Five Civilized Tribes

The term "Five Civilized Tribes" derives from the colonial and early federal period. It refers to five Native American nations—the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek (Muscogee), and Seminole.[1] These are the first five tribes that Anglo-European settlers generally considered to be "civilized" according to their own world view, because these five tribes adopted attributes of the colonists' culture,[2] for example, Christianity, centralized governments, literacy, market participation, written constitutions, intermarriage with white Americans, and plantation slavery practices. The Five Civilized Tribes tended to maintain stable political relations with the Europeans.
History

The Five "Civilized" Tribes were indigenous peoples of the Americas who lived in the Southeastern United States. Most were descendants of what is now called the Mississippian culture, an agrarian culture that grew crops of corn and beans, with hereditary religious and political elites. The Mississippian Culture flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from 800 to 1500. Before European contact these tribes were generally matriarchial societies. Agriculture was the primary economic pursuit. The bulk of the tribes lived in towns (some covering hundreds of acres and populated with thousands of people). These communities regulated their space with planned streets, subdivided into residential and public areas. Their system of government was hereditary. Chiefdoms were of varying size and complexity, with high levels of military organization.[3]
George Washington and Henry Knox pursued an agenda of cultural transformation in relation to Native Americans. The Cherokee and Choctaw tended, in turn, to adopt and appropriate certain cultural aspects of the federation of colonies. At the time of the Declaration of Independence, the culture of the United States as a nation was, itself, emergent. Many of the cultural practices appropriated by The Five Tribes were ones that they found useful.[4]
In the early part of the 19th Century, the US Government initiated a displacement of the existing societies living east of the Mississippi River, including The Five Tribes, to lands west of the river. This displacement initiative was dubbed the Indian Removal. The Indian Removal forced a significant number of the Five Tribes to Indian Territory in other parts of the North American continent. A significant number were displaced to the area that would, in future, become the state of Oklahoma. At the time of their removal, the tribes were suzerain nations.
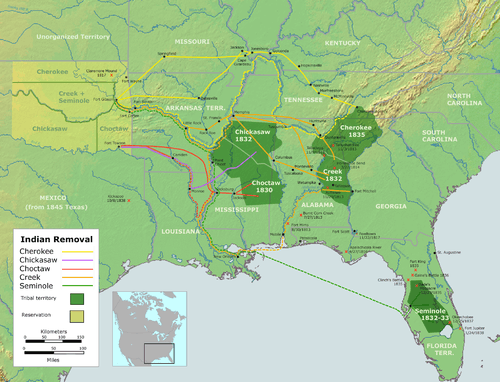
The federally legislated displacement of the tribes from their homes east of the Mississippi River took place over several decades during the series of removals, which is also known as the Trail of Tears. The territory to which they were displaced was, at the time, called Indian Territory, currently eastern Oklahoma. The most infamous removal was the Cherokee Trail of Tears of 1838, when President Martin Van Buren enforced the contentious Treaty of New Echota with the Cherokee Nation. One point of contention regarding the treaty is whether it is an instrument of mass displacement in violation of the human rights on which the new republic had been established, or a legal exchange of territory for land further west.
During the American Civil War, the politics of the Five Tribes were divergent. The Choctaw and Chickasaw fought predominantly alongside the Confederates while the Creek and Seminole fought alongside the Union. The Cherokee fought a civil war within their own nation between the majority Confederates and the minority, pro-Union camps. As an element in Reconstruction after the Civil War, new Reconstruction Treaties were signed with the indigenous nations that had entered into treaties with the Confederate States of America. The Civil War was not good to the tribes. The first three battles of the Civil War were fought in Indian territory, with some tribes joining treaties with the Confederates, and others with the Union.[5]
Once the tribes had been relocated to Indian Territory, the United States government promised that their lands would be free of white settlement. Some settlers violated that with impunity, even before 1893, when the government opened the "Cherokee Strip" to outside settlement in the Oklahoma Land Run. In 1907, the Oklahoma Territory and the Indian Territory were merged to form the state of Oklahoma. Relative to other states, all Five Tribes are represented in significant numbers in the population of Oklahoma today.
