Baroque guitar

The Baroque guitar (c. 1600–1750) is a string instrument with five courses of gut strings and moveable gut frets. The first (highest pitched) course sometimes used only a single string.[1]

History
The Baroque guitar replaced the Renaissance lute as the most common instrument found in the home.[2][3] The earliest attestation of a five-stringed guitar comes from the mid-sixteenth-century Spanish book Declaracion de Instrumentos Musicales by Juan Bermudo, published in 1555.[4] The first treatise published for the Baroque guitar was Guitarra Española de cinco ordenes (The Five-course Spanish Guitar), c. 1590, by Juan Carlos Amat.[5][6] The baroque guitar in contemporary ensembles took on the role of a basso continuo instrument and players would be expected to improvise a chordal accompaniment with another basso continuo instrument playing the bass line.[7] Intimately tied to the development of the Baroque guitar is the alfabeto system of notation.
Tuning
Three different ways of tuning the guitar are well documented in seventeenth-century sources as set out in the following table. This includes the names of composers who are associated with each method. Very few sources clearly indicate that one method of stringing rather than another should be used and it may have been up to the player to decide what was appropriate.
| Composer | Tuning |
|---|---|
| [Ferdinando Valdambrini] (Italy, 1646/7)
[Gaspar Sanz] (Spain, 1674) |
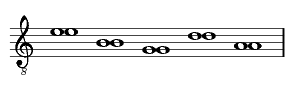 |
| [Francesco Corbetta] (Italy/France/England, 1671)
[Antoine Carre] (France, 1671) [Robert de Visée] (France, 1682)[8] [Nicolas Derosier] (Netherlands, 1690) |
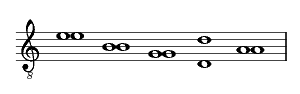 |
| [Girolamo Montesardo] (Italy, 1606)
[Benedetto Sanseverino] (Italy, 1620) [Francisco Guerau] (Spain, 1694) |
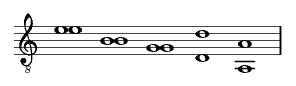 |
Repertoire
- Giovanni Paolo Foscarini (c.1600 - 1650)
- Angelo Michele Bartolotti (c.1615-1680)
- Giovanni Battista Granata (1620 - 1687)
- Gaspar Sanz (c.1640–1710)
- Robert de Visée (c. 1658 – 1725)
- Francisco Guerau (1649 - 1722), Poema harmonico
- Francesco Corbetta (1615–1681)
- Henri Grenerin (fl. mid-17th century)
- Ludovico Roncalli (1654 - 1713)
- Santiago de Murcia (c. 1673 - 1739)
Makers

Historic
- Nicholas Alexandre Voboam II
- René Voboam
- Domenico Sellas
Modern
- R. E. Brune
- Stephen Barber and Sandi Harris
- Daniel Larson
- John J van Gool
- Martin de Witte
- Jaume Bosser
- Paolo Busato
- Daniel Roye
Performers
.jpg)
Historic performers
- David Ryckaert III (Antwerp 1612–1661)
- Anna Kowalska
Modern performers
- Julian Bream
- William Carter
- Eduardo Egüez
- Paul O'Dette
- Hopkinson Smith
- Ulrik Gaston Larsen
- Stephen Stubbs
- Robin Rolfhamre
- Xavier Díaz-Latorre
- Rolf Lislevand
- Nigel North
- Jakob Lindberg
- Stephen Stubbs
- Davide Rebuffa
- Rosario Conte
- Paolo Paolini
- Barry Mason
- Steve Player
- Ugo Nastrucci
- Andrea Damiani
- Massimo Lonardi
- Taro Takeuchi
- William Waters
- Krishnasol Jiménez
- James Tyler
- Ben Salfield
- Frank Pschichholz
- Gérard Rebours
Gallery
-
.jpg)
Baroque guitar by Matteo Seelos (before 1653)
-
_by_Jean-Baptiste_Voboam%2C_and_Joachim_Tielke%2C_National_Museum_of_American_History.jpg)
Five-course guitars by Jean-Baptiste Voboam (ca.1695) and Joachim Tielke (ca.1695–99)
-

