Croatian Army
| Croatian Army | |
|---|---|
 Emblem of the Croatian Army | |
| Active | 1991–present |
| Country | Croatia |
| Type | Army |
| Size | 15,670 personnel As of 2016[1] |
| Part of | Republic of Croatia Armed Forces |
| H/Q | Karlovac |
| Motto(s) | "Domovini vjerni" (Faithful to Homeland) |
| March | Mi smo garda hrvatska (We are the Croatian guard) |
| Anniversaries | 28 May |
| Equipment | 78 MBT,[2] 623 IFV & APC, 350 artillery pieces, mortars |
| Engagements |
|
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Lieutenant General Mate Ostović |
| Notable commanders | General Martin Špegelj, General Janko Bobetko, General Petar Stipetić, General Zvonimir Červenko, Lieutenant General Ante Gotovina, Lieutenant General Marijan Mareković, Lieutenant General Mladen Kruljac |
The Croatian Army (also Croatian Ground Army, Croatian: Hrvatska kopnena vojska, Hrvatska vojska) is a branch of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Croatia.
The fundamental role and purpose of the Croatian Army is to protect vital national interests of the Republic of Croatia and defend the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the state.
The basic tasks of the Croatian Army are:
- to maintain an optimal level of combat readiness of the Armed Forces
- to fight a possible aggressor's main forces on strategic-operational levels and to defend against any land, air and amphibious assaults
- to prevent, in cooperation with the other branches of the Armed Forces, an aggressor from in-depth operations on Croatian territory
- to build and develop the capability to respond to requests of non-traditional tasks that are required of the Croatian Army (floods, fires, natural disasters...)
- to assist its allies and friendly countries in time of need.
History
The Croatian Army was formed in the Croatian War of Independence, when, on November 3, 1991, the Croatian National Guard was renamed the Croatian Army.
Numerous Croatian army units arose from the Croatian National Guard, including:
- 1st Croatian Guards Corps
- 1st Guards Brigade (Croatia)
- 2nd Guards Brigade (Croatia)
- 3rd Guards Brigade (Croatia)
- 4th Guards Brigade (Croatia)
- 7th Guards Brigade (Croatia)
- Croatian 104th Brigade
- 204th Vukovar Brigade
The locally based regiments were named the Home Guard Regiments (Domobranska pukovnija). They were created on 24 December 1991, during the war, and ceased to exist in a 2003 reorganization.[3]
Key: red – mech, gold – armoured
Organizational structure and status
The Croatian Army is an all-volunteer force numbering 7,514 active duty personnel and 193 civil servants and employees as of August 2016.[1] The Army can also call on 6,000 reserve personnel who serve up to 30 days every year.

The Croatian Army is being reorganized to fit in the NATO doctrine of a small, highly capable force with an emphasis on mobility and versatility.
Major combatant commands of the Croatian Army are one mechanized and one motorized brigade, each brigade having a specific role and different responsibilities. In 2012, one motorized infantry company is to be detached and put under the command of the EU Battle Group led by Germany. Croatia continues to deploy 350 personnel in support of NATO International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan.
Croatia achieved NATO membership in April 2009. The defence reforms that Croatia initiated in 2000 have a long-term goal of replacing and modernizing the armed forces to meet the challenges of NATO membership. The plan calls for the modernization of the Army and the introduction of training and doctrine in line with Western (NATO) standards. Replacing ex-Yugoslav/Soviet hardware is also one of the main priorities.
There are various ongoing initiatives, such as the upgrade of the tank fleet, modernization of obsolete anti aircraft systems, introduction of new Armored Personnel Carriers and NATO standard assault rifles, etc. Procurement of new, NATO-compatible equipment takes a significant part of the defense budget.
Until recently, Croatia operated just under 280 main battle tanks, but this number decreased significantly due to the withdrawal of roughly 200 obsolete T-55 tanks in 2006. Most of these units have been scrapped, but a limited number have been stored as operational reserve in case of need. The mainstay now is the M-84A4 Sniper main battle tank. However, modernization of the tank fleet to the M-84D standard is one of the priorities set in the new defense budget.
In July 2007 Patria AMV won the contract to supply the next generation of APCs to the Croatian Army. Only 84 vehicles were ordered at first, but an additional 42 were purchased in an extended contract signed in December 2008. Croatia thus has 126 units on order with the first six vehicles manufactured in Finland delivered by late 2008. All remaining vehicles will be locally produced. According to some reports, at least 50-60 additional APCs are needed. In 2010, an order was placed for an undisclosed number (most probably 56) of Protector (RWS) remote controlled weapons stations (RCWS).[4]
In early 2007, Croatia bought 10 Iveco LMV light armoured vehicles at a cost of 330,000 Euros per unit. According to official documents, 94 of these vehicles were needed by 2017. However, Croatia will rely on US-donated HMMWV and MRAP type vehicles.
Steps have been made to standardize the difficult-to-maintain vehicle inventory of the Croatian military, which is full of various models of different origin, type and age. In 2005, the Army bought 152 light trucks and vehicles, 156 in 2006 with an additional 170 obtained by the end of 2007. All vehicles are from prominent European or Japanese manufacturers including Mercedes-Benz, Land Rover, Iveco, MAN, Toyota and Nissan. These purchases are an ongoing process seen as roughly 150-180 new terrain vehicles are procured annually.
The Croatian Army plans to introduce a new assault rifle in 5.56mm NATO caliber to replace the AK-47 and its derivatives. The preferred model seems to be the locally manufactured VHS developed by HS Produkt. It was reported in the media that the MoD has purchased the initial batch of 1,000 rifles in 2009–2010. Previous Defense Ministers Rončević and Vukelić both went on record stating the requirement for up to 20,000 rifles. The MoD press and photo releases from regular training activities in 2011 indicate that the VHS has been issued to elements of the Military Intelligence Battalion, Combat Swimmer Detachment of the Special Forces Battalion, as well as to one of the infantry companies of the Guards Motorized Brigade that will be made available to the German-led EU Battle Group in 2012. There have been unconfirmed reports that the rifle is being tested in Afghanistan.