Experiment of civilizing
Washington promulgated a doctrine that held that American Indians were equals, but that their society was inferior. He formulated and implemented a policy to encourage the "civilising" process, which Thomas Jefferson continued.[6] The noted Andrew Jackson historian Robert Remini wrote "they presumed that once the Indians adopted the practice of private property, built homes, farmed, educated their children, and embraced Christianity, these Native Americans would win acceptance from white Americans.[6] Washington's six-point plan included impartial justice toward Indians; regulated buying of Indian lands; promotion of commerce; promotion of experiments to civilize or improve Indian society; presidential authority to give presents; and punishing those who violated Indian rights.[7] The government appointed agents, like Benjamin Hawkins, to live among Indians and to encourage them, through example and instruction, to live like whites.[4] The tribes of the southeast adopted Washington's policy as they established schools, took up yeoman farming practices, converted to Christianity, and built homes similar to those of their colonial neighbors.[7]

How different would be the sensation of a philosophic mind to reflect that instead of exterminating a part of the human race by our modes of population that we had persevered through all difficulties and at last had imparted our Knowledge of cultivating and the arts, to the Aboriginals of the Country by which the source of future life and happiness had been preserved and extended. But it has been conceived to be impracticable to civilize the Indians of North America – This opinion is probably more convenient than just.— Henry Knox, Notes to George Washington from Henry Knox.
It is notable that the legal systems among the five tribes reputedly appropriated slavery.
Cherokee
The Cherokee, (/ˈtʃɛrəkiː/; Cherokee Ani-Yunwiya (ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯ)) are people of the Southeastern United States, principally upland Georgia, North Carolina and South Carolina. They speak an Iroquoian language. In the 19th century, historians and ethnographers recorded their oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian-speaking peoples were.[9]
Of the three federally recognized Cherokee tribes, the Cherokee Nation and the United Keetoowah Band of Cherokee Indians (UKB) have headquarters in Tahlequah, Oklahoma. The UKB are mostly descendants of "Old Settlers," Cherokee who migrated to Arkansas and Oklahoma about 1817. They are related to the Cherokee who were forcibly relocated there in the 1830s under the Indian Removal Act. The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians is on the Qualla Boundary in western North Carolina, and are descendants of those who resisted or avoided relocation.[10] In addition, there are numerous Cherokee heritage groups throughout the United States, such as the satellite communities sponsored by the Cherokee Nation. The Cherokee tribe is the second largest tribe in the nation, having more than 300,000 members.[11]
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw are Native American people of the United States who originally resided along the Tennessee River and other parts of Tennessee, west of present-day Huntsville, Alabama, parts of Mississippi and the southwest side of Kentucky. They spoke some French and some English. Some historians credit the Chickasaws' intervention in the French and Indian War on the side of the British as decisive in ensuring that the United States became an English-speaking nation.[12] Originating further west, the Chickasaw moved east of the Mississippi River long before European contact. All historical records indicate the Chickasaw lived in northeastern Mississippi from the first European contact until they were forced to remove to Oklahoma, where most now live. They are related to the Choctaws, who speak a similar language, both forming the Western Group of the Muskogean languages. "Chickasaw" is the English spelling of Chikasha (IPA: [tʃikaʃːa]), that either means "rebel" or "comes from Chicsa". The Chickasaw are divided in two groups: the "Impsaktea" and the "Intcutwalipa". The Chickasaws were one of the "Five Civilized Tribes" who went to the Indian Territory during the era of Indian Removal. Unlike other tribes, who exchanged land grants, the Chickasaw received financial compensation from the United States for their lands east of the Mississippi River.[13] The Chickasaw Nation is the thirteenth largest federally recognized tribe in the United States. The Chickasaws built some of the first banks, schools, and businesses in Indian territory. They also signed a treaty with the Southern United States during the Civil War and brought troops to fight for the Confederates.[14]
Choctaw
The Choctaw are a Native American people originally from the Southeastern United States (Mississippi, Alabama and, to a lesser extent, Louisiana). There were about 20,000 members of this tribe when they were forced to move to Indian territory. Many of them unfortunately did not survive.[15] They are of the Muskogean linguistic group. The word Choctaw (also known as Chahta, Chato, Tchakta, and Chocktaw) is possibly a corruption of the Spanish chato, meaning flattened, in allusion to the tribe's custom of flattening the heads of infants.[16][17] Noted anthropologist John Swanton, however, suggests that the name belonged to a Choctaw leader.[18] They were descended from people of the Mississippian culture which was located throughout the Mississippi River valley. The early Spanish explorers, according to the historian Walter Lee Williams, encountered their ancestors.[19] Although smaller Choctaw groups are located in the southern region, the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma and the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians are the two primary Choctaw associations. This tribe was predominantly farmers (like most Indians were at the time) until they were removed from their land. They have grown substantially since the Trail of Tears and there are currently about 200,000 members, making the Choctaw the third largest Native American population in the United States.[20]
