Francisco Pizarro
| Marquess Francisco Pizarro | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Francisco Pizarro by Amable-Paul Coutan, 1835 | |
| Governor of New Castile | |
|
In office 26 July 1529 – 26 June 1541 | |
| Monarch | Charles I |
| Succeeded by | Cristóbal Vaca de Castro |
| Captain General of New Castile | |
|
In office 26 July 1529 – 26 June 1541 | |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
c. 1471 or 1476 Trujillo, Crown of Castile |
| Died |
26 June 1541 (aged 65–70) Lima, New Castile |
| Spouse(s) | Inés Huaylas Yupanqui |
| Children | Francisca Pizarro Yupanqui |
| Religion | Catholic |
| Signature |
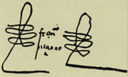 |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance |
|
| Years of service | 1496–1541 |
| Battles/wars | Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire |
Francisco Pizarro González (/pɪˈzɑːroʊ/; Spanish: [piˈθaro]; circa 1471 or 1476 – 26 June 1541) was a Spanish conquistador who led an expedition that conquered the Inca Empire. He captured and killed Incan emperor Atahualpa and claimed the lands for Spain.
Early life
Francisco Pizarro was born in Trujillo, Spain (then in the Crown of Castile) in modern-day Extremadura, Spain. He was the illegitimate son of infantry colonel Gonzalo Pizarro (1446–1522) and Francisca González, a woman of poor means. His date of birth is uncertain, but it is believed to be sometime in the 1470s, probably 1474. Little attention was paid to his education and he grew up illiterate.[1]
His father was a colonel of infantry who served in Navarre and in the Italian campaigns under Córdoba. His mother married late in life and had a son Francisco Martín de Alcántara, who was at the conquest of Peru with his half-brother from its inception.[2] Through his father, Francisco was a second cousin, once removed, of Hernán Cortés.[3]
On 10 November 1509, Pizarro sailed from Spain to the New World with Alonso de Ojeda on an expedition to Gulf of Urabá in Tierra Firme. Pizarro became a participant in Ojeda's failed colony, commanding the remnants until he abandoned it with the survivors.[4]:93 He sailed to Cartagena and joined the fleet of Martín Fernández de Enciso in 1513.
Career
Panama
In 1513, Pizarro accompanied Vasco Núñez de Balboa in his crossing of the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific coast.[5] The following year, Pedrarias Dávila became the newly appointed governor of Castilla de Oro and succeeded Balboa. During the next five years, Pizarro became a close associate of Dávila and the governor assigned him a repartimiento of natives and cattle.[4]:93 When Dávila decided to get rid of Balboa out of distrust, he instructed Pizarro to personally arrest him and bring him to stand trial. Balboa was beheaded in January 1519. For his loyalty to Dávila, Pizarro was rewarded with the positions of mayor (Alcalde) and magistrate of the then recently founded Panama City from 1519 to 1523.
Conquistador
On 10 November 1509, Pizarro sailed from Spain to the New World with Alonzo de Ojeda on an expedition to Urabí. He sailed to Cartagena and joined the fleet of Martín Fernández de Enciso and, in 1513, accompanied Balboa to the Pacific.[1] In 1514, he found a supporter in Pedrarias Dávila, the Governor of Castilla de Oro and was rewarded for his role in the arrest of Balboa with the positions of mayor and magistrate in Panama City, serving from 1519 to 1523.
Reports of Peru's riches and Cortés's success in Mexico tantalized Pizarro. He undertook two expeditions to conquer the Incan Empire in 1524 and in 1526. Both failed as a result of native hostilities, bad weather and lack of provisions.
Pedro de los Ríos, the Governor of Panama, made an effort to recall Pizarro, but the conquistador resisted and remained in the south. In April 1528, he reached northern Peru and found the natives rich with precious metals. This discovery gave Pizarro the motivation to plan a third expedition to conquer the area. He returned to Panama to make arrangements, but the Governor refused to grant permission for the project. Pizarro returned to Spain to appeal directly to King Charles I. His plea was successful and he received not only a license for the proposed expedition, but also authority over any lands conquered during the venture. He was joined by family and friends and the expedition left Panama in 1530.