Current structure of Croatian Army

- Land Forces Command (based in Karlovac) [5]
- Armored Guard Brigade in Vinkovci
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 1st Tank Battalion "Kune"
- 2nd Armoured Battalion
- 3rd Mechanised Battalion "Sokolovi"
- 4th Mechanised Battalion "Pume"
- Artillery Battalion
- Air Defence Battalion
- Engineer Battalion
- Reconnaissance Company
- Signals Company
- Logistics Company
- Motorized Guard Brigade in Knin
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 1st Mechanised Battalion "Tigrovi"
- 2nd Mechanised Battalion "Gromovi"
- 1st Motorised Battalion "Vukovi"
- 2nd Motorised Battalion "Pauci"
- Artillery Battalion
- Air Defence Battalion
- Engineer Battalion
- Reconnaissance Company
- Signals Company
- Logistics Company
- Training and Doctrine Command "Fran Krsto Frankopan" in Osijek
- Infantry Regiment in Gašinci
- Basic Training Centre in Požega
- Combat Training Center in Slunj
- Simulation Center in Zagreb
- Mixed Artillery Regiment in Bjelovar
- Air Defence Regiment in Donji
- Command Battery in Zemunik
- 1st Mixed Battalion in Zemunik
- 2nd Mixed Battalion in Udbina
- 3rd Mixed Battalion in Zagreb
- Engineer Regiment in Karlovac
- Signals Battalion in Velika Gorica
- NBC Defence Battalion in Velika Gorica
- International Operations Training Center in Rakitje
- Armored Guard Brigade in Vinkovci
Modernization plans
.jpg)

.jpg)
Economic recession in much of the EU and in Croatia from 2009 caused the revision of Croatia's plans to modernize its armed forces. Initially it was planned to spend around 15 billion kuna on armed forces modernization not included in this was a special purchase for advanced jet fighters which would cost another 8-12 billion kuna. Croatia's responsibility towards NATO some schedules had to be fulfilled, such as procurement of modern armored personal carrier as well as modernization of infantry soldier, from training to equipping infantry units with best gear army can afford. Program is almost an end, should be fully implemented by the end of 2015.
Although there were quite a few setbacks in Army modernization plans, such as delays in purchase of new infantry fighting vehicles, light armored personal carriers, no real strategy as to what to do with M84A4 main battle tanks and army logistics got little or no new equipment since 2008. However, large donations by US military as well as other NATO allies should ensure that the Croatian Army of 2020 can fully integrate and interoperate with NATO in terms of equipment, logistics and weapon systems.[6]
Main Programs
- Procurement of 126 Patria AMV Modular APC/IFV - 2.8 billion Kuna (additional vehicles might be ordered after 2017).
- Procurement of 162 Oshkosh M-ATV, 30 Navistar MaxxPro MRAP and 20 BAE Systems RG-33L (6x6) Heavy Armored Ground Ambulance (HAGA), the latter also procured as part of the MRAP ID/IQ contract awards. The vehicles were delivered under the US Excess Defense Articles (EDA) programme. Croatia first requested MRAPs under the EDA programme in January 2013, with US Congress granting approval for the transfer of 170 vehicles in August 2013 and for a further 42 vehicles in March 2014. As is typical under the EDA programme, the vehicles were transferred on an 'as is, where is' basis, with Croatia responsible for the cost of shipping the vehicles and for any future refurbishment or modification they may require. Accordingly, the Croatian MoD paid the costs of the transfer of the Maxxpro MRAPs from US Army stores in Italy, and did the same for the shipping of the RG-33 HAGA vehicles from the United States. The M-ATVs, however, were in Afghanistan and their transfer costs were granted for free as part of the US Department of Defence Lift and Sustain programme.[7]
- Procurement of a short and medium-range (ceiling of >12,000 meters) air-defense system around 2020 as a part of the new plan to form a surface-to air battery armed with short and medium range surface to air systems, most likely candidate for this program being IRIS-SL or MBDA MICA systems developed by European consortia Diehl BGT Defence and MBDA respectively, both systems have a range of 35 km and about 12 km altitudes meeting required parameters.
- Procurement of 12+3 surplus German PzH 2000 advanced artillery systems which are to be delivered in 2015 to augment (not replace) existing 2S1 self-propelled howitzers. Cost of program - 300 million Kuna.
- Modernization of 104 BVP M-80A Infantry Fighting Vehicle with new 30mm remote weapon station, new modular armour package and 3rd generation anti tank missile with range of up to 4 km, program cost 320 million kuna to be completed by 2024, replacement by western modern IFV wasn't discounted.[8]
- Procurement of 3rd generation of Anti tank missile including vehicle mounted versions, up to 200 launchers and 2000 missiles and simulators. FGM-148 Javelin and Spike being main contenders for this program. Cost of program - 400 million Kuna.[8]
- Procurement of 550 x 5-ton army trucks, negotiations with Germany over purchase of 2nd hand trucks and support vehicles has ensured much of the program parameters, with some 400 vehicles to be delivered by late 2015 and early 2016. A commercial tender for brand new trucks will be held in 2016 to supply additional 300 vehicles that will replace older no longer viable vehicles currently in service. MAN HX-Serie and Mercedes Zetros being most likely choice.