| “ | I rejoice, brothers, to hear you propose to become cultivators of the earth for the maintenance of your families. Be assured you will support them better and with less labor, by raising stock and bread, and by spinning and weaving clothes, than by hunting. A little land cultivated, and a little labor, will procure more provisions than the most successful hunt; and a woman will clothe more by spinning and weaving, than a man by hunting. Compared with you, we are but as of yesterday in this land. Yet see how much more we have multiplied by industry, and the exercise of that reason which you possess in common with us. Follow then our example, brethren, and we will aid you with great pleasure ... | ” | |
| — President Thomas Jefferson, Brothers of the Choctaw Nation, December 17, 1803[21] | |||
Muscogee Creek
The Muscogee Creek are an American Indian people originally from the southeastern United States, specifically Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and Alabama.[22] They were there from around 1500 AD till they were forced out by the American Government in the early 19th century. Mvskoke is their name in traditional spelling. The Muscogee Creek tribe is not one tribe but a group of several tribes, each of which had their own distinct land. Starting in 1836, the U.S. forced them to move west of the Mississippi along with the other civilized tribes to "Indian territory". About 20,000 Muscogee members were forced to walk the Trail of Tears, the same amount as the Choctaws.[5] Modern Muscogee live primarily in Oklahoma, Alabama, Georgia, and Florida. Their language, Mvskoke, is a member of the Creek branch of the Muskogean language family. The Seminole are related to the Muscogee and speak a Creek language as well.
Federally recognized Creek tribes included the Muscogee Creek Nation, Poarch Band of Creek Indians in Alabama, Alabama-Quassarte Tribal Town, Kialegee Tribal Town, Thlopthlocco Tribal Town, and the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida.
Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people originally of Florida and now residing in Florida and Oklahoma. The Seminole nation came into existence in the 18th century and was composed of renegade and outcast Native Americans from Georgia, Mississippi, and Alabama, most significantly the Creek Nation, as well as African Americans who escaped from slavery in South Carolina and Georgia. While roughly 3,000 Seminoles were forced west of the Mississippi River, including the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, who picked up new members along the way, approximately 300 to 500 Seminoles stayed and fought in and around the Everglades of Florida. In a series of United States wars against the Seminoles in Florida, about 1,500 U.S. soldiers died. The Seminoles never surrendered to the US government, and consequently the Seminole of Florida call themselves the "Unconquered People".[23][24] Federally recognized Seminole tribes today include the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma and Seminole Tribe of Florida. For about twenty years after the move to Indian territory (Oklahoma) the Seminoles refused to live with the Muscogee Creek tribe or under their Government until they finally reached an agreement with the Government to sign a treaty and live with them. The Seminoles favored the North during the Civil war and remained loyal to the Union and proceeded to move north into Kansas.[25]
Terminology and usage
The use of the term "civilized" has historically been employed to differentiate the Five Tribes from other tribes that, by contrast, were referred to during the same period as "wild". Non-indigenous historical texts have used terms like "savages" and "wild" as an identifier of Indian tribes that, after European Contact, maintained their traditional practices, such as hunting for food. Accordingly, the term has virtually fallen out of use in contemporary academic arenas, and is increasingly less favored.
Use of the term "civilized" is of particular significance, however, in reference to the Five Tribes collectively, given that during a particular period of history they had a collective tendency to integrate Anglo-European cultural practices into their own cultures. This common tendency is itself of interest. Sociological, anthropological and interdisciplinary scholars do explore questions of how and why various cultures and sub-cultures adopt, appropriate, and adapt to features of other cultures in their proximity. Suggestions do exist that the concept of "civilization" was itself to a degree internalized among members of the Five Nations, who themselves even used the term. However, much of Native North American history is of the oral tradition, which make this assertion difficult to substantiate. Scholarly research on this particular point is also scarce.
