Wild Bactrian camel
| Wild Bactrian camel | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Wild Bactrian camel | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Camelidae |
| Tribe: | Camelini |
| Genus: | Camelus |
| Species: | C. ferus |
| Binomial name | |
| Camelus ferus Przewalski, 1878 | |
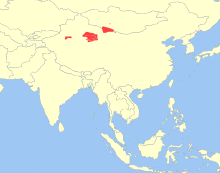 | |
| Current range | |
The wild Bactrian camel (Camelus ferus) is called havtgai ("flat") in Mongolian. It is closely related to the domesticated Bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus). They are both large, even-toed ungulates native to the steppes of central Asia, with a double hump (small and pyramid-shaped).[1] Until recently, wild Bactrian camels were considered to have descended from domesticated Bactrian camels that became feral after escaping from captivity or being returned to the wild. However, a 1.9%[2] difference in Mitochondrial DNA suggests a divergence date of 0.7 to 1.5 million years ago,[3][4] long before the start of domestication. While previously considered to be a subspecies (Camelus bactrianus ferus) of the Bactrian camel, the latest research establishes the wild Bactrian camel as a separate species from the domesticated Bactrian camel due to its distinct genetic makeup.[4][5][6][7] It is restricted in the wild to remote regions of the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts of Mongolia and Xinjiang.
Differences between Camelus ferus and Camelus bactrianus
Compared to the domesticated Bactrian camel, the wild Bactrian camel is slightly smaller and has been described as "relatively small, lithe, and slender-legged, with very narrow feet and a body that looks laterally compressed."[8]
"The wool of C. ferus is "shorter and sparser than that of domestic animals" (Schaller 1998: 152) and its colour is always sandy (Bannikov 1976: 398). And most notably, C. ferus has "low, pointed, cone-shaped humps—usually about half the size of those of the domestic camel in fair condition” (Bannikov 1976: 398)."[9]
It can also survive on water even saltier than seawater – which no other large mammal in the world, including the domestic Bactrian camel, can tolerate.[10]
"The wild Bactrian camel differs from the domestic Bactrian in a number of ways – smaller, more conical humps, flatter skull (havtagai, the Mongolian name for a wild Bactrian camel, means 'flat-head'), a different shape of foot – but the outstanding difference is genetic."[11]
Habitat
Their habitat is in arid plains and hills where water sources are scarce and very little vegetation exists with shrubs as their main food source.[1]
Wild Bactrian camels travel over long distances, seeking water in places close to mountains where springs are found, and hill slopes covered in snow provide some moisture in winter. The size of a herd may vary up to 100 camels but generally of 2-15 members in a group; this is reported to be due to arid environment and heavy poaching. The wild Bactrian camels are limited to three pockets in Mongolia and China;[1] about 600 in the Gobi desert in northwest China and 800 in the Mongolian desert.[12]
In ancient times, wild Bactrian camels were seen from the great bend of the Yellow River extending west to the Southern Mongolia deserts and further to Northwest China and central Kazakhstan. In the 1800s, due to hunting for its meat and hide, its presence was noted in remote areas of the Gobi and Taklimakan deserts in Mongolia and China. In the 1920s, only remnant populations were recorded in Mongolia and China.[1]
Description
The habitats of the wild Bactrian camel have widely varying temperatures: the summer temperature ranges from 40-50 deg C (100 – 120 deg F) and winter temperature a low of -30 deg C (-22 deg F). Their long, narrow slit-like nostrils and thick eyelashes (double row of long eyelashes), and the ears with hairs provide protection against desert sandstorms. They have tough undivided soles with two large toes that spread wide apart, and a horny layer which enables them to walk on rough and hot stony or sandy terrain. Their body hair, thick and shaggy, changes colour to light brown or beige during winter.[1][13] The legend that camels storing water in their stomachs is a misconception: though they have capacity to conserve water they cannot survive without water for long periods.[1]
Like its close relative, the domesticated Bactrian camel, it is one of the few mammals able to eat snow to provide itself with liquids in the winter.[14]
Wild Bactrian camels generally move in groups of up to 30 individuals, although 6 to 20 is more common depending on the amount of food available. They are fully migratory and widely scattered with a population density as low as 5 per 100 km2 . They travel with a single adult male in the lead and assemble near water points where larger groups can also be seen. Their lifespan is about 40 years and they breed during winter with an overlap into the rainy season. Females produce offspring starting at age 5, and thereafter in a cycle of 2 years.[13] Typically, Bactrian camels seen alone are postdispersal young individuals which have just reached sexual maturity.
