1954 Pacific typhoon season
1954 Pacific typhoon season
| |
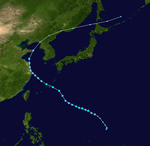
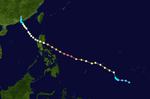
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
March 1, 1954 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 26, 1954 |
| Strongest storm1 |
Ida – 890 hPa (mbar), 280 km/h (175 mph) |
| Total depressions |
33 |
| Total storms |
19 |
| Typhoons |
15 |
| Super typhoons |
5 |
| Total fatalities |
1530 |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
| 1Strongest storm is determined by lowest pressure |
Pacific typhoon seasons
1952, 1953, 1954, 1955, 1956 |
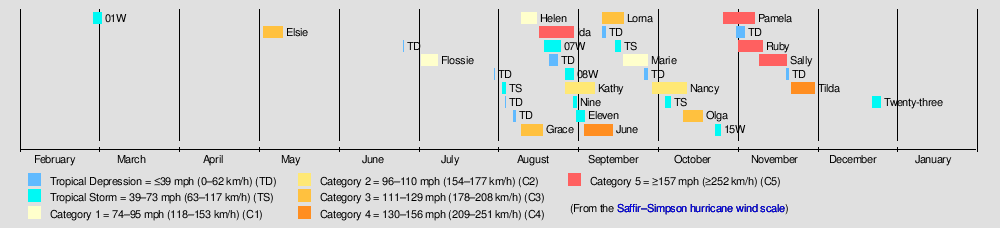
The 1954 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1954, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1954 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Fleet Weather Center on Guam.
Storms
Tropical Storm 01W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 1 – March 4 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Elsie
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 5 – May 12 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 945 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Flossie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 4 – July 10 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 985 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Grace
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 11 – August 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Grace struck the Southern Japanese islands of Kyūshū and Shikoku. 28 people were killed and 33 were missing.[1]
Typhoon Helen
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 11 – August 17 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 965 hPa (mbar) |
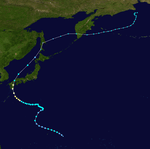
Typhoon Ida
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 18 – August 31 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 890 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm 07W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 20 – August 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm 08W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 28 – August 31 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 995 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Kathy
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 28 – September 8 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
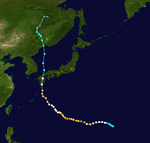
Typhoon June
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 4 – September 15 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 910 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon June struck the Southern Japanese hitting the area west of Kanto especially hard. 107 people were killed and 39 were missing.[2]
Typhoon Lorna
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 11 – September 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Lorna brushed the southern coast of the Japanese island of Shikoku. 34 people were killed and 20 were missing.[3]
Marie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 19 – September 28 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 956 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Marie had a minimum pressure of 956 mb and a maximum windspeeds of 85 mph. Marie crossed the southern islands of Kyūshū and Shikoku before turning northeast and striking Hokkaidō island. Marie caused the ship Toya Maru to sink in the Hokkaidō Strait. 1,361 people were killed and 400 were left missing.[4]
Typhoon Nancy
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 30 – October 13 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 965 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Olga
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 12 – October 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 935 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm 15W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 24 – October 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
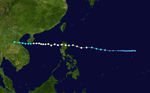
Typhoon Pamela
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 27 – November 8 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 900 hPa (mbar) |
On October 27, Typhoom Pamela formed as a tropical depression. Pamela reached a peak of 900 mbar and 175 mph on November 1 and reached a secondary peak of 935 mbars on November 5.
Pamela was one of two storms that reached Category 5 super typhoon status in the South China Sea, with the other being Typhoon Rammasun of 2014.
Typhoon Ruby
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 2 – November 11 |
| Peak intensity |
270 km/h (165 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Sally
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 10 – November 20 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 925 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Tilda
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 22 – December 1 |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
1954 storm names
- Elsie
- Flossie
- Grace
- Helen
- Ida
- June
- Kathy
- Lorna
|
- Marie
- Nancy
- Olga
- Pamela
- Ruby
- Sally
- Tilda
|
See also
References