Endoscopy
| Endoscope | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
 An example of a flexible endoscope | |
| MeSH | D004724 |
| OPS-301 code | 1-40...1-49, 1-61...1-69 |
| MedlinePlus | 003338 |

Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope,[1] an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ.
There are many different types of endoscope, and depending on the site in the body and the type of procedure, endoscopy may be performed by a doctor or a surgeon, and the patient may be fully conscious or anaesthetised. Most often the term endoscopy is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy.[2]
For non-medical use, similar instruments are called borescopes.
Medical uses
A health care provider may use endoscopy for any of the following:
- investigation of symptoms, such as symptoms in the digestive system including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing and gastrointestinal bleeding.[3]
- confirmation of a diagnosis, most commonly by performing a biopsy to check for conditions such as anemia, bleeding, inflammation, and cancers of the digestive system.[3]
- giving treatment, such as cauterization of a bleeding vessel, widening a narrow esophagus, clipping off a polyp or removing a foreign object.[3]
Specialty professional organizations which specialize in digestive problems advise that many patients with Barrett's esophagus are too frequently receiving endoscopies.[4] Such societies recommend that patients with Barrett's esophagus and no cancer symptoms after two biopsies receive biopsies as indicated and no more often than the recommended rate.[5][6]
Applications

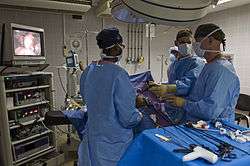
Health care providers can use endoscopy to review any of the following body parts:
- The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract):
- oesophagus, stomach and duodenum (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
- small intestine (enteroscopy)
- large intestine/colon (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy)
- Magnification endoscopy
- bile duct
- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), duodenoscope-assisted cholangiopancreatoscopy, intraoperative cholangioscopy
- rectum (rectoscopy) and anus (anoscopy), both also referred to as (proctoscopy)
- The respiratory tract
- The nose (rhinoscopy)
- The lower respiratory tract (bronchoscopy)
- The ear (otoscope)
- The urinary tract (cystoscopy)
- The female reproductive system (gynoscopy)
- The cervix (colposcopy)
- The uterus (hysteroscopy)
- The fallopian tubes (falloposcopy)
- Normally closed body cavities (through a small incision):
- The abdominal or pelvic cavity (laparoscopy)
- The interior of a joint (arthroscopy)
- Organs of the chest (thoracoscopy and mediastinoscopy)
Endoscopy is used for many procedures:
- During pregnancy
- Plastic surgery
- Panendoscopy (or triple endoscopy)
- Combines laryngoscopy, esophagoscopy, and bronchoscopy
- Orthopedic surgery
- Hand surgery, such as endoscopic carpal tunnel release
- Knee surgery, such as anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Epidural space (Epiduroscopy)
- Bursae (Bursectomy)
- Endodontic surgery
- Maxillary sinus surgery
- Apicoectomy
- Endoscopic endonasal surgery
- Endoscopic spinal surgery
An Endoscopy is a simple procedure which allows a doctor to look inside human bodies using an instrument called an endoscope. A cutting tool can be attached to the end of the endoscope, and the apparatus can then be used to perform surgery. This type of surgery is called Key hole surgery, and usually leaves only a tiny scar externally.
Application in other fields
- The planning and architectural community use architectural endoscopy for pre-visualization of scale models of proposed buildings and cities
- Internal inspection of complex technical systems (borescope)
- Endoscopes are also a tool helpful in the examination of improvised explosive devices by bomb disposal personnel.
- The FBI uses endoscopes for conducting surveillance via tight spaces.
Risks
The main risks are infection, over-sedation, perforation, or a tear of the stomach or esophagus lining and bleeding. Although perforation generally requires surgery, certain cases may be treated with antibiotics and intravenous fluids. Bleeding may occur at the site of a biopsy or polyp removal. Such typically minor bleeding may simply stop on its own or be controlled by cauterisation. Seldom does surgery become necessary.
Perforation and bleeding are rare during gastroscopy.
Other minor risks include drug reactions and complications related to other diseases the patient may have. Consequently, patients should inform their doctor of all allergic tendencies and medical problems.
Occasionally, the site of the sedative injection may become inflamed and tender for a short time. This is usually not serious and warm compresses for a few days are usually helpful.
While any of these complications may possibly occur, it is good to remember that each of them occurs quite infrequently.