- Modernization of M-84A4 Sniper MBTs. Program calls for an upgrade and modernization of 16 tanks. Modernization of 16 M84A4 tanks to M84A5 (also known as M-84D) standard will be completed by the end of 2016, Army is to retain additional 32 M-84A4 tanks with the remainder used for spare parts.[8][9]
- Additional 6000 VHSHS Produkt rifles will be purchased by 2018 for total of 12000.
- Complete overhaul and modernization of two engineer company sized units with latest NATO engineering equipment including battlefield support and engineering equipment.
- Overhaul and modernization of communication and data link networks as well as battlefield management systems – program cost: 150 million kuna, program finalized in 2003 and 2007, Croatian army purchased 135 TRC4000 communication and data link full sets[10] as well as 700 SINCGARS-RT-1702G sets and in 2013 donation by US Government of additional 18 Harris 117G[11] sets completes the overall requirements for Croatian Army for modern NATO standard communication and data link equipment.,[12] procurement of communication and night vision equipment for all units and vehicles to comply with NATO standards. Program will be financed by Croatian budget but also though donations by US.
Other programs:
- Equipping motorized infantry battalion (800-1,000 men) with night vision equipment, including advanced optoelectronics and sensors, ground radars, thermal imaging cameras – 120 million Croatian Kuna
- NBC equipment for biological/chemical-decontamination unit – 150 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of new army engineering vehicles, armored recovery vehicles, mine clearance vehicles and armored personal vehicles designed to withstand mine blasts – 320 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of modern communication and battlefield management systems –
- Procurement of new logistic and amphibious vehicles – 250 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of 3-4 Artillery Radars – 30–40 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of 8-12 Mobile air defense radars – 200–300 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of Army Field Hospital - 80-100 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of 16 Army Tank transporters, Heavy Equipment Transporters – 80–100 million Croatian Kuna
- Procurement of Bridge laying equipment – 100 million Croatian Kuna
Equipment
The Croatian Army's requirement for personal protection side arms is being fulfilled by the locally produced and very popular HS2000 hand gun design, which has also become increasingly popular in the USA and elsewhere.
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS Produkt HS 2000 |  | 9×19mm | | 40,000 | standard sidearm |
| HS XDM[13] |  | 9×19mm | | 20,000 | standard sidearm |
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H&K MP5 |  | 9×19mm | | 80-100 | special forces and anti terrorist police |
| H&K UMP |  | 9×19mm | | 80-100~ | special forces and anti terrorist police |
| H&K MP7 |  | 4.6×30mm | | 70-80~ | special forces and anti terrorist police |
The Croatian Army's current standard assault rifle is the M70, with around 10,000 still in active service. This is being replaced by the Croatian made HS Produkt VHS, of which 5,000+ are currently in use. The VHS will entirely replace the M70 by 2015. Croatian peackeepers and serviceman who serve on NATO/EU missions tend to be supplied with the German-made H&K G36C rifle and, to a lesser extent, the US Colt M4 carbine.
The Croatian Army inherited large quantities of Yugoslav Army light infantry weaponry, much of it captured during the Battle of the Barracks. These were supplemented by indigenous designs, some of which were very successful and found export markets. During the 1990s, these were perfectly acceptable light infantry weapons; however, with Croatia's entry into NATO, many older Yugoslav-era designs were seen as redundant and surplus to the requirement. Much of stock of small arms is being replaced by western designs and will lead to the eventual withdrawal of some older models such as Zastava M76, RT-20, MSCS M1 &2, and older Remington rifles. Croatia has acquired a substantial quantity of Sako TRG 42 sniper rifles with the aim of equipping the current army (around 7 infantry battalions) with 32 Sako TRG 42 sniper rifles per battalion. Additional equipment, such as optics and grenade launchers, were also obtained from domestic and German suppliers. Machine guns inherited from the Yugoslav era are also being supplemented by a large number of western models, namely FN MAG, Ultimax 100, M249 light machine gun and, contentiously, an ever growing quantity of M2 Browning machine guns (of which Croatia had some 570 examples at the end of 2010, but numbers are likely to grow to well over 800 by mid-2015 due to number of new armored vehicles being armed with remote overhead weapon stations, as well as stand alone firing ports on a number of new armored vehicles Croatia has acquired or is to acquire from US and other NATO partners).
