Association of Caribbean States
| Association of Caribbean States (ACS) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
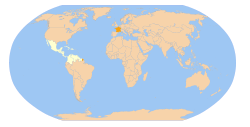 Map indicating ACS members (white).
|
||||
| Seat of Secretariat | ||||
| Largest cities | Bogotá | |||
| Membership |
|
|||
| Leaders | ||||
| • | Secretary General | |||
| • | Ministerial Council Chair | |||
| Establishment | July 24, 1994 | |||
| Website http://www.acs-aec.org/ |
||||
The Association of Caribbean States (ACS; Spanish: Asociación de Estados del Caribe; French: Association des États de la Caraïbe) is a union of nations centered on the Caribbean Basin. It was formed with the aim of promoting consultation, cooperation, and concerted action among all the countries of the Caribbean. The primary purpose of the ACS is to develop greater trade between the nations, enhance transportation, develop sustainable tourism, and facilitate greater and more effective responses to local natural disasters.
It comprises twenty-five member states and seven associate members.[1] The convention establishing the ACS was signed on July 24, 1994 in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia. The secretariat of the organisation is located in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago.
ACS objectives and goals
The Association of Caribbean States is intended to promote regionalism amongst the member states. The success and functionality of the ACS is greatly debated among scholars. The main goals of the association are "to confirm the new concept of the Caribbean Basin by (A) accentuating those interests the Caribbean nations hold in common and (B) working to eliminate barriers left over from its colonial past."[2]
The organization seeks to use geographic proximity and regional cooperation (regionalism) for political and economic advantage[2] with respect to the global economy and trade blocs such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), European Union and South Asia. The ACS has four distinct areas of interest: Trade, Transport, Sustainable Tourism, and Natural Disasters. Each is pursued by a Special Committee which meets at least twice yearly in order to discuss current regional issues and draft treaties.[3]
- The Special Committee on Trade Development and External Economic Relations works in an effort to create larger economic actions in the Caribbean by uniting its member states through integration and cooperation. Through various annual forums the ACS attempts to create economic cooperation in an attempt to benefit and expand the regions economy.[3]
- The Special Committee on Transport works to promote an Air Transport Agreement amongst the countries which have ratified the agreement. Security of travelers and the policing of airborne crime like drug trafficking also falls under the auspices of the Special Committee on Transport.[3]
- The Special Committee on Sustainable Tourism aims to promote tourism which is environmentally friendly.[3] The committee promotes the use of sustainable tourism which is healthy for the environment, and at the same time economically beneficial to the Caribbean as a region.
- The Special Committee on Disaster Risk Reduction which aims to coordinate the prevention and response to natural disasters in the Caribbean.[3] The main focus of this committee is to maintain organization and attempt to maintain a high level of ability to cope with disasters.
Caribbean Sea agenda
One agenda adopted by the ACS has been an attempt to secure the designation of the Caribbean Sea as a special zone in the context of sustainable development, it is pushing for the UN to consider the Caribbean sea as an invaluable asset that is worth protecting and treasuring.[4] The organisation has sought to form a coalition among member states to devise a United Nations General Assembly resolution to ban the transshipment of nuclear materials through the Caribbean Sea and the Panama Canal.
Performance evaluation
The success of the ACS is debated by many scholars on both sides. Those who suggest the ACS is successful would point to the many initiatives the developmental coalition has undertaken as well as its large membership and relations with other international organisations like the European Union. Those who suggest it is unsuccessful note how by the end of the 1990s, unlike CARICOM, the ACS had failed to establish a track record which was worthy enough to allow for the evaluation of the ACS as a developmental coalition.[5] Furthermore, some scholars suggest that the ACS is unlikely to become a true player on the international level. Skeptics often point to other failed attempts at economic coalition building like the Central American Common Market (CACM) as an example of the instability of the region.[5] The influence of NAFTA on the Caribbean outlines the future struggle of the ACS. The future of the ACS in relation to the western hemisphere is uncertain. "Despite governmental statements of commitment to liberalisation, it will be difficult for Caribbean countries to succeed in putting their economies on a firmer footing that would enable them to compete effectively."[6]
Summits
The ACS has held five summits involving Heads of State and/or Government:
- I ACS Summit, at Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, August 17–18, 1995.
- II ACS Summit, at Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, April 16–17, 1999.
- III ACS Summit, at Isla Margarita, Venezuela, December 12, 2001.
- IV ACS Summit, at Panama City, Panama, July 29, 2005.
- V ACS Summit, at Pétionville, Haiti, April 23–26, 2013.
