1802
This article is about the year 1802. For the microprocessor, see RCA 1802. For other uses, see 1802 (disambiguation).
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 18th century · 19th century · 20th century |
| Decades: | 1770s · 1780s · 1790s · 1800s · 1810s · 1820s · 1830s |
| Years: | 1799 · 1800 · 1801 · 1802 · 1803 · 1804 · 1805 |
| 1802 in topic: |
| Humanities |
| Archaeology – Architecture – Art – Literature – Music |
| By country |
| Australia – Brazil - Canada – Denmark - France – Germany – Mexico – Norway - Philippines - Portugal– Russia - South Africa – Spain - Sweden - United Kingdom – United States |
| Other topics |
| Rail Transport – Science – Sports |
| Lists of leaders |
| Colonial Governors – State leaders |
| Birth and death categories |
| Births – Deaths |
| Establishments and disestablishments categories |
| Establishments – Disestablishments |
| Works category |
| Works |
| Gregorian calendar | 1802 MDCCCII |
| French Republican calendar | 10–11 |
| Ab urbe condita | 2555 |
| Armenian calendar | 1251 ԹՎ ՌՄԾԱ |
| Assyrian calendar | 6552 |
| Bengali calendar | 1209 |
| Berber calendar | 2752 |
| British Regnal year | 42 Geo. 3 – 43 Geo. 3 |
| Buddhist calendar | 2346 |
| Burmese calendar | 1164 |
| Byzantine calendar | 7310–7311 |
| Chinese calendar | 辛酉年 (Metal Rooster) 4498 or 4438 — to — 壬戌年 (Water Dog) 4499 or 4439 |
| Coptic calendar | 1518–1519 |
| Discordian calendar | 2968 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1794–1795 |
| Hebrew calendar | 5562–5563 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 1858–1859 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 1723–1724 |
| - Kali Yuga | 4902–4903 |
| Holocene calendar | 11802 |
| Igbo calendar | 802–803 |
| Iranian calendar | 1180–1181 |
| Islamic calendar | 1216–1217 |
| Japanese calendar | Kansei 14 / Kyōwa 1 (享和元年) |
| Javanese calendar | 1728–1729 |
| Julian calendar | Gregorian minus 12 days |
| Korean calendar | 4135 |
| Minguo calendar | 110 before ROC 民前110年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | 334 |
| Thai solar calendar | 2344–2345 |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1802. |

1802 (MDCCCII) was a common year starting on Friday (dominical letter C) of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday (dominical letter E) of the Julian calendar, the 1802nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 802nd year of the 2nd millennium, the 2nd year of the 19th century, and the 3rd year of the 1800s decade. As of the start of 1802, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1918.
Events
January–March
- January 15 – Canonsburg Academy (the modern-day Washington & Jefferson College) is chartered by the Pennsylvania General Assembly.[1]
- January 29 – A French expeditionary force (40,000 troops) led by General Charles Leclerc (Bonaparte's brother-in-law) lands in Saint-Domingue (modern Haiti) to restore colonial rule. Where Toussaint Louverture (a black former slave) has himself proclaimed Governor-General for Life and established control over Hispaniola.
- March 16 – The United States Army Corps of Engineers is re-established and the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York established under its management, opening on July 4.
- March 25–27 – Napoleonic Wars: The Treaty of Amiens between France and the United Kingdom ends the War of the Second Coalition.
- March 28 – H. W. Olbers discovers the asteroid Pallas.
April–June
- April 10 – Great Trigonometrical Survey of India begins with the measurement of a baseline near Madras.
- April 26 – A general amnesty signed by Napoleon allows all but about 1,000 of the most notorious émigrés of the French Revolution to return to France, as part of a conciliatory gesture to make peace with the various factions of the Ancien Régime that ultimately consolidates his own rule.
- May 19 – Napoleon Bonaparte establishes the French Légion d'honneur (Legion of Honour).
- May 20 – By the Law of 20 May 1802, Napoleon reinstates slavery in the French colonies, revoking its abolition in the French Revolution.
- June 1 – United States Patent and Trademark Office established within the Department of State.
- June 2 – Indigenous Australian Pemulwuy, a leader of the resistance to European settlement of Australia, is shot dead by Henry Hacking.
- June 8 – Haitian revolutionary Toussaint Louverture is seized by French troops and imprisoned at the Fort de Joux.
- June – Gia Long is crowned as first Emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty in Vietnam.
July–September
- July – Éleuthère Irénée du Pont founds E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, the modern DuPont chemical company, as a gunpowder manufactory near Wilmington, Delaware.
- July 5–August 28 – A United Kingdom general election brings victory for the Tories, led by Henry Addington.
- July 22 – Gia Long captures Hanoi, completing his unification of Vietnam.
- August 2 – In a plebiscite, Napoleon Bonaparte is confirmed as the First Consul of France.
- September 3 – William Wordsworth composes the poem "Westminster Bridge" in London.
- September 11 – The Italian region of Piedmont becomes a part of the French First Republic.