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS Produkt VHS/VHS2 | 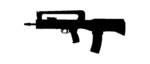 | 5.56×45mm | | 10650 VHS1, 2500 VHS2 and 1500 VHS2 on order | around 3000 rifles in service as of early 2013, with additional 1580~ acquired under original 2008 contract,[14] 500 VHS1 Rifles intended for Croatian Army sold to US DOD.[15][16][17] Army Order for 300 VHS 2 Rifles made with future order for 20 000 VHS 2 agreed. VHS2 Rifles to replace VHS 1 which will be relegated in to reserve status.[18] |
| Zastava M70 |  | 7.62×39mm | | 640~ | 88,000 stored and offered for sale, 44,000 sold to Afghanistan in 2010, 4000 donated to Mali in 2013,[19] some 6000 rifles sold to Syrian Rebels via Jordan and Saudi Arabia. To be completely withdrawn from use by the end of 2015.[20][21] To be completely withdrawn from active service by end of 2015, with 400~ left for use in opfor training. |
| H&K G36C |  | 5.56×45mm | | 550 | standard assault rifle in service with the Special Forces and Ministry of the Interior, additional 200 acquired for MUP for total of 750. |
| HK416 |  | 5.56×45mm | | 250 | standard assault rifle in service with the Special Forces and elite units. Image of Croatian Army's own [22]HK416 |
| FN SCAR[23] |  | 5.56×45mm | | 50~ | used by BSD (1 Comp. Parachute) and for weapon familiarization and special forces training. |
| FN F2000 |  | 5.56×45mm | | 120 | used by BSD (1 Comp. Parachute) |
| Colt M4 |  | 5.56×45mm | | 200 | - used by ISF contingent and BSD [24] |
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sako TRG-42 |  | 8.6×70mm | | 240 | standard sniper rifle of Croatian Army replacing older models. |
| MACS M3 |  | 12.7×99mm | | 32~ | standard sniper rifle, 48~ stored, supplements Sako TRG. |
| RT-20 | 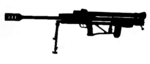 | 20×110mm | | 20~ | anti-materiel rifle, some stored |
| Remington M40A5 |  | 7.62×51mm | | 70~ | 100~ older A1 models being phased out, with few remaining for familiarization and training. |
| Barrett M82 |  | 12.7×99mm | | 24~ | anti-materiel rifle, a dozen or so kept in reserve status. |
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBG-6 |  | 40×46mm | | 124 | 112 with Croatian Army and 12 with special forces and anti terrorist units. |
| H&K AG36 |  | 40×46mm | | 300 | Comes as standard with all H&K G36C deployed in ISAF and other NATO/EU missions. |
| Mk 19 grenade launcher |  | 40×53mm | | 32 | For the first time seen in the public at recent Military parade held in Zagreb, 32 weapons purchased for 4.8 million kuna. Mounted on to MATV and M1151 Up-Armored Capable HMMWV vehicles. More to be purchased, requirement calls for 224 weapon systems.[25][26][27] |
| Model | Image | Caliber | Origin | Quantity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Browning M2 |  | 12.7×99mm | | 570+ | more to be acquired. |
| FN M249 |  | 5.56×45mm | | 100+ | more to be acquired. |
| FN MAG |  | 7.62×51mm | | 400+ | number purchased for new light armored vehicles and infantry mobility vehicles armored |
| Ultimax 100 |  | 5.56×45mm | | 100 | purchased in mid 1990s, just after the Homeland War. |
On April 24, 2013 the Defence Minister signed a memorandum with Đuro Đaković – Specijalna vozila for the upkeep, maintenance and modernization of the M-84 fleet (48 tanks) with the aim to improve the serviceability of the fleet.[28] According to current plans only 4 tanks are to be fully overhauled at cost of $1.8 million or $450,000 per tank with potential for further 44 tanks to be fully overhauled by late 2017 at cost of $20 million or 110 million Kuna.
Long-term plans regarding the future role of M-84 tanks in Croatian Army is to be defined by MOD. The new proposed defence white paper envisages only a fleet of 48 tanks.[8] This program includes a full upgrade and overhaul of M-84 A4 tanks to A5/D standard by 2020. However, the program isn't complete as public consultation is being held.
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-84A4 Sniper | | MBT | | 72 | All M-84A tanks brought to this standard by 2008 and are awaiting further upgrade. The fleet is undergoing limited overhaul with 4 tanks to be refurbished by the year's end at the cost of 440,000 USD per vehicle.[29] 16 Tanks to be upgraded to M-84A5 standard by 2017. Under new proposed Defence White paper only 48 (44+4) tanks will be kept and modernized, remaining tanks either sold or put in to reserve status. |
The Croatian Army relies on M-80A infantry fighting vehicles, of which there are 128 in service. These vehicles are deployed in two mechanized infantry battalions. Croatian MOD stated that the M-80 will be replaced at some point in the future and that there are no plans to modernize these vehicles. Croatian Government is negotiating a purchase of second hand Marder 1A3[30] vheicles from German army stock as an interim solution before the next generation of infantry fighting vehicles are purchased sometimes after 2020. Croatian requirements call for 104 vehicles in standard IFV role and 8-12 vehicles as armoured ambulance. Contract value wasn't disclosed but it was mentioned that is affordable for Croatian Army. M80A vehicles for which Croatia lacks proper maintenance and spare parts due to parts no longer being manufactured will be retired and relegated in to reserve status.
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVP M-80A |  | IFV | | 128 | A total of 104 vehicles operational in two battalions, additional 24 converted or surplus units. Possible modernization of the fleet has been dismissed and additional Patria AMV IFVs were considered as an alternative but this also has now been rejected due to the fact that requirements call for a tracked IFV capable of keeping up with the tanks.[16] |
Since the purchase and equipping of 126 Patria AMV has been posing a significant financial strain on the military budget for quite some time now, the current needs of the Army are going to be met primarily by acquiring second-hand hardware from allied sources.NATO, with the USA being the prime supplier of such vehicles. Previous needs for additional Patria IFVs and Iveco LMVs are now going to be met by introducing large numbers of Oshkosh M-ATVs of which 162 are to be introduced into service in 2014. Cost of the program is merely $10 million, with Croatian MOD only paying for the transport of said vehicles.