- VI ACS Summit, at Mérida, México, April 28–30, 2014.
- VII ACS Summit, at La Havana, Cuba, June 4, 2016.
Membership
Member states
Associate member states
|
Observer states
Relationship with other supranational organisations
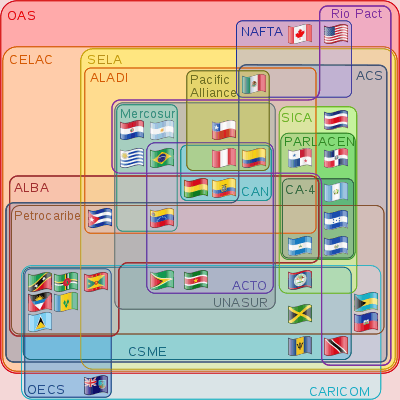
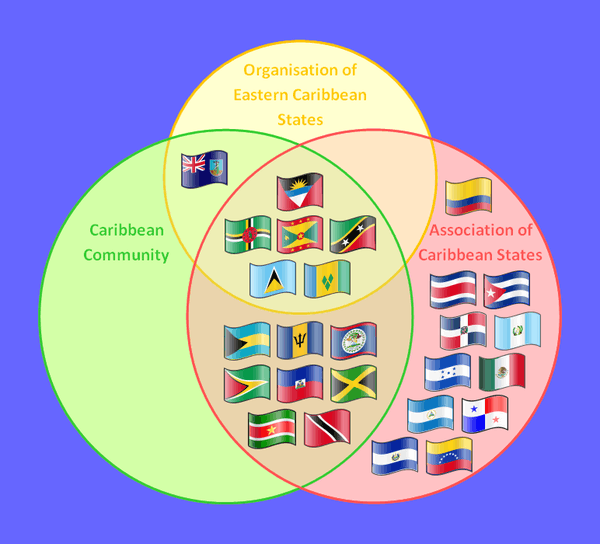
Observer organisations
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM) Secretariat
- Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO)
- Central American Integration System (SICA)
- General Agreement on Central American Economic Integration (SIECA) Permanent Secretariat
- Latin American Economic System (SELA)
- United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC)
- List of regional organizations by population
Further reading
- Gowricharn, Ruben. Caribbean Transnationalism: Migraton, Pluralization and Social Cohesion. Lanham: Lexington Books, 2006.
- Henke, Holger, and Fred Reno, eds. Modern Political Culture in the Caribbean. Kingston: University of West Indies P, 2003.
- Heuman, Gad. The Caribbean: Brief Histories. London: A Hodder Arnold Publication, 2006.
- Hillman, Richard S. and Thomas J. D'agostino (editors). Understanding the Contemporary Caribbean. London: Lynne Rienner, 2003.
- Knight, Franklin W. The Modern Caribbean. na: The University of North Carolina Press, 1989.
- Langley, Lester D. The United States and the Caribbean in the Twentieth Century. London: University of Georgia P, 1989.
- Maingot, Anthony P. The United States and the Caribbean: Challenges of an Asymmetrical Relationship. San Francisco: Westview P, 1994.
- Serbin, Andres. "Towards an Association of Caribbean States: Raising Some Awkward Questions". Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs (2004): 1-19. (This scholar has many articles referencing the politics of the Caribbean.)
References
- ↑ ACS Membership increases Archived September 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 Serbin, Andres. "Towards an Association of Caribbean States: Raising Some Awkward Questions." Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs (2004): 1-19
- 1 2 3 4 5 Association of Caribbean States. 2007. Association of Caribbean States. 21 October-November 2007. Archived December 18, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ The Caribbean Sea: A constant in the ACS agenda Archived August 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. September 30, 2006
- 1 2 Hillman, Richard S., and Thomas J. D'agostino, eds. Understanding the Contemporary Caribbean. London: Lynne Rienner, 2003. pp. 169
- ↑ Benn, Denis. "Global and Regional Trends: Impact on Caribbean Development." In, Caribbean Public Policy: Regional, Cultural, and Socioeconomic Issues for the 21st Century, edited by Jacqueline Braveboy-Wagner and Dennis Gayle. London: Boulder Westview, 1997.
- ↑ "About The ACS". Association of Caribbean States. Retrieved August 24, 2014.
- ↑ "ACS Members and Associate Members". ACS. Retrieved August 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Key address by Raul Castro Ruz, President of the Council of State and Ministers of the Republic of Cuba to the Opening Session of the 7th Summit of the Association of Caribbean States. Havana, Cuba, June 4, 2016.". Association of Caribbean States. 2016-06-04. Retrieved 2016-07-15.