October–December
- October 2 – War ends between Sweden and Tripoli. The United States also negotiates peace, but war continues over the size of compensation.
- October – The French army enters Switzerland.
- December 2 – The Health and Morals of Apprentices Act in the United Kingdom comes into effect, regulating conditions for child labour in factories. Although poorly enforced, it pioneers a series of Factory Acts.
Date unknown
- Thomas Wedgwood publishes an account of his experiments in photography, along with Humphry Davy. Since they have no means of fixing the image, their photographs quickly fade.
- Ludwig van Beethoven publishes his Piano Sonata No. 14 (the "Moonlight") in Vienna.
- Marie Tussaud first exhibits her wax sculptures in London, having been commissioned during the Reign of Terror in France to make death masks of the victims.
Births
January–June
- January 3 – Charles Pelham Villiers, British politician (d. 1898)
- January 10 – Carl Ritter von Ghega, Venetian road engineer of Albanian origin (d. 1860)
- January 22 – Richard Upjohn, English-American architect (d. 1878)
- February 11 – Lydia Maria Child, American abolitionist author (d. 1880)
- February 16 – Phineas Quimby, American physician (d. 1866)
- February 19 – Wilhelm Matthias Naeff, Swiss Federal Councillor (d. 1881)
- February 26 – Victor Hugo, French author (d. 1885)
- March 7 – Edwin Henry Landseer, British painter (d. 1873)
- March 25 – Maria Silfvan, Finnish actor (d. 1865)
- April 4 – Dorothea Dix, American activist (d. 1887)
- April 9 – Elias Lönnrot, Finnish folklorist and philologist who created the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala (d. 1884)
- May 2 – Heinrich Gustav Magnus, German chemist and physicist (d. 1870)
- May 26 – Karl Ferdinand Ranke, German educator (d. 1876)
- June 12 – Harriet Martineau, British social theorist and writer (d. 1876)
July–December
- July 5 (June 23 O.S.) – Pavel Nakhimov, Russian admiral (d. 1855)
- July 24 – Alexandre Dumas, French author (d. 1870)
- July 26 – Mariano Arista, President of Mexico (d. 1855)
- August 4 – Joseph Bonnell, Hero of the Texas Revolution (d. 1840)
- August 5 – Niels Henrik Abel, Norwegian mathematician (d. 1829)
- September 19 – Lajos Kossuth, Hungarian politician (d. 1894)
- September 30 – Antoine Jérôme Balard, French chemist (d. 1876)
- October 31 – Benoît Fourneyron, French engineer (d. 1867)
- November 9 – Elijah P. Lovejoy, American abolitionist (d. 1837)
- November 19 – Solomon Foot, American politician (d. 1866)
- December 15 – János Bolyai, Hungarian mathematician (d. 1860)
- December 23 – Sara Coleridge, British scholar (d. 1852)
Date unknown
- Friedrich Hohe, German lithographer and painter (d. 1870)
- Emma Fürstenhoff, Swedish florist (d. 1871)
Deaths
January–June
- February 2 – Welbore Ellis, 1st Baron Mendip, British statesman (b. 1713)
- February 3 – Pedro Rodríguez, Count of Campomanes, Spanish statesman and writer (b. 1723)
- February 26 – Esek Hopkins, American Revolutionary War admiral (b. 1718)
- April 18 – Erasmus Darwin, English physician and botanist (b. 1731)
- May 9 – Erik Magnus Staël von Holstein, Swedish ambassador (b. 1749)
- May 22 – Martha Washington, first First Lady of the United States (b. 1731)
July–December
- July 22 – Marie François Xavier Bichat, French anatomist and physiologist (b. 1771)
- August 10 – Franz Aepinus, German philosopher (b. 1724)
- August 12 – Louis Lebègue Duportail French military leader in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War (b. 1743)
- September 19 – Princess Luisa of Naples and Sicily (b. 1773)
- September 26 – Jurij Vega, Slovenian mathematician, physicist, and soldier (b. 1754)
- October 5 – Suzanne Bélair, Haitian national heroine (b. 1781)
- October 8 – Emmanuele Vitale, Maltese military leader (b.1758)
- October 31 – Sir William Parker, 1st Baronet, of Harburn, British admiral (b. 1743)
- November 9 – Thomas Girtin, English artist (b. 1775)
- November 15 – George Romney, English artist (b. 1734)
- November 16 – André Michaux, French botanist (b. 1746)
- December 5 – Lemuel Francis Abbott, English portrait painter (b. 1716)
References
- ↑ Coleman, Helen Turnbull Waite (1956). Banners in the Wilderness: The Early Years of Washington and Jefferson College. University of Pittsburgh Press. p. 206. OCLC 2191890.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/12/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
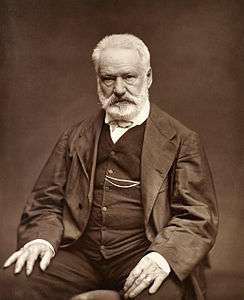
_-_Google_Art_Project_2.jpg)