Status
The wild Bactrian camel is critically endangered. The United Kingdom-based Wild Camel Protection Foundation (WCPF) estimates that there are only about 1400 of them left in the world.[15] The London Zoological Society recognizes it as the eighth most endangered large mammal in the world,[11] and it is on the critically endangered list. The wild Bactrian camel was identified as one of the top ten "focal species" in 2007 by the Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered (EDGE) project, which prioritises unique and threatened species for conservation.[29] Observations made during five field expeditions starting in 1993 by John Hare and the WCPF suggest that the surviving populations may be facing an 80% decline within the next three generations. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) its status was critical in the 1960s and gradually declined to critically endangered (Criteria: A3de + 4ade) status in 2000-2004 (IUCN 2004).[1] Research carried out by the WCPF in association with John Hare from 1993 onwards indicated that this species of camel could suffer an 80% reduction in numbers in the next 30 years.[16]
Threats
Wild Bactrian camels face many threats. The main threat is hunting: in the Gobi Reserve Area, 25 to 30 camels are reported to be poached for domestic use every year, and about 20 in the Arjin Shan Lop Nur Nature Sanctuary. Other threats include land mines laid in the salt water springs,[17] scarcity of access to water (oases), attacks by wolves, hybridization with domestic Bactrians leading to a concern of a loss of genetically distinct populations or infertile individuals which could potentially ward off viable bulls from a large number of females during its lifetime, toxic effluent releases from illegal mining, re-designation of wildlife areas as industrial zones, and sharing grazing areas with domestic animals.[18] Due to increasing human populations, wild camels that migrate in search of grazing land may compete for food and water sources with introduced domestic stock and are sometimes shot by farmers.
The only extant predators that regularly target wild Bactrian camels are gray wolves, which have been seen to pursue weaker and weather-battered camels as they try to reach oases.[19] Due to increasingly dry conditions in the species' range, the numbers of cases of wolf predation on wild camels at oases has reportedly increased.[20] Historically, the Caspian tiger was also known to prey on wild Bactrian camels, but this subspecies is almost certainly extinct.[21]
Conservation
Several actions have been initiated by the Governments of China and Mongolia to conserve this species of mammal such as the ecosystem-based management programme; two programmes instituted in this respect are based in the Great Gobi Reserve A (funded by UNEP & Global Environment Facility of the order of $1,650,000 in 1979[17]) in Mongolia set up in 1982, and the Lop Nur Wild Camel National Nature Reserve (funded by UNEP and Global Environment Facility to the extent of $750,000[17]), on the border of Kum Tagh sand dunes in the Tibetan mountains reserve, established in China in 2000.[13] The Wild Camel Protection Foundation, the only such charity of its kind, has as its main goal conservation of the wild Bactrian in its natural desert environment to ensure that they do not get listed in the extinct category of IUCN.[12][17] The actions taken by the various organizations, motivated and supported by IUCN and WCPF are: Establishment of more nature reserves (in China and Mongolia) for their conservation, and breeding them in captivity, 15 animals in captivity, (as females can give two litters every two years which may not happen when they are in the wild) to prevent extinction.[18] The captive breeding initiated by WCPF in 2003 is the Zakhyn-Us Sanctuary in Mongolia, where the initial programme of breeding last non-hybridised herds of Bactrian camels has proved a success with the birth of several calves.[13]
The wild Bactrian camel is also being considered for introduction at Pleistocene Park in Northern Siberia as a proxy for extinct Pleistocene camel species.[22][23] If this proves feasible, it would increase their geographic range considerably, adding a safety margin to their survival.
See also
Notes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wild camels in Mongolia. |
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Animal Info - Endangered Animals: Camelus bactrianus (Camelus bactrianus ferus)". Animal Information Organization. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ Silbermayr, K.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Charruau, P.; Enkhbileg, D.; Walzer, C.; Vogl, C.; Schwarzenberger, F.; Kaczensky, P.; Burger, P. A. (2010-06-01). "High mitochondrial differentiation levels between wild and domestic Bactrian camels: a basis for rapid detection of maternal hybridization". Animal Genetics. 41 (3): 315–318. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2009.01993.x. ISSN 1365-2052.
