Cheapside, Texas
| Cheapside | |
|---|---|
| Ghost town | |
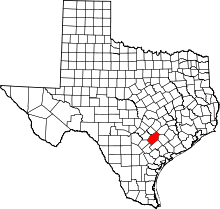
 Cheapside  Cheapside Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 29°16′42″N 97°24′11″W / 29.27833°N 97.40306°WCoordinates: 29°16′42″N 97°24′11″W / 29.27833°N 97.40306°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Texas |
| County | Gonzales |
| Elevation | 299 ft (91 m) |
| Time zone | Central (CST) (UTC-6) |
| • Summer (DST) | CDT (UTC-5) |
| GNIS feature ID | 1354334[1] |
Cheapside is a ghost town in Gonzales County, Texas. It is located 21 mi (34 km) south of Gonzales.[1]
Once a thriving community and commercial center for cotton, only a church and the crumbling remnants of the former settlement remain.
History
The first settler was Thomas Baker, who built a log cabin in the area in 1857.[2]
The settlement may have been named after Cheapside, Virginia,[2] or after Cheapside Street in London, England.[3]
A post office was established in 1882.[2]
Cheapside's economy was based on agriculture, particularly cotton, as well as poultry, livestock and grain. Cheapside had three grocery and general stores, a drugstore, a broom factory, a blacksmith shop, a hotel, a butcher shop, a barbershop, a confectionery, several doctors, a Masonic lodge and a Woodmen lodge, a daily stagecoach, and at least two saloons. To keep order there was a deputy sheriff.[2][3] Cheapside also had a baseball team that played on weekends, with rodeo events between games.[3]
In 1889, a combined cotton and gin gristmill was built, and from about 1890 to 1913 a private school was located in Cheapside.[2]
The Cheapside Community Church was built in 1897, and moved to its present location in Cheapside in 1949.[3]
A small power plant was installed in 1925, and 1939 the county's electrical grid was extended to Cheapside.[2]
Cheapside's population peaked at about 500 during the Great Depression of the 1930s.[3]
Decline
Some of the factors which led to Cheapside's decline include a weakening in the price of cotton—a major commodity in the community—during the Great Depression.[2] Soil in neighboring farmland had also lost its fertility due to over-cultivation.[3] The gin closed during the 1940s, and most of the neighboring farmland reverted to open pasture.[2]
As well, during World War II, the war effort created work in the cities, and returning soldiers were less willing to return to small communities. With the rise in consumerism, "places like Cheapside...were casualties of an upwardly mobile society".[3]
Cheapside's school was consolidated with the Cuero Independent School District in 1949 due to low enrollment, and by 1960, the only remaining business in Cheapside was a small grocery store with a post office. It closed in 1989.[2]
The Victoria Advocate wrote in 2012 that in Cheapside there are "a few buildings teetering on collapse that become less and less visible through the trees and weeds, which have started to reclaim the abandoned town".[4]
Notable people
- Keyes Fawcett Carson Jr. - While a cadet at Texas A&M University in 1936, Carson became an expert at hitchhiking, traveling 251,000 mi (404,000 km) in 6,680 different vehicles with his pet turkey.[5]
References
- 1 2 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cheapside
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Fly, W. Lamar (June 12, 2010). "Cheapside, Tx". Texas State Historical Association.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Racine, Marty (July 22, 2001). "Last Days of Cheapside: A Few Members of Town's Former Populace Keep It Alive". Houston Chronicle.
- ↑ "Ghost Town Between Cuero and Gonzales". Victoria Advocate. June 21, 2012.
- ↑ "Keyes Fawcett Carson". Victoria Advocate. November 28, 2007.