When hostile natives along the coast threatened the expedition, Pizarro moved inland and founded the first Spanish settlement in Peru, San Miguel de Piura. Atahualpa refused to tolerate a Spanish presence in his lands, but was captured by Pizarro during the Battle of Cajamarca on 16 November 1532. A ransom for the emperor's release was demanded and Atahualpa filled a room with gold, but Pizarro charged him with various crimes and executed him on 26 July 1533, overriding his associates who thought he was overstepping his authority. The same year, Pizarro entered the Inca capital of Cuzco and completed his conquest of Peru. In January 1535, Pizarro founded the city of Lima, a project he considered his greatest achievement. Quarrels between Pizarro and his longtime comrade-in-arms Diego Almagro culminated in the Battle of Las Salinas. Almagro was captured and executed and, on 26 June 1541, his embittered son, Diego de Almagro "el mozo", assassinated Pizarro in Lima. The conquistador of Peru was laid to rest in the Lima Cathedral.
Expeditions to South America
The first attempt to explore western South America was undertaken in 1522 by Pascual de Andagoya. The native South Americans he encountered told him about a gold-rich territory called Virú, which was on a river called Pirú (later corrupted to Perú).[5]:24 These reports were related by the Spanish-Inca mestizo writer Garcilaso de la Vega in Comentarios Reales de los Incas (1609).
Andagoya eventually established contact with several Native American curacas (chiefs), some of whom he later claimed were sorcerers and witches. Having reached as far as the San Juan River (part of the present boundary between Ecuador and Colombia) Andagoya fell ill and returned to Panama. He spread the news and stories about "Pirú" – a great land to the south rich with gold (the legendary El Dorado). These revelations, along with the accounts for Cortés' success in Mexico, caught the attention of Pizarro, prompting a series of expeditions to the south.
In 1524, while still in Panama, Pizarro formed a partnership with a priest, Hernando de Luque and a soldier, Diego de Almagro, to explore and conquer the South. Pizarro, Almagro and Luque later explicitly renewed their compact,[5]:24 agreeing to conquer and divide equally among themselves the empire they hoped to vanquish. While their accord was strictly oral, they dubbed their enterprise the Empresa del Levante and determined that Pizarro would command the expedition, Almagro would provide military and food supplies and Luque would be in charge of finances and additional provisions.[4]:95
First expedition (1524)
In November 1524, the first of three expeditions left Panama for the conquest of Peru with about 80 men and 40 horses.[5]:24 Juan de Salcedo was the standard bearer, Nicolas de Ribera was the treasurer and Juan Carvallo was the inspector.[6]:45,47
Diego de Almagro was left behind because he was to recruit men, gather additional supplies and join Pizarro later. The Governor of Panama, Pedro Arias Dávila, at first approved in principle of exploring South America. Pizarro's first expedition, however, turned out to be a failure as his conquistadores, sailing down the Pacific coast, reached no farther than Colombia before succumbing to bad weather, lack of food and skirmishes with hostile natives, one of which caused Almagro to lose an eye by arrow-shot. The place names the Spanish bestowed along their route, including Puerto Deseado (desired port), Puerto del Hambre (port of hunger) and Punta Quemado or Puebla Quemado (burned port), confirmed their difficulties. Fearing subsequent hostile encounters like the one the expedition endured at the Battle of Punta Quemada, Pizarro ended his first expedition and returned to Panama.[4]:94–102
Second expedition (1526)
Two years later Pizarro, Almagro and Luque started the arrangements for a second expedition with permission from Pedrarias Dávila. The governor, who himself was preparing an expedition north to Nicaragua, was reluctant to permit another expedition, having lost confidence in Pizarro. The three associates eventually won his trust and he acquiesced. By this time, a new governor was to arrive and succeed Dávila. Pedro de los Ríos took charge in July 1526 and initially approved Pizarro's expeditions (he would join him several years later in Peru).[4]:103–104
On 10 March 1526 Pizarro left Panama with two ships with 160 men and several horses, reaching as far as the Colombian San Juan River. Soon after arriving the party separated, with Pizarro staying to explore the new and often perilous territory off the swampy Colombian coasts, while the expedition's co-commander, Almagro, returned to Panama for reinforcements. Pizarro's Piloto Mayor (main pilot), Bartolomé Ruiz, continued sailing south and, after crossing the equator, found and captured a balsa (raft) under sail, with natives from Tumbes. To everyone's surprise, these carried textiles, ceramic objects and some pieces of gold, silver and emeralds, making Ruiz's findings the central focus of this second expedition. Some natives were taken aboard Ruiz's ship to serve as interpreters.[4]:105–109[5]:24–25