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patria AMV |  | APC | | 126 | All units were delivered by mid-2013 but final fitting out and equipping to be concluded no sooner than 2016. An additional third battalion might be ordered after 2015 to fulfill all NATO obligations.[16] |
| Iveco LMV | .jpg) | IMV | | 14 | An additional 84 vehicles were planned to enter service by 2017 but this option has been dropped due to the delivery of large quantities of M1151 Up-Armored Capable HMMWVs and similar vehicles. |
| M1151 Up-Armored Capable HMMWV |  | IMV | | 93 | The vehicles are mostly used by the ISAF forces in Afghanistan, but at least 13 newly built units delivered in 2012 are home-based + additional 8 delivered in 2015 for total of 21. . 65 M1151s and 20 M1141 vehicles in service.[31] |
| Oshkosh M-ATV |  | MRAP | | 172 | The initial order was made for 122 M-ATV but additional 40 units were requested and approved by US Senate.[32][33] Of 162 M-ATVs received as EDA, 15 are going to the Croatian Special Forces Command (SFCOM), 5 will be with the Support Command (SCOM), 2 with the Military Police Regiment, and 78 are to enter service with the Croatian Army in 2015, with a further 62 to follow in 2016 (equipping the 1st Battalion of the Motorized Guards Brigade in Gospic).[34] Additional 10 vehicles are still deployed in ISAF to return to Croatia in 2015 for total of 172 vehicles.[35] |
| International MaxxPro | | MRAP | | 40 | A total of 30 vehicles are in Croatia and additional 4 in Afghanistan. Of the 30 MaxxPro vehicles received EDA, 21 are for the Croatian Army, 5 will join SFCOM, and 2 each will go into SCOM and the Military Police Regiment. 6 MaxPro Recovery Vehicles[34][36] |
| RG-33 |  | MRAP | | 20 | A total of 20 RG-33L (6x6) MRAP HAGA delivered and to enter service with SCOM during 2015.[34] |
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-84AI | Armoured Recovery Vehicle | | 4 | The last vehicle entered service in 2002. | |
| T-55TZI |  | Armoured Recovery Vehicle | | 4 | Are awaiting replacement. |
| MT-55A |  | Armoured Bridge Vehicle | | 2+ | Additional bridge units are mounted on KrAZ 6x6 heavy trucks, but are awaiting replacement. |
| GSP-55 self-propelled amphibious ferry |  | Amphibious Vehicle | | 2 | Only 2 operational and used with engineering unit. awaiting replacement by modern NATO system.[37] |
| PTS-M | | Amphibious Vehicle | | 4 | Actively participated in transport actions during the floods of 2014. |
| PMS | | Pontoon Bridge | | 4-5 | All are mounted on Tatra T813 8x8 trucks. 4 System seen at the parade, but number could be higher, serving with engineering regiment, awaiting replacement by modern NATO system. |
| MV-4 | .jpg) | Combat engineer | | 4 | used for demining operations |
Under the newly proposed plan, the Croatian Army is set to revive its capability of hitting targets beyond the 10 km range. Current systems in service are all short-ranged with Strijela-10CROA1 (Croatian army's only SAM systems) having a maximum range of 7 km. The purchase of new systems will be highly dependent on price and support packages, with VL Mica, Crotale, SPYDER and NASAMS 2 being among most likely choices.
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strijela - 10CROA1 |  | short range surface-to-air missile system | | 9 | The systems were modernized throughout the years. |
| BOV 20/3 | | SPAAG | | 44 | The triple M55 20mm anti-aircraft guns mounted on a BOV APC. The systems are set to remain in service due to their secondary role as heavily armed APCs. |
| Bofors 40 mm L/70 |  | anti-aircraft autocannon | | 12 | Paired to Giraffe radars. |
| 9K38 Igla | .jpg) | MANPADS | | 67 | |
| 9K32 Strela-2M | | MANPADS | | 141 (+372) | |
- Although Croatia acquired the S-300 long-range surface-to-air missile system in 1994, and demonstrated some of its parts on the 1995 military parade, it is believed that the system was never fully completed and operational although the training of crews was sought as late as 1998. Some sources claim that the weapon was subsequently handed-over to the United States or Israel in 2002–2004. However, officials still claim that the system is stored somewhere in Croatia.
- Anti-tank weapons
Croatian Army has relied heavily on Russian and domestically made anti-tank systems and rocket-propelled grenades, many of which by modern standards are obsolete or inadequate. The procurement of modern anti-tank system is being addressed and current plans call for the purchase of several dozen launchers for Patria AMVs which are to be fully integrated with 30mm license-built Kongsberg RWS. Swedish AT4 systems are viewed as the future unguided anti-tank weapon of the Army and a certain number of these has already entered service. The unguided M80s are being relegated to reserve status while the other domestically manufactured RPG weapon, RL90 M95 is set to remain in active service for some time. Spike and Javlin being main contenders for Croatian army choice of next generation anti tank missile systems replacing older soviet made systems currently in service. up to €20 million order for launchers will be made in 2016, with up to 64 launchers being delivered to army, of which up to 16 will be LR or mounted to a 30mm RWS turret developed by Kongsberg. Longer term Croatian army requirements call for 200~ launchers including infantry and vehicle mounted.[38]
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9К115-2 Metis-M/9K115 Metis |  | wire-guided anti-tank missile | | 54 | System purchased from Russia and Ukraine in early 1990s, during the war of Croatian Independence, 54 launchers and over 300 missiles in service. |
| 9M113 Konkurs |  | wire-guided anti-tank missile | | 42 | System purchased from Russia and Ukraine in early 1990s, during the war of Croatian Independence, 42 launchers and over 300 missiles in service.[39][40] To be replaced by Javelin or Eurospike at some point in near future. |
| 9K111 Fagot |  | wire-guided anti-tank missile | | 119 | Awaiting replacement by a modern tandem warhead anti tank system. |
| 9K11 Malyutka |  | wire-guided anti-tank missile | | 216 | 216 modernized launchers/missiles integrated with M-83 Polo armoured vehicle with 6 launchers installed per each vehicle and with 18 vehicles deployed per each combat brigade, complete withdrawal from service by end of 2016, to be replaced by modern tandem warhead system after 2015. Javelin and EuroSpike are being considered as a replacement, with Javelin having considerable advantage due to commonality issue with Patria AMV 30mm ATGM RWS turrets. |
| RL90 M95 |  | RPG | | 770 | over 1500 systems available, with 770 in service deployed with 4-6 with each combat platoon. To be phased out by 2017 and kept in reserve, replaced entirely by Swedish made Carl Gustav recoilless rifle after 2017. |
| AT4 |  | RPG | | ~ | The exact number of these weapons is unknown.[41] |
With the end of the conflict in Croatia at the end of 1995 Croatia inherited large stockpile of Yugoslav era weapons systems. Decision was made to modify two battalions of D-30 HR M94 Soviet-made artillery systems to be compatible with NATO firing tables as an interim and cheap solution, with rest of the artillery stockpile kept in prepared state of reediness.
