Windows Vista startup process
The startup process of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and their successors differs from the startup process part of previous versions of Windows.
In this article, unless otherwise specified, what is said about "Windows Vista" also applies to all later NT operating systems. For Windows Vista, the boot sector loads the Windows Boot Manager (a file named BOOTMGR on either the system or the boot partition), accesses the Boot Configuration Data store and uses the information to load the operating system. Then, the BCD invokes the boot loader and in turn proceeds to initiate the Windows Kernel.
History
Windows Vista introduces a complete overhaul of the Windows operating system loader architecture.[1] The earliest known reference to this revised architecture is included within PowerPoint slides distributed by Microsoft during the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference of 2004 when the operating system was codenamed "Longhorn." This documentation mentions that the Windows operating system loader would be undergoing a significant restructuring in order to support EFI and to "do some major overhaul of legacy code."[2] The new boot architecture completely replaces the NTLDR architecture used in previous versions of Windows NT.[1]
Boot Configuration Data
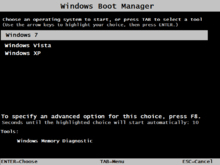
Boot Configuration Data (BCD) is a firmware-independent database for boot-time configuration data. It is used by Microsoft's new Windows Boot Manager and replaces the boot.ini that was used by NTLDR.
Boot Configuration Data are stored in a data file that has the same format as the Windows Registry hives and is eventually mounted at registry key [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\BCD00000][3] (with restricted permissions[4]). For UEFI boot, the file is located at \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD on the EFI System Partition. For traditional BIOS boot, the file is at \boot\BCD on the active partition.[5]
Boot Configuration Data may be altered using a command-line tool (bcdedit.exe), using Registry Editor[3] (regedit.exe), using Windows Management Instrumentation, or with third-party tools such as EasyBCD, BOOTICE,[6] or Visual BCD Editor.[7]
Boot Configuration Data contain the menu entries that are presented by the Windows Boot Manager, just as boot.ini contained the menu entries that were presented by NTLDR. These menu entries can include:
- Options to boot Windows Vista by invoking winload.exe.
- Options to resume Windows Vista from hibernation by invoking winresume.exe.
- Options to boot a prior version of the Windows NT family by invoking its NTLDR.
- Options to load and to execute a volume boot record.
Boot Configuration Data allows for third-party integration, so anyone can implement tools like diagnostics or recovery options.
Boot loaders
winload.exe
The Windows Boot Manager invokes winload.exe—the operating system boot loader—to load the operating system kernel executive (ntoskrnl.exe) and core device drivers. In that respect, winload.exe is functionally equivalent to the operating system loader function of NTLDR in prior versions of Windows NT. In UEFI systems, the file is called winload.efi and the file is always located at \windows\system32.
winresume.exe
If the computer has recently hibernated, then bootmgr will instead invoke winresume.exe. The only difference is the alternate boot mode and the splash screen displaying "Resuming Windows". In UEFI systems, the file is called winresume.efi and is always located at \windows\system32.
Advanced Boot Options
With the advent of the new boot manager in Windows Vista, many components have been changed; one is the Advanced Boot Options menu that provides options for advanced boot modes (i.e. Safe Mode). Due to the implementation of Hybrid Boot in Windows 8 and up, access to the ABO menu has been disabled by default. However, access is still possible with a BCD modification. These are the possible boot modes:
- Repair Your Computer - Boots Windows Recovery Environment
- Safe Mode - Loads Safe Mode, a boot mode with minimal drivers and resources intended for malware removal or replacing faulty drivers.
- Safe Mode with Networking - Loads Safe Mode along with the network drivers.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt - Loads Safe Mode with the Command Prompt as the shell instead of Windows Explorer
- Enable Boot Logging - Enables writing of
ntbtlog.txt, a file that will log the boot process; listing drivers that loaded and drivers that did not. - Enable low resolution video - Disables the default graphics driver and uses the standard VGA driver. Intended in case you changed the resolution to an unusable level (i.e. 320x200)
- Last Known Good Configuration - Loads configuration based on the last successful boot process. Intended for Registry corruptions.
- Directory Services Restore Mode - Boot mode used to reboot the Domain Controller in case it is not working as intended.
- Debugging Mode - Boots while loading the kernel debugger.
- Disable automatic reboot on system failure - Disables the auto-reboot function after a Blue Screen of Death is experienced.
- Disable Driver Signature Enforcement - Disables the kernel setting that prohibits unsigned drivers from loading.
- Start Windows Normally - Boots Windows as if you did not enter the ABO menu; in other words, a normal boot.
The ABO menu is accessible by pressing F8 rapidly before Windows boots.
See also
References
- 1 2 Microsoft (February 4, 2008). "Boot Configuration Data in Windows Vista" (DOCX). Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ↑ Ritz, Andrew (2004). "EFI and Windows 'Longhorn'". Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 9, 2004. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- 1 2 Russinovich, Mark (8 November 2011). "Fixing Disk Signature Collisions". Mark's Blog. Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft TechNet. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ↑ http://superuser.com/questions/654971/why-cant-i-edit-the-system-bcd-store-via-regedit. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Microsoft. "Knowledge Base Article ID: 2004518".
- ↑ Pauly. "BOOTICE board index".
- ↑ Bo Yans. "Visual BCD Editor".
Further reading
- de Boyne Pollard, Jonathan. "The Windows NT 6 boot process". Frequently Given Answers.
.svg.png)