He then set sail north for the San Juan River, arriving to find Pizarro and his men exhausted from the difficulties they had faced exploring the new territory. Soon Almagro sailed into the port laden with supplies and a reinforcement of at least eighty recruits who had arrived at Panama from Spain with an expeditionary spirit. The findings and excellent news from Ruiz along with Almagro's new reinforcements cheered Pizarro and his tired followers. They decided to sail back to the territory already explored by Ruiz and, after a difficult voyage due to strong winds and currents, reached Atacames on the Ecuadorian coast. Here, they found a large native population recently brought under Inca rule. Unfortunately for the conquistadores, the warlike spirit of the people they encountered seemed so defiant and dangerous in numbers that the Spanish decided not to enter the land.[4]:110–112
The Famous Thirteen
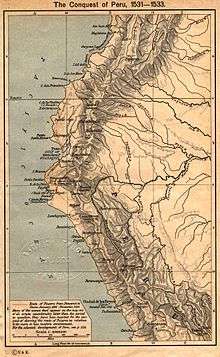
After much wrangling between Pizarro and Almagro, it was decided that Pizarro would stay at a safer place, the Isla de Gallo,[5]:25–26 near the coast, while Almagro would return to Panama with Luque for more reinforcements – this time with proof of the gold they had found and the news of the discovery of the obviously wealthy land they had explored. The new governor of Panama, Pedro de los Ríos, had learned of the mishaps of Pizarro's expeditions and the deaths of various settlers who had gone with him. Fearing an unsuccessful outcome, he rejected Almagro's application for continued resources. In addition, he ordered two ships commanded by Juan Tafur to be sent immediately with the intention of bringing Pizarro and his crew back to Panama.[4]:112–115
Pizarro had no intention of returning and when Tafur arrived at Isla de Gallo, Pizarro drew a line in the sand, saying: "There lies Peru with its riches; Here, Panama and its poverty. Choose, each man, what best becomes a brave Castilian. For my part, I go to the south."[4]:116
Only 13 men stayed with Pizarro. They later became known as "The Famous Thirteen" (Los trece de la fama),[5]:26 while the rest of the expeditioners stayed with Tafur. Ruiz left in one of the ships with the intention of joining Almagro and Luque in their efforts to gather reinforcements. Soon after the ships left, Pizarro and his men constructed a crude boat and journeyed 25 leagues north to La Isla Gorgona, where they would remain for seven months before the arrival of new provisions.[4]:117–118
Back in Panama, Pedro de los Ríos (after much convincing by Luque) had finally acquiesced to the requests for another ship, but only to bring Pizarro back within six months and completely abandon the expedition. Almagro and Luque grasped the opportunity and left Panama (this time without new recruits) for La Isla Gorgona to once again join Pizarro. On meeting with Pizarro, the associates decided to continue sailing south on the recommendations of Ruiz's Indian interpreters.[4]:118
By April 1528, they finally reached the northwestern Peruvian Tumbes Region. Tumbes became the first success the Spanish had so long desired. They were received with a warm welcome of hospitality and provisions from the Tumpis, the local inhabitants. On subsequent days two of Pizarro's men, Alonso de Molina and Pedro de Candia, reconnoitered the territory and both, on separate accounts, reported back the riches of the land, including the decorations of silver and gold around the chief's residence and the hospitable attentions with which they were received by everyone. The Spanish also saw for the first time the Peruvian llama,[5]:26 which Pizarro called "little camels". The natives began calling the Spanish the "Children of the Sun" due to their fair complexions and brilliant armor. Pizarro, meanwhile, continued receiving the same accounts of a powerful monarch who ruled over the land they were exploring. These events served as evidence to convince the expedition that the wealth and power displayed at Tumbes were an example of the riches of the Peruvian territory. The conquistadors decided to return to Panama to prepare the final expedition of conquest with more recruits and provisions. Before leaving, however, Pizarro and his followers sailed south along the coast to see if anything of interest could be found. Historian William H. Prescott recounts that after passing through territories they named such as Cabo Blanco, port of Payta, Sechura, Punta de Aguja, Santa Cruz and Trujillo (founded by Almagro years later), they finally reached for the first time the ninth degree of the southern latitude in South America.