The situation is very dire, with the Croatian Army having no artillery system capable of hitting targets beyond 20 km, to avert what was a serious shortcoming the Croatian MOD placed an order for modern NATO artillery system with capability that can exceeds 20 km range requirement. According to media reports, the Croatian MOD chose to purchase 12+3 Panzerhaubitze 2000 (or one battalion) howitzers from the German Army stock for $48 million. The system will be delivered in 2015 and 2016 with all the support infrastructure required including training and logistic and supply trucks.[42][43]
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M57 | | 60mm Mortar | | 69 | 1253 kept in reserve [16] mortar has effective range of 3500m with standard projectile. Mortar underwent modification to meet NATO requirements. |
| M96 | | 82mm Mortar | | 69 | 360 kept in reserve, improved copy of the Yugoslav M69 mortar[16] Mortar has 5600m effective range with a standard projectile, 4200m illuminating projectile and 4800m with light anti armour projectile. Mortar underwent modification to meet NATO requirements. |
| M75 | | 120mm Mortar | | 43 | 201 kept in reserve[16] Mortar has 9500m effective range with a standard round projectile, and 5500m with illuminating projectile. Mortar underwent modification to meet NATO requirements. |
| 75 mm M116 howitzer |  | Howitzer 75mm | | 12 | of 57 artillery pieces only 12 are kept in active service primarily as ceremonial cannons, remaining cannons to be phased out by the end of 2015/6. |
| M56/M101 |  | Howitzer105mm | | 48 | Some are US and some Yugoslav-built under license. Some 44 kept in reserve with additional 4 used for training. Last ammunition check was conducted in October, 2015.[44] |
| D-30 RH M94 |  | Howitzer 122mm | | 54 | Modified Russian D-30 howitzers brought in line with NATO commonality standards. One is in a museum and 3 loaned to NATO's Joint Multinational Training Centre in Hohenfels in Germany for extend time.[45] To be kept in service for the foreseeable future. Four units took part in the military parade in 2015.[11] |
| 130 mm towed field gun M1954 (M-46) |  | Howitzer 130mm | | 72 | To be kept serviceable for the reserve forces. Two units took part in the military parade in 2015. Last ammunition check was conducted in October, 2015.[44] |
| CITER 155mm L33 Gun | | Howitzer 155mm | | 18 | All systems operational.[16][46] |
| 2S1 Gvozdika |  | Self-propelled howitzer 122mm | | 9[16] | Due to be augmented by 12 Panzerhaubitze 2000 and possibly replaced by 6 additional PzH2000 in the long term. Plan for limited modernization the system including installation of NATO compatible combat and communication equipment. 6 systems in use and 3 used as spare. To form armoured self-propelled artillery battalion. |
| Panzerhaubitze 2000 |  | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | | 15+Simulator | Ordered from German Army reserve stock, the $54 million contract for 12 (plus three for spare parts) howitzers includes modernization and upgrade to said howitzers with support equipment, spare parts and training simulator included. With delivery starting in 2015, with the first 6 to join the Croatian Army in the second half of 2015 and the remaining vehicles to be delivered after a general overhaul by the German Army in mid-2016/7.[47][48] Originally Croatia was negotiating 18 systems, but German Army will retain additional vehicles envisaged under earlier announced defence cuts thus only 12 Howitzers were offered to Croatia as part of the deal, which also included complete modernization of the system and overhaul to meet the latest NATO standards.[49] First two howitzers delivered, 13+1 simulator more to be delivered over coming 18 months[50] |
| RAK-12 |  | MRL 128mm Towed | | 68 | Some 8 systems are in active service while additional 60 are kept in reserve status. |
| APR–40 |  | MRL 122mm | | 36 | Ordered from Romania in 1992–1993. Replacement by modern NATO system is a priority under new defence white paper, no mention of what system would replace current Multiple launch Systems in service, talks are being held with US and German governments on possible purchase of M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (M270 MLRS), Croatian requirements call for initially 8 systems to form a two battery teams at independent Artillery regiment, with potential for further 16 systems to equip 2 active brigades for total of 24 systems + simulators and training aids. Number of systems Croatian Army might purchase will solely depend on price of the entire purchase and delivery dates, Croatian Defence budget has set aside some 200 million kuna or $32 million for this program, although it is likely said systems might be donated by the US for symbolic price in turn Croatian MOD paying only VAT for said vehicles in which case price tag might be negligible and affordable. |
The logistic component of the Croatian Army is being renewed continuously and over the past decade a number of new vehicle have been procured. Stated requirement calls for 1,250 5-10 ton military trucks, 550 4WD Jeeps of all sorts and a number of other support and utility vehicles. In recent times, the Croatian MOD has signed procurement agreements with MAN, Iveco, Mercedes and Astra Iveco. Most notably in recent history was a corruption affair that resulted in the dismissal and subsequent custodial sentence for former defence minister Berislav Rončević who 'approved procurement of 33 Iveco Astra Military Trucks at inflated price without holding a public procurement tender that is a standard procedure in any major defence procurement program.'
The Croatian MOD has since purchased a number of new military trucks and 4WD vehicles through public procurement program; the latest being a 2011 procurement of some 80 Mercedes, MAN Trucks and 120 Toyota and Nissan 4WD vehicles. Although, as of late 2012, nearly half of the Croatian Army's logistics inventory is obsolete or near obsolete and in need of a replacement.[51]
As of late 2012, the Croatian Army lacks some 400 Military trucks of all sorts. Also, many vehicles in the current stock are quite obsolete and in need of replacing. The problem is furthermore escalated by the fact that the Defence Budget for 2013 has been slashed by 250 million kuna, further reducing the probability of the Croatian Army receiving new logistic vehicles.
