]
The system has wells, dams and underground canals built to store the water and control the amount of water flow. Vertical wells are dug at various points to tap into the groundwater flowing down sloping land from the source, the mountain runoff. The water is then channeled through underground canals dug from the bottom of one well to the next well and then to the desired destination, Turpan's irrigation system.[3] This irrigation system of special connected wells has been claimed to originate in Iran (e.g, the qanat system), to have originated indigenously, or to have been invented in other parts of China. Both historical and archaeological research convincingly point to the origins of this technology as arriving from more western regions along with indigenous innovations.[4]
In Xinjiang, the greatest number of karez wells are in the Turpan Depression, where today there remain over 1100 karez wells and channels having a total length of over 5,000 kilometres (3,100 mi). The local geography makes karez wells practical for agricultural irrigation and other uses. Turpan is located in the second deepest geographical depression in the world, with over 4,000 km2 (1,500 sq mi) of land below sea level and with soil that forms a sturdy basin.[3] Water naturally flows down from the nearby mountains during the rainy season in an underground current to the low depression basin under the desert. The Turpan summer is very hot and dry with periods of wind and blowing sand. The water from the underground channels provides a stable water source year round, independent of season.[1]
Importance
Ample water was crucial to Turpan, so that the oasis city could service the many caravans on the Silk Route resting there near a route skirting the Taklamakan Desert. The caravans included merchant traders and missionaries with their armed escorts, animals including camels, sometimes numbering into the thousands, along with camel drivers, agents and other personnel, all of whom might stay for a week or more. The caravans needed pastures for their animals, resting facilities, trading bazaars for conducting business, and replenishment of food and water.[2]
See also
Footnotes
- 1 2 "Karez Well". www.xj.gov.cn. Retrieved 2007-09-23.
- 1 2 Boulnois, Luce (2005). Silk Road: Monks, Warriors & Merchants. Hong Kong: Odessey Books & Guides. pp. 148–149, 201. ISBN 962-217-721-2.
- 1 2 3 "Karez (Qanats) of Turpan, China". water history.org. Retrieved 2007-09-23.
- ↑ "The hydraulic systems in Turfan (Xinjiang)". The Silk Road. Retrieved 2016-09-06.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Turpan karez. |
- Satellite map showing deep basin from Google
- Link to Silk Road map
- Turpan – Ancient Stop on the Silk Road
- Karez close to Turfan
Coordinates: 42°52′23″N 89°23′53″E / 42.873°N 89.398°E