On their return towards Panama, Pizarro briefly stopped at Tumbes, where two of his men had decided to stay to learn the customs and language of the natives. Pizarro was also given two Peruvian boys to learn Spanish, one of whom was later baptized as Felipillo and served as an important interpreter, the equivalent of Cortés' La Malinche of Mexico, and another called Martinillo.[6]:126,128 Their final stop was at La Isla Gorgona, where two of his ill men (one had died) had stayed. After at least 18 months away, Pizarro and his followers anchored off the coasts of Panama to prepare for the final expedition.[4]:119–126
Capitulación de Toledo
When the new governor of Panama, Pedro de los Ríos, refused to allow for a third expedition to the south, the associates resolved for Pizarro to leave for Spain and appeal to the sovereign in person. Pizarro sailed from Panama for Spain in the spring of 1528, accompanied by Pedro de Candia, some natives and llamas, plus samples of fabric, gold and silver.[4]:127–128
Pizzaro reached Seville in early summer. King Charles I, who was at Toledo, had an interview with Pizarro and heard of his expeditions in South America. The conquistador described the territory as rich in gold and silver that he and his followers had bravely explored "to extend the empire of Castile". The king, who was soon to leave for Italy, was impressed at his accounts and promised his support for the conquest of Peru. Queen Isabel, though, in the absence of the king, signed the Capitulación de Toledo on 6 July 1529,[7] a license document that authorized Pizarro to proceed with the conquest of Peru. Pizarro was officially named the Governor, Captain general, Adelantado and Alguacil Mayor, of New Castile for the distance of 200 leagues along the newly discovered coast and invested with all authority and prerogatives, leaving his associates in secondary positions (a fact that later incensed Almagro and would lead to eventual discord). One of the grant conditions was that within six months, Pizarro should raise a sufficiently equipped force of 250 men, of whom 100 might be drawn from the colonies.[4]:132–134,137
This gave Pizarro time to leave for his native Trujillo and convince his brother Hernando Pizarro and other close friends to join him on his third expedition.[4]:136 Francisco de Orellana joined the group and would later discover and explore the length of the Amazon River. Two more of his brothers from his father, Juan Pizarro and Gonzalo Pizarro,[5]:27 and a brother from his mother, Francisco Martin de Alcantara,[4]:136 later decided to join him, as well as his cousin Pedro Pizarro, who served as his page.[8]:13 When the expedition left the following year, it numbered three ships, 180 men and 27 horses.[4]:138
Pizarro could not raise the number of men the Capitulación required and sailed clandestinely from the port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda for the Canary Island of La Gomera in January 1530. He was there joined by his brother Hernando and the remaining men in two vessels that would sail back to Panama.[4]:137 Pizarro's third and final expedition left Panama for Peru on 27 December 1530.[5]:27
Conquest of Peru (1532)
In 1531, Pizarro once again landed in the coasts near Ecuador, the province of Coaque and the region of esmeraldas, where some gold, silver and emeralds were procured and then dispatched to Almagro. The latter had stayed in Panama to gather more recruits.[4]:139–140 Sebastián de Belalcázar soon arrived with 30 men.[4]:141 Though Pizarro's main objective was then to set sail and dock at Tumbes like his previous expedition, he was forced to confront the Punian natives in the Battle of Puná, leaving three or four Spaniards dead and many wounded. Soon after, Hernando de Soto, another conquistador who had joined the expedition, arrived with 100 volunteers and horses to aid Pizarro and with him sailed towards Tumbes,[4]:143 only to find the place deserted and destroyed. The two conquistadors expected that the settlers had disappeared or died under murky circumstances. The chiefs explained that the fierce tribes of Punians had attacked them and ransacked the place.[4]:152–153
As Tumbes no longer afforded safe accommodations, Pizarro led an excursion into the interior in May 1532 and established the first Spanish settlement in Peru, San Miguel de Piura, and a repartimiento.[4]:153–154