The Croatian Army is now looking at getting some German Army surplus stock that is in good condition and available for use; 300–400 Army trucks are needed and it is likely they'll all come from German Army surplus – most likely MAN KAT1 army trucks.
Logistic vehicles
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iveco | .jpg) | 5T Transport Truck | | 120+ | initial order of 39 vehicles made in 2005 and subsequent order for additional 80 vehicles in 2008 and 2009.Currently over 120 vehicles in service. |
| Iveco |  | Medium and Heavy Trucks | | 120+ | initial order of a half a dozen or so vehicles made in 2007. Most are used along with the MAN Trucks for heavy Transporter role. . Chosen as the main heavy truck for Croatian Army Service. To replace older FAP, TAM, MAN trucks in service with the Army. Number to vehicles to rise, however due to shortage of funds major purchases are avoided. Currently about dozen or so new vehicles are ordered and delivered each year. |
| TAM |  | Utility Truck | | 600~ | large number of these trucks in various configurations still serve in many roles within Croatian Army, they're being replaced by modern models but, due to defence cutbacks, these vehicles are likely to remain in service for the foreseeable future. These vehicles are, in many cases, now over 40 years old; replacement is sought when and where possible. |
| Mercedes-Benz Actros 6x6, 8x8 |  | Heavy Utility Vehicle | | 40 | Standard heavy utility vehicle of the Croatian Army, 40 units ordered in 2010, all delivered and in service by mid-2012. Iveco chosen as preferred heavy truck over Mercedes, Scania, Volvo, Renault and MAN. |
| LkW MAN 5t MIL GL 4x4 |  | 5T Truck, Troop transport | | 400 | Initial purchase of 27 German Army trucks that were stored and now being refurbished for Croatian Army for total of 380-400~ of MAN-KT types Croatian Army ordered from German Army reserve to full fill initial requirement for 1000 army trucks Croatian army needs to replace in coming years.[52][53][54] |
| MAN Tank Transporter Truck | .jpg) | 40T Truck, Tank Transporter | | 16 | 16 older MAN units in service, being replaced by modern equivalent soon. |
| Astra Truck |  | Medium Utility Vehicle | | 12~ | Standard utility vehicle of the Croatian Army, 33 units ordered in 2004, all delivered and in service. Iveco Trekker chosen as a heavy truck, future orders unlikely. |
| Daf Truck | .jpg) | Medium Utility Vehicle | | 60~ | Standard utility vehicle of the Croatian Army; 60 units received from the Dutch Army reserve stock in 2001. |
| Toyota Landcruiser |  | Utility | | 80~ | 150 Ordered in 2008 and delivered in 2010, half went to other government departments, including the Ministry of the Interior. All are in good serviceable condition; it is a standard utility vehicle in service with the Croatian Army and other governmental agencies of Croatia. |
| Mercedes G 4WD |  | Light Utility Vehicle | | 324 | Standard utility vehicle of the Croatian Army, 250 units ordered in 2002/3, all delivered and in service. An additional 74 vehicles ordered in 2008 and delivered in 2010. |
| Nissan Navara 4WD |  | Light Utility Vehicle | | 80 | Standard utility vehicle of the Croatian Army, 80 units ordered in 2010, all delivered and in service by mid-2012. Additional vehicles might be ordered to replace older vehicles currently in service. |
| Land Rover Wolf 4WD |  | Light Utility Vehicle | | 32~ | Primarily used by the Croatian Army's special forces and military police; many transferred to the Croatian Police. Of the 200 ordered in 1998, only 32 remain in service with the armed forces; some 120 transferred to civilian use, many ending up with the MUP, ministry of interior in various roles, some with Croatian Mountain Rescue Service and some with Border Patrol Units. |
- Withdrawn from service or in store
- FN FAL 7.62×51mm 5,000 stored to be sold off
- Zastava M84 7.62×54mmR, totally phased out and replaced by Western systems.
- Zastava M76, 7.92×57mm sniper rifle was phased out entirely replaced by Remington and SAKO in service with the Army.
- | M80 "Zolja" RPG - phased out due to dwindling stock, replaced by AT4
- T-55A withdrawal of over 280 units started in 2006 with a dozen or so tanks used for training until late 2009, but even that is no longer the case due to shortage of funds and all units have now been withdrawn and awaiting disposal.
- M-47 Patton (16) (2 in the local army museum and rest are target practice)
- M60P/M60SAN (45) (Yugoslav-made APCs – scrap heap and 2 in the local army museum)
- BRDM-2
- BTR-60 (16) (2 in the local army museum, scrap heap)
- ZSU-57-2 (2) (target practice)
- M53/59 Praga (24) (2 in the local army museum, scrap heap)
- MT-LB (10) 2 in local museum rest scraped and replaced by Patria AMV
- M-63 Plamen 128mm Towed MRL - retired due to lack of ammunition and costly upkeep, no spare parts for the system
- M-94 'Plamen S 128mm MRL - no longer fit for purpose, retired and awaiting disposal
- M-87 Orkan MRL 260mm, Captured during Battle of the Barracks in 1991, systems are kept in reserve status due to lack of proper ammunition.
- RPG 7 Systesm retired but some might be used by army reserve and for training purposes only.
- RPG 22 system replaced by AT4 and other RPGs currently in use with the Army.