- ↑ Ji, R.; Cui, P.; Ding, F.; Geng, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Hu, S.; Meng, H. (2009-08-01). "Monophyletic origin of domestic bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus) and its evolutionary relationship with the extant wild camel (Camelus bactrianus ferus)". Animal Genetics. 40 (4): 377–382. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2008.01848.x. ISSN 1365-2052. PMC 2721964
 . PMID 19292708.
. PMID 19292708. - 1 2 Burger, Pamela Anna (2016-04-05). "The history of Old World camelids in the light of molecular genetics". Tropical Animal Health and Production. 48 (5): 905–913. doi:10.1007/s11250-016-1032-7. ISSN 0049-4747. PMC 4884201
 . PMID 27048619.
. PMID 27048619. - ↑ Burger, P., Silbermayr, K., Charruau, P., Lipp, L., Dulamtseren, E., Yadmasuren, A. and Walzer, C. (in press). Genetic status of wild camels (Camelus ferus) in Mongolia.
- ↑ See, for example: Hare (2008) and Potts (2004)
- ↑ Cui, Peng; Ji, Rimutu; Ding, Feng; Qi, Dan; Gao, Hongwei; Meng, He; Yu, Jun; Hu, Songnian; Zhang, Heping (2007-01-01). "A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the wild two-humped camel (Camelus bactrianus ferus): an evolutionary history of camelidae". BMC Genomics. 8: 241. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-241. ISSN 1471-2164. PMC 1939714
 . PMID 17640355.
. PMID 17640355. - ↑ Potts (2004), p. 145.
- ↑ Potts (2004), p. 146.
- ↑ Hare (2009), pp. 6, 28.
- 1 2 Hare (2009), p. 197.
- 1 2 "Help Us". Wild Camel Protection Foundation. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "13. Bactrian Camel (Camelus ferus)". Evolutionarily Distinct & Globally Endangered. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ Video showing wild Bactrian camels eating snow.
- ↑ "Wild Camels | Wild Camel". www.wildcamels.com. Retrieved 2016-09-26.
- ↑ "Wild Bactrian Camels Critically Endangered, Group Says". National geographic Service News. 3 December 2002. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "New' camel lives on salty water". BBC Nature. 6 February 2001. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- 1 2 Hare (2008).
- ↑ Kara Rogers. The Last Wild Camels. Encyclopedia Britannica Blog. (Posted: February 18, 2010). Britannica.com. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.
- ↑ Camelus ferus (Bactrian Camel, Wild Bactrian Camel). Iucnredlist.org. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.
- ↑ tabaristan: Caspian Tiger. Enmazeroni.blogspot.com. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.
- ↑ Martin W. Lewis (12 April 2012). "Pleistocene Park: The Regeneration of the Mammoth Steppe?". GeoCurrents. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- ↑ Lidia Kruglova (2 May 2011). "Pleistocene Park: so far without mammoths". Voice of Russia. Article also to be found in www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Media about us. Retrieved 5 May 2013. External link in
|publisher=(help)
References
- Bulliet, Richard W. (1975). The Camel and the Wheel. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Hare, J (2008). "Camelus ferus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. IUCN. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- Hare, John (2009). Mysteries of the Gobi: Searching for Wild Camels and Lost Cities in the Heart of Asia. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-512-8.
- Potts, D. T. (2004). "Camel Hybridization and the Role of Camelus Bactrianus in the Ancient Near East.". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 47: 143–165. doi:10.1163/1568520041262314.
- "Bactrian camel". Saving the World's Most Extraordinary Species. EDGE of Existence.
- "Discovery of camels in the Gashun Gobi region". BBC.
External links
- Camelus ferus on the ICUN Red List
- National Geographic – "Wild Bactrian Camels Critically Endangered, Group Says"
- Wild Camel Protection Foundation
- Planet Earth: "Deserts" shows footage of wild Bactrian camels from a two-month trek in the Gobi desert. It includes a "diary" section, explaining the difficulties in obtaining the footage.
- Journalist Aaron Sneddon Bactrian Camels at the Highland Wildlife Park Scotland
- Video showing Wild Bactrian camels eating snow.