Leaving 50 men back at the settlement under the command of Antonio Navarro, Pizarro proceeded with his conquest accompanied by 200 men on 24 Sept. 1532.[4]:155–156 After arriving at Zaran, de Soto was dispatched to a Peruvian garrison at Caxas. After a week, he returned with an envoy from the Inca himself, with presents and an invitation to visit the Inca ruler's camp.[4]:156–158
Following the defeat of his brother, Huáscar, Atahualpa had been resting in the Sierra of northern Peru, near Cajamarca, in the nearby thermal baths known today as the Inca Baths. Arriving at Cajamarca on 15 November 1532, Pizarro had a force of just 110 foot soldiers, 67 cavalry, three arquebuses and two falconets. He sent Hernando Pizarro and de Soto to meet with Atahualpa in his camp. Atahualpa agreed to meet Pizarro in his Cajamarca plaza fortress the next day. Fray Vincente de Valverde and native interpreter Felipillo approached Atahualpa in Cajamarca's central plaza. After the Dominican friar expounded the "true faith" and the need to pay tribute to the Emperor Charles V, Atahualpa replied, "I will be no man's tributary." His complacency, because fewer than 200 Spanish remained, as opposed to his 50,000-man army, of which 6,000 accompanied him to Cajamarca, sealed his fate and that of the Inca empire.[4]:157,161,166–177


Atahualpa's refusal led Pizarro and his force to attack the Inca army in what became the Battle of Cajamarca on 16 November 1532. The Spanish were successful. Pizarro executed Atahualpa's 12-man honor guard and took the Inca captive at the so-called Ransom Room. By February 1533, Almagro had joined Pizarro in Cajamarca with an additional 150 men with 50 horses.[4]:186–194
Despite fulfilling his promise of filling one room (22 by 17 feet or 7 by 5 metres)[9] with gold and two with silver, Atahualpa was convicted of 12 charges, including killing his brother and plotting against Pizarro and his forces. He was executed by garrote on 29 August 1533. Francisco Pizarro and de Soto were opposed to Atahualpa's execution, but Francisco consented to the trial due to the "great agitation among the soldiers", particularly by Almagro. De Soto was on a reconnaissance mission the day of the trial and execution and upon his return expressed his dismay, stating, "he should have been taken to Castile and judged by the emperor."[4]:202–204,206[10] King Charles later wrote to Pizarro: "We have been displeased by the death of Atahualpa, since he was a monarch and particularly as it was done in the name of justice."
Pizarro advanced with his army of 500 Spaniards toward Cuzco, accompanied by Chalcuchimac, before he was burned at the stake. Manco Inca Yupanqui joined Pizarro after the death of Túpac Huallpa.[4]:191,210,216 During the exploration of Cuzco, Pizarro was impressed and through his officers wrote back to King Charles I of Spain, saying: "This city is the greatest and the finest ever seen in this country or anywhere in the Indies... We can assure your Majesty that it is so beautiful and has such fine buildings that it would be remarkable even in Spain."
The Spanish sealed the conquest of Peru by entering Cuzco on 15 November 1533.[4]:216 Jauja, in the fertile Mantaro Valley, was established as Peru's provisional capital in April 1534,[6]:286 but it was high up in the mountains and too distant from the sea to serve as the capital. Pizarro founded the city of Lima on Peru's central coast on 6 January 1535, which he considered to be one of the most important things he had created in life.[4]:227–229
After the final effort of the Inca to recover Cuzco had been defeated by Almagro, a dispute occurred between Pizarro and Almagro respecting the limits of their jurisdiction, as both claimed the city of Cuzco. The king of Spain had awarded the Governorate of New Toledo to Almagro and the Governorate of New Castile to Pizarro. The dispute had originated from a disagreement on how to interpret the limit between the governorates.[4]:254–256 This led to confrontations between the Pizarro brothers and Almagro, who was eventually defeated during the Battle of Las Salinas (1538) and executed. Almagro's son, also named Diego and known as El Mozo, was later stripped of his lands and left bankrupt by Pizarro.