The term "civilized" in present-day discussion of Native American culture, nationhood, or people, is nonetheless contentious and has largely fallen out of common use. At various places and times (for example in the writings of Vine Deloria, Jr.) the term has been identified as insulting or derogatory, with its implication that the various nations of people indigenous to the North American continent were objectively "uncivilized" without the influence of Anglo-European ways of life. As such, the term raises questions of what constitutes "civilization" and assumes that qualitative "degrees" of civilization exist between peoples. It is therefore regarded as a judgment-laden term at worst, or highly perspective-dependent at best. Accordingly, its application in contemporary scholarly, journalistic, or political narrative puts those who would use it at risk of criticism for ethnocentricity or bias.
Owing to its historical usage, however, The Five "Civilized" Tribes is a term that can be used to advantage in a piece of writing provided that an explanation addresses the notion of "civilized" at its first mention. "The Five Tribes" functions as a more neutral form of the term thereafter. An alternative term in use is the Five Tribes of the Mississippian Culture, or simply, the Mississippian Culture. Similarly, and depending on the context, terms such as "culturally retentive", "culturally resilient", "culturally resolute" could function as possible variants to replace the highly pejorative adjective "wild" when referring to members of the human race.[26]
See also
References
- ↑ Clinton, Fred S. Oklahoma Indian History, from The Tulsa World. The Indian School Journal, Volume 16, Number 4, 1915, page 175-187.
- ↑ "Five Civilized Tribes". Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History & Culture. Oklahoma Historical Society. Retrieved 2015-01-22.
- ↑ "The Native People of North America: Southeast Culture Area". Retrieved 2012-05-27.
- 1 2 Perdue, Theda (2003). "Chapter 2 "Both White and Red"". Mixed Blood Indians: Racial Construction in the Early South. The University of Georgia Press. p. 51. ISBN 0-8203-2731-X.
- 1 2 "Muscogee (Creek) Nation". Muscogeenation-nsn.gov. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- 1 2 Remini, Robert (1998) [1977]. "The Reform Begins". Andrew Jackson. History Book Club. p. 201. ISBN 0-9650631-0-7.
- 1 2 Miller, Eric (1994). "George Washington And Indians". Eric Miller. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ↑ Moser, George W. A Brief History of Cherokee Lodge #10. (retrieved 26 June 2009)
- ↑ Mooney, James (1900). Myths of the Cherokee and Sacred Formulas of the Cherokees. 393: Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4286-4864-7.
- ↑ Cherokee Nation. "The Trail of Tears and the Creation of the Eastern Band of Cherokees".
- ↑ "Cherokee History". Fivecivilizedtribes.org. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ "The Official Site of the Chickasaw Nation | History". Chickasaw.net. 2014-10-31. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ Jesse Burt & Bob Ferguson (1973). "The Removal". Indians of the Southeast: Then and Now. Abingdon Press, Nashville and New York. pp. 170–173. ISBN 0-687-18793-1.
- ↑ Foreman, Grant 1971. "The Five Civilized Tribes: Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, Seminole" (Civilization of the American Indian)
- ↑ "Choctaw History". Fivecivilizedtribes.org. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ Frederick Webb Hodge (1907). ... Handbook of American Indians North of Mexico: A-M. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 288.
- ↑ Horatio Bardwell Cushman (1899). History of the Choctaw, Chickasaw and Natchez Indians. Headlight printing house. p. 564.
- ↑ Swanton, John (1931). Source Material for the Social and Ceremonial Life of the Choctaw Indians. The University of Alabama Press. p. 29. ISBN 0-8173-1109-2.
- ↑ Williams, Walter (1979). "Southeastern Indians before Removal, Prehistory, Contact, Decline". Southeastern Indians: Since the Removal Era. Athens, Georgia: University of Georgia Press. pp. 7–10.
- ↑ "History". Choctaw Nation. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ "To the Brothers of the Choctaw Nation". Yale Law School. 1803. Retrieved 24 October 2010.
- ↑ Transcribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives Archived February 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Mark I. Greenberg; Samuel Proctor; William Warren Rogers; Canter Brown (1997). Mark I. Greenberg; William Warren Rogers; Canter Brown, eds. Florida's heritage of diversity: essays in honor of Samuel Proctor. Sentry Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-1-889574-03-5.
- ↑ "Seminole History". DOS.Myflorida.com. Florida Department of State. 2016. Archived from the original on May 30, 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ↑ "Seminole History". Fivecivilizedtribes.org. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ Kaithy Weiser (August 2010). "Native American Legends: Five Civilized Tribes". Legends of America. Retrieved 2015-01-22.