A doctor can further discuss risks with the patient with regard to the particular need for gastroscopy.
After the endoscopy
After the procedure the patient will be observed and monitored by a qualified individual in the endoscopy room or a recovery area until a significant portion of the medication has worn off. Occasionally the patient is left with a mild sore throat, which may respond to saline gargles, or chamomile tea. It may last for weeks or not happen at all. The patient may have a feeling of distention from the insufflated air that was used during the procedure. Both problems are mild and fleeting. When fully recovered, the patient will be instructed when to resume their usual diet (probably within a few hours) and will be allowed to be taken home. Where sedation has been used, most facilities mandate that the patient be taken home by another person and that he or she not drive or handle machinery for the remainder of the day. Patients who have had an endoscopy without sedation are able to leave unassisted.
Endoscope
An endoscope can consist of:
- a rigid or flexible tube.
- a light delivery system to illuminate the organ or object under inspection. The light source is normally outside the body and the light is typically directed via an optical fiber system.
- a lens system transmitting the image from the objective lens to the viewer, typically a relay lens system in the case of rigid endoscopes or a bundle of fiberoptics in the case of a fiberscope.
- an eyepiece. Modern instruments may be videoscopes, with no eyepiece. A camera transmits image to a screen for image capture.
- an additional channel to allow entry of medical instruments or manipulators.
Patients undergoing the procedure may be offered sedation, which includes its own risks, including permanent cognitive impairments.
History
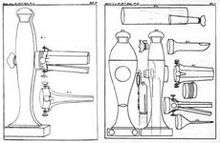
The first endoscope was developed in 1806 by Philipp Bozzini in Mainz with his introduction of a "Lichtleiter" (light conductor) "for the examinations of the canals and cavities of the human body".[7] However, the Vienna Medical Society disapproved of such curiosity. The first to use an endoscope in a successful operation was Antonin Jean Desormeaux whose invention was the state of the art before the invention of electricity.
The use of electric light was a major step in the improvement of endoscopy. The first such lights were external although sufficiently capable of illumination to allow cystoscopy, hysteroscopy and sigmoidoscopy as well as examination of the nasal (and later thoracic) cavities as was being performed routinely in human patients by Sir Francis Cruise (using his own commercially available endoscope) by 1865 in the Mater Misericordiae Hospital in Dublin, Ireland.[8] Later, smaller bulbs became available making internal light possible, for instance in a hysteroscope by Charles David in 1908.
Hans Christian Jacobaeus has been given credit for the first large published series of endoscopic explorations of the abdomen and the thorax with laparoscopy (1912) and thoracoscopy (1910) although the first reported thoracoscopic examination in a human was also by Cruise.[9]
Laparoscopy was used in the diagnosis of liver and gallbladder disease by Heinz Kalk in the 1930s.[10] Hope reported in 1937 on the use of laparoscopy to diagnose ectopic pregnancy. In 1944, Raoul Palmer placed his patients in the Trendelenburg position after gaseous distention of the abdomen and thus was able to reliably perform gynecologic laparoscopy.
Wolf and Storz
Georg Wolf (1873–1938) a Berlin manufacturer of rigid endoscopes, established in 1906, produced the Sussmann flexible gastroscope in 1911(Modlin,Farhadi-Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 2000).[11] Karl Storz began producing instruments for ENT specialists in 1945.[12] His intention was to develop instruments which would enable the practitioner to look inside the human body. The technology available at the end of the Second World War was still very modest: The area under examination in the interior of the human body was illuminated with miniature electric lamps; alternatively, attempts were made to reflect light from an external source into the body through the endoscopic tube. Karl Storz pursued a plan: he set out to introduce very bright, but cold light into the body cavities through the instrument, thus providing excellent visibility while at the same time allowing objective documentation by means of image transmission.
With more than 400 patents and operative samples to his name, which were to play a major role in showing the way ahead, Karl Storz played a crucial role in the development of endoscopy. It was however, the combination of his engineering skills and vision, coupled with the work of optical designer Harold Hopkins that ultimately would revolutionize the field of medical optics.[13]
Fiber optics
Basil Hirschowitz and Larry Curtiss invented the first fiber optic endoscope in 1957.[14] Earlier in the 1950s Harold Hopkins had designed a "fibroscope" consisting of a bundle of flexible glass fibres able to coherently transmit an image. This proved useful both medically and industrially, and subsequent research led to further improvements in image quality. Further innovations included using additional fibres to channel light to the objective end from a powerful external source, thereby achieving the high level of full spectrum illumination that was needed for detailed viewing, and colour photography.