Atahualpa's wife, 10-year-old Cuxirimay Ocllo Yupanqui, was with Atahualpa's army in Cajamarca and had stayed with him while he was imprisoned. Following his execution, she was taken to Cuzco and given the name Dona Angelina. By 1538, it was known she had borne Pizarro two sons, Juan and Francisco.[11]
Pizarro's death

In Lima, on 26 June 1541 "a group of 20 heavily armed supporters of Diego de Almagro "el mozo" stormed Pizarro's palace, assassinating him and then forced the terrified city council to appoint young Almagro as the new governor of Peru", according to Burkholder and Johnson.[12] "Most of Pizarro's guests fled, but a few fought the intruders, numbered variously between seven and 25. While Pizarro struggled to buckle on his breastplate, his defenders, including his half-brother Martin de Alcántara, were killed".[6]:143 For his part, Pizarro killed two attackers and ran through a third. While trying to pull out his sword, he was stabbed in the throat, then fell to the floor where he was stabbed many times."[13] Pizarro (who now was maybe as old as 70 years and at least 62), collapsed on the floor, alone, painted a cross in his own blood and cried for Jesus Christ. He died moments after. Diego de Almagro the younger was caught and executed the following year after losing the battle of Chupas.
Pizarro's remains were briefly interred in the cathedral courtyard; at some later time, his head and body were separated and buried in separate boxes underneath the floor of the cathedral. In 1892, in preparation for the anniversary of Columbus' discovery of the Americas, a body believed to be that of Pizarro was exhumed and put on display in a glass coffin. However, in 1977, men working on the cathedral's foundation discovered a lead box in a sealed niche, which bore the inscription "Here is the head of Don Francisco Pizarro Demarkes, Don Francisco Pizarro who discovered Peru and presented it to the crown of Castile." A team of forensic scientists from the United States, led by Dr. William Maples, was invited to examine the two bodies and they soon determined that the body which had been honored in the glass case for nearly a century had been incorrectly identified. The skull within the lead box not only bore the marks of multiple sword blows, but the features bore a remarkable resemblance to portraits made of the man in life.[14][15]
Legacy
_01.jpg)
By his marriage to N de Trujillo, Pizarro had a son also named Francisco, who married his relative Inés Pizarro, without issue. After Pizarro's death, Inés Yupanqui, whom he took as a mistress, favourite sister of Atahualpa, who had been given to Francisco in marriage by her brother, married a Spanish cavalier named Ampuero and left for Spain, taking her daughter who would later be legitimized by imperial decree. Francisca Pizarro Yupanqui eventually married her uncle Hernando Pizarro in Spain, on 10 October 1537; a third son of Pizarro who was never legitimized, Francisco, by Dona Angelina, a wife of Atahualpa that he had taken as a mistress, died shortly after reaching Spain.[16]
Historians have often compared the conquests of Pizarro and Cortés in North and South America as very similar in style and career. Pizarro, however, faced the Incas with a smaller army and fewer resources than Cortés, at a much greater distance from the Spanish Caribbean outposts that could easily support him, which has led some to rank Pizarro slightly ahead of Cortés in their battles for conquest. Based on sheer numbers alone, Pizarro's military victory was one of the most improbable in recorded history.
Pizarro is well known in Peru as the leader of the Spanish conquest. Peruvians — including, but not limited to, many of mainly indigenous descent — regard him negatively. After his invasion, Pizarro destroyed the Inca state and while ruling the area for almost a decade, initiated the decline of local cultures. The Incas’ polytheistic religion was replaced by Christianity and much of the local population was reduced to serfdom under Spanish elites. The cities of the Inca Empire were transformed into Spanish, Catholic cities. Pizarro is also reviled for ordering Atahualpa's death despite the ransom payment (which Pizarro kept, after paying the Spanish king his due). Until relatively recently, Pizarro was portrayed positively — in textbooks, for instance — for imposing Catholicism and creating a privileged class of mainly Spanish descent.