- M-84 Nora A
- |-|M-46H1
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Army of Croatia. |
References and notes
- 1 2 Oružane snage Republike Hrvatske
- ↑ "Home – Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Croatia". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Braniteljski portal - ...Ne pitaj što domovina može učiniti za tebe, nego što ti možeš učiniti za Domovinu...". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ siser. "PROTECTOR Contract with Croatia". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Request Rejected" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 21, 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- ↑ "Republic of Croatia - Annual Exchange of Information on Defence Planning - OSCE 2012-cor1" (PDF). 18 May 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Croatia receives donated Maxxpro MRAPs". Jane's Defence Weekly. 4 September 2014. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Dugoročni plan razvoja Oružanih snaga Republike Hrvatske 2015 2024 pripremljen za objavljivanje" (PDF). 24 September 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "GODIŠNJE IZVJEŠĆE O SPREMNOSTI OBRAMBENOG SUSTAVA, PROVOĐENJU KADROVSKE POLITIKE I UKUPNOM STANJU U ORUŽANIM SNAGAMA REPUBLIKE HRVATSKE ZA 2012. GODINU, S IZVJEŠĆEM O STANJU OBRAMBENIH PRIPREMA U REPUBLICI HRVATSKOJ ZA 2012. GODINU" (PDF). REPUBLIKA HRVATSKA MINISTARSTVO OBRANE. 29 May 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Hrvatski vojnik - Internet izdanje". web.archive.org. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- 1 2 "Hrvatski vojnik - Internet izdanje". hrvatski-vojnik.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Hrvatski vojnik - Internet izdanje". web.archive.org. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Modern Firearms - IM Metal HS 2000". world.guns.ru. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Potpisivanje Ugovora o nabavi vojnih odora i jurišnih pušaka za potrebe OS RH". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Amerikanci hitno naručili 500 komada hrvatske jurišne puške – Zadarski list". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 http://arhiva.morh.hr/katalog/documents/dpr_final.pdf
- ↑ "Image: hvu_konferencija_01042014_17.jpg, (1200 × 798 px)". morh.hr. 1 April 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "HV nabavlja 20.000 novih pušaka, ugovor vrijedan 50 milijuna kuna - Večernji.hr". vecernji.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ Drazen. "Croatia delivers donated infantry weapons to Mali – Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Croatia". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Hrvatska vlada donirala Maliju oružje vrijednosti milijun kuna". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Za mir i sigurnost u Afganistanu Hrvatska donira 15.000 pušaka i 300 topova". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0d/HK_417_080810_44.jpg
- ↑ "FN Herstal delivers SCAR-H precision rifles to Lithuanian Army - Army Technology". army-technology.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "File:HK 417 080810 44.jpg". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Image: 5b2eef04df_mimohod-b-tehnika-4_750x550.jpg, (750 × 550 px)". hrvatski-vojnik.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Image: mimohod_0150.jpg, (1200 × 800 px)". osrh.hr. 5 August 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Image: mimohod_0151.jpg, (1200 × 800 px)". osrh.hr. 5 August 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Potpisano Pismo namjere između MORH-a i Đure Đakovića :: MORH - Ministarstvo obrane Republike Hrvatske - službeni web portal". web.archive.org. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "MORH plaća 10 milijuna kuna za remont četiri tenka M-84". Poslovni dnevnik. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "FOTO: Bacanje novca - nakon što je razgledao američke MRAP-ove Milanović najavio: 'Kupujemo i nova njemačka oklopna vozila' | Dnevno.hr". dnevno.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Od Linićevih rezova OSRH spašavaju jedino američki saveznici". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Neslana šala: SAD poslala Hrvatskoj vozila koja se prelako prevrću > Slobodna Dalmacija > Hrvatska". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "HRT: Emisije na zahtjev: Dnevnik: Dnevnik, 23.12.2014.". Hrvatska radiotelevizija. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- 1 2 3 "Croatia displays new AFV fleets". Jane's Defence Weekly. 25 March 2014. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- ↑ "Image: sYbuwie.jpg, (2448 × 1836 px)". i.imgur.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "HRT: HV-u predano 30 MRAP vozila - američka donacija". Hrvatska radiotelevizija. 7 April 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Prvi mimohod Oružanih snaga Republike Hrvatske 30.05.1995". YouTube. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "MINISTAR U AKCIJI Kotromanović poništio pokušaj namještanja posla Izraelcima - Jutarnji.hr". jutarnji.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ Drazen. "Bojevo gađanje protuoklopnim raketnim sustavima na Gašincima – Ministarstvo obrane RH". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Image: gadjanje_23082013_v.jpg, (1200 × 900 px)". morh.hr. 23 August 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ Richard D (January 27, 2009), Infantry Weapons 2009/2010 (35 ed.), Jane's Information, ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- ↑ "Kotromanovićev shopping za 275 milijuna za HV – Jutarnji.hr". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "SAD besplatno oprema Hrvatsku vojsku > Slobodna Dalmacija > Spektar". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- 1 2 http://www.hrvatski-vojnik.hr/multimedija/videoprilozi/vojne-vjezbe/item/1282-balisticka-ispitivanja-ubs-a.html
- ↑ "NATO – Balkan Monitor – A Defence & Security Daily". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Hrvatski vojnik - Internet izdanje". web.archive.org. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "FOTO: Vojna vježba hrvatske kopnene vojske i američkih zračnih snaga | Dnevno.hr". dnevno.hr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Hrvatska kupuje 12 njemačkih 'Panzerhaubitza'". Večernji.hr. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Croatia seeks PzH 2000 purchase". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "29.7.2015 - Prve PzH 2000 u Hrvatskoj - odlazak - YouTube". youtube.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Odbor za obranu o Godišnjem izvješću o spremnosti". Obrana i sigurnost. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "MORH traži hitan remont 27 njemačkih kamiona LkW MAN 5t MIL GL 4x4". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Image: grrc129sbd300w4elo6x.jpg, (2048 × 1158 px)". zaslike.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "Image: iuqj30g7ugwu7vagb1vw.jpg, (2048 × 1158 px)". zaslike.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.