The previous practice of a small filament lamp on the tip of the endoscope had left the choice of either viewing in a dim red light or increasing the light output - which carried the risk of burning the inside of the patient. Alongside the advances to the optics, the ability to 'steer' the tip was developed, as well as innovations in remotely operated surgical instruments contained within the body of the endoscope itself. This was the beginning of "key-hole surgery" as we know it today.
Rod-lens endoscopes
There were physical limits to the image quality of a fibroscope. A bundle of say 50,000 fibers gives effectively only a 50,000-pixel image, and continued flexing from use breaks fibers and so progressively loses pixels. Eventually so many are lost that the whole bundle must be replaced (at considerable expense). Harold Hopkins realised that any further optical improvement would require a different approach. Previous rigid endoscopes suffered from low light transmittance and poor image quality. The surgical requirement of passing surgical tools as well as the illumination system within the endoscope's tube - which itself is limited in dimensions by the human body - left very little room for the imaging optics. The tiny lenses of a conventional system required supporting rings that would obscure the bulk of the lens area; they were difficult to manufacture and assemble and optically nearly useless.
The elegant solution that Hopkins invented was to fill the air-spaces between the 'little lenses' with rods of glass. These fitted exactly the endoscope's tube, making them self-aligning, and required no other support. This allowed the little lenses to be dispensed with altogether. The rod-lenses were much easier to handle and used the maximum possible diameter available.
With the appropriate curvature and coatings to the rod ends and optimal choices of glass-types, all calculated and specified by Hopkins, the image quality was transformed - even with tubes of only 1mm in diameter. With a high quality 'telescope' of such small diameter the tools and illumination system could be comfortably housed within an outer tube. Once again it was Karl Storz who produced the first of these new endoscopes as part of a long and productive partnership between the two men.[15]
Whilst there are regions of the body that will always require flexible endoscopes (principally the gastrointestinal tract), the rigid rod-lens endoscopes have such exceptional performance that they are still the preferred instrument and have enabled modern key-hole surgery. (Harold Hopkins was recognized and honoured for his advancement of medical-optic by the medical community worldwide. It formed a major part of the citation when he was awarded the Rumford Medal by the Royal Society in 1984.)
By measuring absorption of light by the blood (by passing the light through one fibre and collecting the light through another fibre) a doctor can estimate the proportion of haemoglobin in the blood and diagnose ulceration in the stomach.
Disinfection
Disinfection is essential for all types of endoscopes. The first disinfection device was constructed by S.E. Miederer in 1976 at the University of Bonn in Germany.
In the UK, stringent guidelines exist regarding the decontamination and disinfection of flexible endoscopes, the most recent being CfPP 01–06, released in 2013[16]
Rigid endoscopes, such as an Arthroscope, can be sterilized in the same way as surgical instruments, whereas heat labile flexible endoscopes cannot.
Recent developments

With the application of robotic systems, telesurgery was introduced as the surgeon could be at a site far removed from the patient. The first transatlantic surgery has been called the Lindbergh Operation.
Wireless oesophageal pH measuring devices can now be placed endoscopically, to record ph trends in an area remotely.
Endoscopy VR simulators
Virtual reality simulators are being developed for training doctors on various endoscopy skills.[17]
Disposable endoscopy
Disposable endoscopy is an emerging category of endoscopic instruments. Recent developments[18] have allowed the manufacture of endoscopes inexpensive enough to be used on a single patient only. It is meeting a growing demand to lessen the risk of cross contamination and hospital acquired diseases. A European consortium of SME are working on the DUET project to build a disposable endoscope.[19]
Capsule endoscopy
A new endoscopy technology uses a Magnetically Guided Capsule Endoscope (MGCE) for wireless control, monitor and imaging.[20]
Augmented reality
The endoscopic image can be combined with other image sources to provide the surgeon with additional information. For instance, the position of an anatomical structure or tumor might be shown in the endoscopic video.[21]
Measuring endoscopy
Current research works on the endoscopic collection of dimensional 3D-data, such as using laser triangulation or the approach of structured light projection. Depending on the optics used, inner geometries can be measured with accuracies in the low µm region. Other emerging endoscope technologies are emerging that measure additional optical properties of light, such as optical polarization,[22] optical phase,[23] and hyperspectral endoscopy, which records images at many different wavelengths.[24]
References
- ↑ "Endoscopy". British Medical Association Complete Family Health Encyclopedia. Dorling Kindersley Limited. 1990.