Sculptures
In the early 1930s, sculptor Ramsey MacDonald created three copies of an anonymous European foot soldier resembling a conquistador with a helmet, wielding a sword and riding a horse. The first copy was offered to Mexico to represent Cortés, though it was rejected. The statue was taken to Lima in 1934 and repurposed to represent Pizarro. One other copy of the statue resides in Wisconsin. The mounted statue of Pizarro in the Plaza Mayor in Trujillo, Spain, was created by American sculptor Charles Rumsey. It was presented to the city by his widow in 1926.
In 2003, after years of lobbying by indigenous and mixed-raced majority requesting for the equestrian statue of Pizarro to be removed, the mayor of Lima, Luis Castañeda Lossio, approved the transfer of the statue to another location: an adjacent square to the country's Government Palace. Since 2004, however, Pizarro's statue has been placed in a rehabilitated park surrounded by the recently restored 17th-century walls in the Rímac District. The statue faces the Rímac River and the Government Palace.
Palace of the conquest

After their return from Peru and notoriously rich, the Pizarro family erected a plateresque-style palace on the corner of the Plaza Mayor in Trujillo. Francisca Pizarro Yupanqui and her uncle/husband Hernando Pizarro ordered the building of the palace; it features busts of them and others.[17] It instantly became a recognizable symbol of the plaza.
The opulent palace is structured in four stands, giving it the significance of the coat of arms of the Pizarro family, which is situated at one of its corner balconies displaying its iconographic content. The building's decor includes plateresque ornaments and balustrades.
In popular culture
- Pizarro is the title and subject of a dramatic tragedy by Richard Brinsley Sheridan, presented in 1799.[18] Sheridan based his work on the German tragedy by August von Kotzebue, Die Spanier in Peru.
- Francisco Pizarro is depicted as a villain in the 1980s animated series The Mysterious Cities of Gold. In it, Pizarro is a ruthless conqueror of the Incas who values gold above all else.
- Ron Pardo portrays Francisco Pizarro in an episode of History Bites as a parody of Star Trek's James T. Kirk.
- Francisco Pizarro is the main character in Peter Schaffer's play The Royal Hunt of the Sun.
- Pizarro is a character in the novel Inés of My Soul (Inés del alma mía) by Isabel Allende.
- In Jared Diamond's Pulitzer Prize-winning book, Guns, Germs and Steel, the Battle of Cajamarca is used to introduce Diamond's theory: Eurasian hegemony stemmed from environmental factors alone.
- Francisco Pizarro (played as a vampire by Venezuelan actor and singer José Luis Rodríguez) is the main villain in Mega TV miniseries Gabriel. Pizarro is presented there in modern days as "the first Latin-American vampire".
- In the book Evil Star from the Power of Five series by Anthony Horowitz, a historian claims a monk traveled with Pizarro to Peru and discovered an alternate creation story recorded by the Incas.
- Analog Science Fiction and Fact, in Anthology 4, "Analog's Lighter Side", featured a story by Randall Garrett from Astounding Science Fiction March 1959, "Despoilers of the Golden Empire", which recast the conquest of Peru in the language of a sci-fi story, while staying true to history. The story is also available at Project Gutenberg.
- Bruce Ramsay portrayed Pizarro in 2010's Riverworld.
- Pizarro is mentioned in Assassin's Creed II in the glyphs, where he was killed by the Assassins instead.
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Francisco Pizarro | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Works of Pizarro
- Pizarro, Francisco. "Cartas del Marqués Don Francisco Pizarro (1533-1541)". www.bloknot.info (A. Skromnitsky). Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- Pizarro, Francisco. "Cédula de encomienda de Francisco Pizarro a Diego Maldonado, Cuzco, 15 de abril de 1539". www.bloknot.info (A. Skromnitsky, in Russian). Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- Francisco Pizarro Response to a Petition by Pedro del Barco, 14 April 1539. From the Collections at the Library of Congress
References
- 1 2 "Francisco Pizarro". The Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ↑ "Pizarro". Euskalnet.net. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
- ↑ Machado, José Timoteo Montalvão (1970). Dos Pizarros de Espanha Aos de Portugal E Brasil: História E Genealogia.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Prescott, W.H., 2011, The History of the Conquest of Peru, Digireads.com Publishing, ISBN 9781420941142
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Hemming, John (1 January 1970). The Conquest of the Incas. Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-15-122560-6.