Stradavarius guitar (1700), violin, mandolin and case
-

Modern copy of Baroque guitar
See also
References
- ↑ Harvey Turnbull, The Guitar (From The Renaissance to the Present Day) (3rd impression 1978), London: Batsford (ISBN 0 7134 3251 9), p. 15: "Early lutes, vihuelas and guitars share one important feature that would have been of practical concern to the player; the frets, unlike the fixed metal frets on the modern guitar, were made of gut and tied round the neck" (Chapter 1 - The Development of the Instrument).
- ↑ Manfred F Bukofzer, Music In The Baroque Era (From Monteverdi to Bach), London: J. M. Dent & Sons (1st UK edition 1948), p. 47: "The Spanish fashion in Italy brought a speedy victory of the nosiy guitar over the dignified lute".
- ↑ Donald Jay Grout, A History Of Western Music, London: J. M. Dent & Sons, 1962, Chapter 7: New Currents In The Sixteenth Century, p. 202: "By far the most popular household solo instrument of the Renaissance was the lute."
- ↑ Tom and Mary Anne Evans, Guitars: From the Renaissance to Rock, London: Paddington Press, 1977, p. 24: "The first incontrovertible evidence of five-course instruments can be found in Miguel Fuenllana's Orphenica Lyre of 1554, which contains music for a vihuela de cinco ordenes. In the following year Juan Bermudo wrote in his Declaracion de Instrumentos Musicales: 'We have seen a guitar in Spain with five courses of strings.' Bermudo later mentions in the same book that 'Guitars usually have four strings,' which implies that the five-course guitar was of comparatively recent origin, and still something of an oddity."
- ↑ Harvey Turnbull, The Guitar (1978), p. 41 (Chapter 3 - The Baroque, Era Of The Five Course Guitar): "The new era is heralded by Juan Carlos Amat's little treatise Guitarra Espanola de cinco ordenes...."
- ↑ Evans, Guitars (1977), p. 24: "We know from literary sources that the five course guitar was immensely popular in Spain in the early seventeenth century and was also widely played in France and Italy....Yet almost all the surviving guitars were built in Italy....This apparent disparity between the documentary and instrumental evidence can be explained by the fact that, in general, only the more expensively made guitars have been kept as collectors' pieces. During the early seventeenth century the guitar was an instrument of the people of Spain, but was widely played by the Italian aristocracy."
- ↑ Manfred F. Bukofzer, Music In The Baroque Era (From Monteverdi to Bach), London: J. M. Dent & Sons (1st UK edition 1948), p. 26: "The basso continuo ... required at least two players, one to sustain the bass line (string bass, or wind instrument) and the other for the chordal accompaniment (keybooard instruments, lute, theorboe, and the popular guitar)."
- ↑ Robert de Visée, Livre de guitare dédié au roy: "...il ne faut pas oublier une octave à la quatrième corde, elle y est très nécessaire".
Bibliography
- James Tyler, "The Early Guitar", Oxford University Press, 1980
- James Tyler/Paul Sparks, The Guitar and its Music", Oxford University Press, 2002
- James Tyler, " A guide to playing the Baroque Guitar" Indiana University Press, 2011.
- Monica Hall: Baroque Guitar Stringing : a survey of the evidence (Guildford: The Lute Society, 2010) ISBN 0-905655-40-0
- Monica Hall: "Recovering a lost book of guitar music by Corbetta". In Consort: The Journal of the Dolmetsch Foundation, Vol. 61 (2005). ISSN 0268-9111
- Monica Hall: "The "Guitarra espanola" of Joan Carles Amat". In Early Music, Vol. 6, no. 3, July 1978.
- Monica Hall: "Dissonance in the guitar music of Francesco Corbetta". In Lute: The Journal of the Lute Society, Vol. XLVII (2007)
- Monica Hall: "Angiol Bartolotti's Lettere tagliate". In Lute: The Journal of the Lute Society, Vol. XLVII (2007)
- Monica Hall: "Tuning instructions for the baroque guitar in Bibliotheque Nationale Res. Vmc Ms. 59, f. 108v". In Lute: The Journal of the Lute Society, Vol. XLVII (2007)
- Antoni Pizà: Francesc Guerau i el seu temps (Palma de Mallorca: Govern de les Illes Balears, Conselleria d'Educació i Cultura, Direcció General de Cultura, Institut d'Estudis Baleàrics, 2000). ISBN 84-89868-50-6
- Hélène Charnassé, Rafael Andia, Gérard Rebours, The Guitar Books of Robert de Visée, Paris: Editions Musicales Transatlantiques,2000, 235 pages.
- Thomas Schmitt: "Sobre la ornamentación en el repertorio para guitarra barroca en España (1600-1750)". In: Revista de Musicología, XV, nº 1, 1992
- Giovanni Accornero, Eraldo Guerci (edited and translated by Davide Rebuffa) - The Guitar: "Four Centuries of Masterpieces", (Italian/English), Edizioni Il Salabue, 2008. ISBN 978-88-87618-13-6
- Carlo Alberto Carutti, "Passioni di un collezionista", Catalogue by Giovanni Accornero (edited and translated by Davide Rebuffa), (Italian/English), Edizioni Il Salabue, 2011. ISBN 978-88-87618-15-0 (also available on CD rom)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Baroque guitars. |
- Ulrik Gaston Larsen, lutenist
- Technique "Baroque guitar for the modern performer - a practical compromise", by Don Rowe and Richard d’A Jensen.
- "The baroque guitar made simple", by Monica Hall
- The Baroque Guitar Printed Music from 1606–1737 by Dr. Gary R. Boye
- Francois Campion - Pieces for Baroque guitar in alternate tunings
- Instructions for the Baroque Guitar by The Lute Society, UK.
- The Guitar, Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Baroque guitar music
- "The Five-course guitar"