- ↑ "Endoscopy". Cancer Research UK. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 Mayo Clinic staff (2012). "Upper endoscopy". mayoclinic.com. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- ↑ American Gastroenterological Association, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF), Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Gastroenterological Association, retrieved August 17, 2012
- ↑ Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ; Spechler; Sharma; Souza; Inadomi; Shaheen (2011). "American Gastroenterological Association Medical Position Statement on the Management of Barrett's Esophagus". Gastroenterology. 140 (3): 1084–1091. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.030. PMID 21376940.
- ↑ Wang KK, Sampliner RE; Sampliner; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology (2008). "Updated Guidelines 2008 for the Diagnosis, Surveillance and Therapy of Barrett's Esophagus". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 103 (3): 788–797. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01835.x. PMID 18341497.
- ↑ Bozzini (1806) "Lichtleiter, eine Erfindung zur Anschauung innerer Teile und Krankheiten, nebst der Abbildung" (Light conductor, an invention for examining internal parts and diseases, together with illustrations), Journal der practischen Arzneykunde und Wundarzneykunst (Journal of Practical Medicine and Surgery), 24 : 107-124.
- ↑ "The utility of the endoscope as an aid in the diagnosis and treatment of disease" by Francis Richard Cruise. The Dublin Quarterly Journal of Medical Science. February 1, 1865.
- ↑ "Clinical Reports of Rare Cases, occurring in the Whitworth and Harwicke Hospitals" by Samuel Gordon. Dublin Quarterly Journal of Medical Science February 1, 1866
- ↑ Egmont Wildhirt: Kalk, Heinrich-Otto. In: Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB). Band 11, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin 1977, ISBN 3-428-00192-3, S. 60 f. (Digitalisat).
- ↑ Georg Wolf
- ↑ Camran Nezhat. The Legacy of Karl Storz - Engineering Endoscopic Magic
- ↑ Harold Hopkins THE KARL STORZ CONNECTION
- ↑ Edmonson JM (1991). "History of the instruments for gastrointestinal endoscopy". Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 37 (2 Suppl): S27–S56. doi:10.1016/S0016-5107(91)70910-3. PMID 2044933.
- ↑ Harold Hopkins and Karl Storz
- ↑ https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/148559/CFPP_01-06_Operational_mgmt_Final.pdf
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ogMr5u5oqN8
- ↑ "Dokument nicht gefunden".
- ↑ "Development of a Disposable Use Endoscopy Tool".
- ↑ "Health imaging hub".
- ↑ Augmented Reality: Path guidance to craniopharyngioma on YouTube
- ↑ Manhas S, Vizet J, Deby S, Vanel J, Boito P, Verdier M, De Martino A, Pagnoux D; Manhas; Vizet; Deby; Vanel; Boito; Verider; De Martino; Pagnoux (2015). "Demonstration of full 4×4 Mueller polarimetry through an optical fiber for endoscopic applications". Optics Express. 23 (3): 3047–3054. doi:10.1364/OE.23.003047.
- ↑ Gordon GSD, Joseph J, Bohndiek SE, Wilkinson TD; Gordon; Joseph; Bohndiek; Wilkinson (2015). "Single-Pixel Phase-Corrected Fiber Bundle Endomicroscopy With Lensless Focussing Capability". IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology. 33 (16): 3419–3425. doi:10.1109/JLT.2015.2436816.
- ↑ Kester RT, Bernard N, Gao L, Tkaczyk TS; Kester; Bernard; Gao; Tkaczyk (2011). "Real-time snapshot hyperspectral imaging endoscope". Journal of Biomedical Optics. 16 (5). doi:10.1117/1.3574756.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Endoscopy. |
- The Atlas of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy endoatlas.com
- El Salvador Atlas of Gastroinstestinal Endoscopy
- Gastrolab: Site in English, Swedish and Finnish with gastrointestinal endoscopy photolibrary
- Preventing cross-contamination from flexible endoscopes massdevice.com
- Advances in Endoscopy advancedimagingpro.com