- 1 2 3 4 Leon, P., 1998, The Discovery and Conquest of Peru, Chronicles of the New World Encounter, edited and translated by Cook and Cook, Durham: Duke University Press, ISBN 9780822321460
- ↑ college.hmco.com
- ↑ Pizzaro, P., 1571, Relation of the Discovery and Conquest of the Kingdoms of Peru, Vol. 1-2, New York: Cortes Society, RareBooksClub.com, ISBN 9781235937859
- ↑ Francisco Pizarro, Catholic Encyclopedia.
- ↑ fullbooks.com
- ↑ de Betanzos, Juan; Hamilton, Roland; Buchanan, Dana (1996). Narrative of the Incas. University of Texas Press. ISBN 978-0-292-75559-8. Following Pizarro's assassination, Dona Angelina married the interpreter Juan de Betanzos.
- ↑ Burkholder, Mark A.; Johnson, Lyman L. (2004). Colonial Latin America. Oxford University Press. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-19-515685-0.
- ↑ "Exploring the Inca Heartland: Pizarro's Family and His Head", Archaeology, Archaeological Institute of America. 1 September 1999.
- ↑ Maples, WR; Gatliff, BP; Ludeña, H; Benfer, R; Goza, W (1989). "The death and mortal remains of Francisco Pizarro". Journal of forensic sciences. 34 (4): 1021–36. PMID 2668443.
- ↑ Maxey, R. "The Misplaced Conquistador-Francisco Pizarro."
- ↑ Prescott, William. History of the Conquest of Peru, chapter 28.
- ↑ "Palacio de la Conquista".
- ↑ The New Cambridge Bibliography of English Literature: Volume 2; Volumes 1660-1800. Books.google.co.uk. 30 July 1971. ISBN 978-0-521-07934-1. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
- ↑ https://www.geni.com/people/Leonor-Traperos/6000000019328584134
- ↑ "The Pizarro Brothers". LatinAmerican History. Retrieved 10 March 2015.
Further reading
- Cajamarca o la Leyenda Negra, a tragedy for the theater in Spanish by Santiago Sevilla in Liceus El Portal de las Humanidades
- Pizarro, a tragedy, by Richard Brinsley Sheridan, in Google books
- Conquest of the Incas, John Hemming, 1973. ISBN 0-15-602826-3
- Francisco Pizarro and the Conquést of the Inca by Gina DeAngelis, 2000. ISBN 0-613-32584-2
- The Discovery and Conquest of Peru by William H. Prescott. ISBN 0-7607-6137-X
External links
| Library resources about Francisco Pizarro |
- Pizarro & the Fall of the Inca Empire - Ancient History Encyclopedia
- Francisco Pizarro Chronology
 Crivelli, Camillus (1913). "Francisco Pizarro". Catholic Encyclopedia.
Crivelli, Camillus (1913). "Francisco Pizarro". Catholic Encyclopedia. "Pizarro, Francisco". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1900.
"Pizarro, Francisco". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1900. "Pizarro". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
"Pizarro". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
- PBS Special: Conquistadors — Pizarro and the conquest of the Incas
- The Conquest of the Incas by Pizarro - University of California Press
- The European Voyages of Exploration
- "Francisco Pizarro", February 1992, National Geographic
- Relacion de los primeros descubrimientos de Francisco Pizarro y Diego de Almagro, 1526 BlokNOT (A. Skromnitsky). 2009-10-09. Colleccion de documentos ineditos para la historia de Espana. Tomo V. — Madrid, 1844
| Government offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Position founded |
Governor of New Castile 1528–1541 |
Succeeded by Cristóbal Vaca de Castro |